Top 35+ Most Asked Kafka Interview Questions and Answers1) What is Apache Kafka?Apache Kafka is a publish-subscribe messaging application developed by Apache and written in Scala programming language. It is an open-source distributed, partitioned and replicated log service and a message broker application. The design pattern of Kafka is mainly based on the design of the transactional log. 2) What are some key features of Apache Kafka?Following is the list of some of the key features of Apache Kafka: 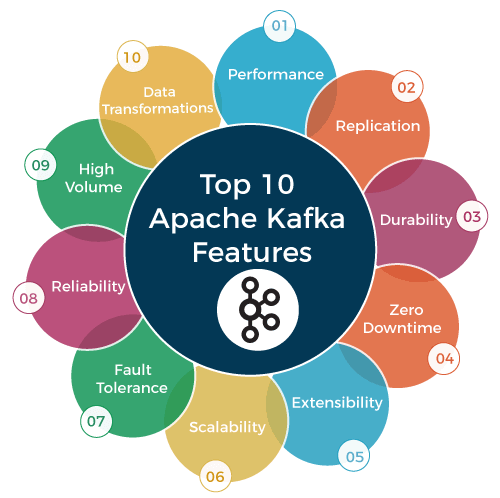
3) What are the different elements or components available in Apache Kafka?Following are some important elements or components available in Apache Kafka: 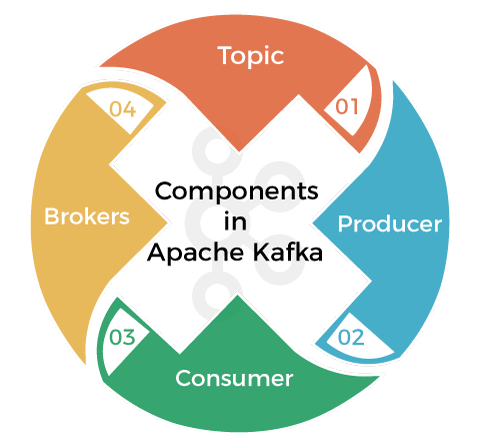
4) What do you understand by a consumer group in Apache Kafka?A consumer group is an exclusive concept of Kafka, which specifies that we will have one or more consumers who consume subscribed topics within each Kafka consumer group. 5) What is the role of the ZooKeeper in Kafka?Apache Kafka is a distributed system. Within the Kafka environment, the ZooKeeper stores offset-related information, which is used to consume a specific topic and by a specific consumer group. The main role of Zookeeper is to build coordination between different nodes in a cluster, but it can also be used to recover from previously committed offset if any node fails as it works as periodically commit offset. 6) Can we use Apache Kafka without ZooKeeper? / Is it possible to use Kafka without ZooKeeper?It is impossible to sideline Zookeeper and connect directly to the Kafka server. So, we cannot use Apache Kafka without ZooKeeper. If ZooKeeper is down, we cannot serve any client request in Kafka. 7) What is the traditional method of message transfer in Kafka?In Apache Kafka, the traditional method of message transfer has two ways:
8) What is the role of offset in Apache Kafka?Offset is a sequential ID number or a unique id assigned to the messages in the partitions. Offsets are used to identify each message in the partition uniquely with the id available within the partition. 9) What do you understand by a Consumer Group in Kafka?Consumer Group in Kafka is nothing but an exclusive concept of Kafka. Every Kafka consumer group consists of one or more consumers who consume a set of subscribed topics. 10) What are the key benefits of Apache Kafka over the other traditional techniques?Following is a list of key benefits of Apache Kafka above other traditional messaging techniques:
11) What are the four core API architectures that Kafka uses?Following are the four core APIs that Kafka uses: 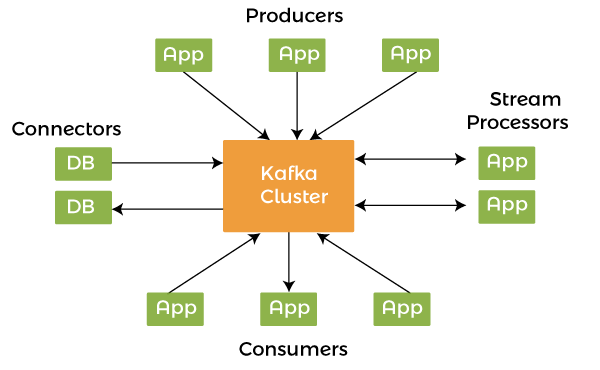
12) What do you understand by the terms leader and follower in the Kafka environment?The terms leader and follower are used in the Apache Kafka environment to maintain the overall system and ensure the load balancing on the servers. Following is a list of some important features of leader and follower in Kafka:
13) What do you understand by the partition in Kafka?In every Kafka broker, some partitions are available, either a leader or a replica of a topic.
14) Why is Kafka technology significant to use? / What are some key advantages of using Kafka?Following are some key advantages of Kafka, which makes it significant to use:
15) What is the importance of Topic Replication in Kafka? What do you understand by ISR in Kafka?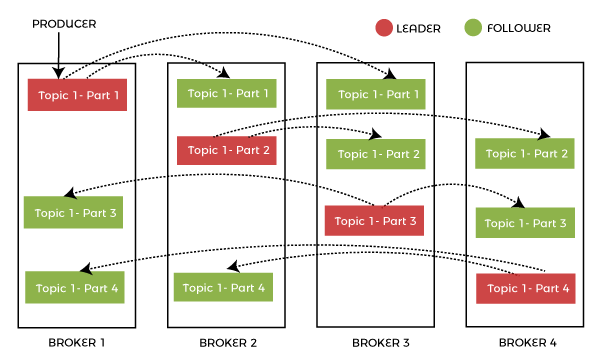
Topic replication is very important in Kafka. It is used to construct Kafka deployments to ensure durability and high availability. When one broker fails, topic replicas on other brokers remain available to ensure that data is not lost and Kafka deployment is not disrupted in any case. The replication ensures that the messages published are not lost. The replication factor specifies the number of copies of a topic kept across the Kafka cluster. It takes place at the partition level and is defined at the subject level. For example, taking a replication factor of two will keep two copies of a topic for each partition. The replication factor cannot be more than the cluster's total number of brokers. ISR stands for In-Sync Replica, and it is a replica that is up to date with the partition's leader. 16) What would be if a replica stays out of the ISR for a very long time?If a replica stays out of the ISR for a very long time, or if a replica is not in sync with the ISR, then it means that the follower server cannot receive and execute data as fast as possible the leader is doing. So, it specifies that the follower is not able to come up with the leader activities. 17) What is the process of starting a Kafka server?When you start to run the Kafka environment on a zookeeper, you must ensure to run the zookeeper server first and then start the Kafka server. This is the correct way to start the Kafka server. Follow the steps given below:
Use the following commands to start the Kafka server and ensure that all services are started in the correct order:
18) What do you understand by a consumer group in Kafka?In Apache Kafka, a consumer group is a collection of consumers who work together to ingest data from the same topic or range of topics. 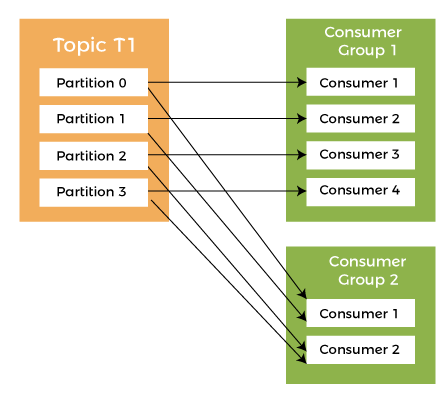
In Apache Kafka, a consumer group is a collection of consumers who work together to ingest data from the same topic or range of topics. The consumer group essentially represents the name of an application. There are several categories of consumers in Kafka. The '-group' command must be used to consume messages from a consumer group. 19) What is the role of Kafka producer API?The Kafka procedure API does the producer functionality through one API call to the client. Especially, the Kafka producer API combines the efforts of Kafka.producer.SyncProducer and the Kafka.producer.async.Async Producer. 20) What is the maximum size of a message that Kafka can receive?By default, the maximum size of a Kafka message is 1MB (megabyte), but we can modify it accordingly. The broker settings facilitate us to modify the size. 21) What are the key differences between Apache Kafka and Apache Flume?A list of key differences between Apache Kafka and Apache Flume:
22) What do you understand by geo-replication in Kafka?In Kafka, geo-replication is a feature that facilitates you to copy messages form one cluster to many other data centers or cloud regions. Using geo-replication, you can replicate all of the files and store them throughout the globe if required. We can accomplish geo-replication by using Kafka's MirrorMaker Tool. By using the geo-replication technique, we can ensure data backup without any failure. 23) Is Apache Kafka a distributed streaming platform? What can you do with it?Yes. Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform. A streaming platform contains the following three important capabilities:
Kafka technology facilitates us to do the following things:
24) What are the types of the traditional method of message transfer?There are mainly two types of the traditional message transfer method. These types are:
25) What are the biggest disadvantages of Kafka?Following is the list of most critical disadvantages of Kafka:
26) What is the purpose of the retention period in the Kafka cluster?Within the Kafka cluster, the retention period is used to retain all the published records without checking whether they have been consumed or not. Using a configuration setting for the retention period, we can easily discard the records. The main purpose of discarding the records from the Kafka cluster is to free up some space. 27) What do you understand by load balancing? What ensures load balancing of the server in Kafka?In Apache Kafka, load balancing is a straightforward process that the Kafka producers by default handle. The load balancing process spreads out the message load between partitions while preserving message ordering. Kafka enables users to specify the exact partition for a message. In Kafka, leaders perform the task of all read and write requests for the partition. On the other hand, followers passively replicate the leader. At the time of leader failure, one of the followers takes over the role of the leader, and this entire process ensures load balancing of the servers. 28) When does the broker leave the ISR?ISR is a set of message replicas that are completely synced up with the leaders. It means ISR contains all the committed messages, and ISR always includes all the replicas until it gets a real failure. An ISR can drop a replica if it deviates from the leader. 29) How can you get exactly-once messaging from Kafka during data production?To get exactly-once messaging during data production from Kafka, we must follow the two things avoiding duplicates during data consumption and avoiding duplication during data production. Following are the two ways to get exactly one semantics while data production:
30) What is the use of Apache Kafka Cluster?Apache Kafka Cluster is a messaging system used to overcome the challenges of collecting a large volume of data and analyzing the collected data. Following are the main benefits of Apache Kafka Cluster:
31) What are some of the real-world usages of Apache Kafka?Following are some of the real-world usages of Apache Kafka:
32) What do you understand by the term "Log Anatomy" in Apache Kafka?Log Anatomy is a way to view a partition. We view the log as the partitions, and a data source writes messages to the log. It facilitates that one or more consumers read that data from the log at any time they want. It specifies that the data source can write a log, and the log is being read by consumers at different offsets simultaneously. 33) What are the ways to tune Kafka for optimal performance?There are mainly three ways to tune Kafka for optimal performance:
34) What are the use cases of Kafka monitoring?Following are the use cases of Apache Kafka monitoring:
35) What is the difference between Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ?RabbitMQ is one of Apache Kafka's alternatives. Let's see the key differences between Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ: Differences between Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ:
|
You may also like:
- Java Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- HR Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- C++ Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- DBMS Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- IAS Interview Questions
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions
- .Net Interview Questions
- C# Interview Questions
- ReactJS Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Accounting Interview Questions






