Computer Network SecurityComputer network security consists of measures taken by business or some organizations to monitor and prevent unauthorized access from the outside attackers. Different approaches to computer network security management have different requirements depending on the size of the computer network. For example, a home office requires basic network security while large businesses require high maintenance to prevent the network from malicious attacks. Network Administrator controls access to the data and software on the network. A network administrator assigns the user ID and password to the authorized person. What is Network Security?All the measures used to safeguard a computer network's integrity and the data on it are collectively referred to as network security. Network security is crucial because it protects sensitive data from online threats and guarantees the network's dependability. Multiple security measures are used in successful network security plans to shield users and organizations from malware and online threats like distributed denial of service. Computers, servers, wireless networks, and other associated devices make up a network. Many of these gadgets are open to possible intruders. Utilizing a range of hardware and software tools on a network or as software as a service is necessary for network security. As networks get increasingly complicated and businesses rely more on their networks and data to operate, security becomes more crucial. As threat actors develop new ways to target these more complex networks, security techniques must change. Security is typically described as everyone's duty since every user on the network represents a potential vulnerability in that network, regardless of the exact method or business security plan. Advantages of Network Security
Aspects of Network SecurityFollowing are the desirable properties to achieve secure communication: 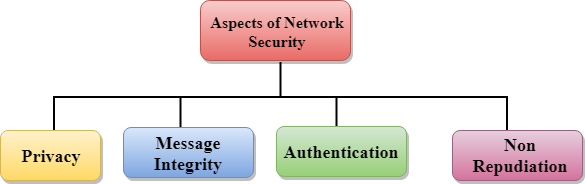
How is Network Security Implemented?Hardware and software technologies are used in conjunction to ensure network security. Network security's main objective is to stop unauthorized access to or communication inside a network. A security officer or team decides upon an organization's network security plans and policies to assist the organization in meeting security requirements. These security guidelines must be followed by everyone using the network. Data can be compromised anywhere in the network where an authorized user could access it, whether by a violent actor or by a negligent or mistaken user. In the modern environment, no method can guarantee complete security. However, measures may be taken to protect data when it is sent across an unprotected network or the internet. The most popular method is cryptography. Encrypting plain-text data using cryptography makes it more difficult to decipher and understand. Today, a variety of cryptographic algorithms are accessible, as follows: 1. Secret Key Cryptography:The sender and the receiver share one secret key. The data is encrypted at the sender's end using this secret key. Data is encrypted before being transferred to the recipient via a public network. The recipient may readily decipher the encrypted data packets because they are both aware of and possess the Secret Key. The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is an illustration of secret key encryption. It is challenging to administer Secret Key encryption since each computer on the network needs a unique key. 2. Public Key CryptographyEach user in this encryption scheme has a unique Secret Key that is not kept in the common domain. The secret key is kept from the public. Every user has a unique but public key in addition to a secret key. Senders encrypt the data using a public key that is always made available to the public. Using the user's personal Secret Key, he can quickly decode the encrypted data once he receives it. Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA), a kind of public key encryption, is an illustration. 3. Message DigestIn this approach, a hash value is computed and delivered in place of actual data. The second end user generates its hash value and contrasts it with the most recent one. It is approved if both hash values match; otherwise, it is refused. Message Digest example using MD5 hashing. It is mostly utilized in authentication processes when server passwords are compared against user passwords. Tools and Software for Network SecurityNetwork to network, and with time, there are changes in the security tools and rules available. Strong security frequently requires various strategies, sometimes known as layered security or defence, to provide organizations with the most feasible security controls. The following are some examples of frequently used tools and software for network security: 1. Firewalls Web pages, pop-ups, and other service entry and departure decisions are made by firewalls, which are guardian services or devices. Depending on the needs, these firewalls utilize a preset set of rules to help block or allow traffic. Depending on the requirements of the system, firewalls might be either software- or hardware-based, or both. 2. Access Control Access control enables businesses to stop unauthorized people and devices from connecting to a specific network and to stop prospective attackers from accessing sensitive data. This limits network access to users who are authorized to utilize the specified resources. 3. Virtual Private Networks (VPN) In most cases, a VPN encrypts the communication between an endpoint device and a network via the internet. Additionally, VPN enables experts to verify the connection between the network and the device. As a consequence, an online tunnel that is encrypted and safe is created. 4. Intrusion Prevention Systems Intrusion prevention systems scan network traffic to identify and stop assaults. This is accomplished by connecting network activity with databases of attack methods that experts are familiar with. 5. Wireless Security In comparison to wireless networks, wired networks could be more secure. It would help if you had control over the computers and people who may access the network of your business. It would help if you had wireless security, especially in light of the fact that fraudsters are increasingly extorting people for their private information. 6. Application Security Applications' weak points may be tracked down and secured using a combination of software, hardware, and processes, which makes it harder for hackers to access your network. 7. Behavioural Analysis You need to have a solid understanding of the typical behaviour of your network if you want to be able to spot abnormalities and different network breaches as they happen. Different behavioural analytics solutions are available that may quickly identify unusual activity. Problems with Network SecurityThere are several difficulties in maintaining network security, such as the following:
Best Tools for Network SecurityThe following is a list of some of the security software, hardware, and tools required to guarantee that the network is, in fact, secure:
Attack against Network SecurityCybercriminals' malicious attempts to undermine a network's security are known as network security attacks. These assaults are the main causes of the critical need for network security. These assaults on the network infrastructure must be stopped via network security. Let's find out more about these types of assaults so you can determine how to stop them. Attack Types in Network SecurityThe following list includes a few of the several network security attack types: 1. VirusIt is a malicious file that may be downloaded, and after a user has opened it, it begins to overwrite the computer's code with a new set of codes. The system files on the computer will become corrupt as the infection spreads, which may cause the files on other computer systems in the network to become corrupt as well. 2. MalwareIt is one of the swiftest, most severe, and worst attack methods that aid in gaining unauthorized access to a system or network of systems. The majority of malware is self-replicating, which means that once it infects one system, it may quickly infect all other computers linked to the network through the internet. Malware can corrupt any external device that is plugged into the system.
Next TopicPrivacy
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










