MIME ProtocolMIME stands for Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions. It is used to extend the capabilities of Internet e-mail protocols such as SMTP. The MIME protocol allows the users to exchange various types of digital content such as pictures, audio, video, and various types of documents and files in the e-mail. MIME was created in 1991 by a computer scientist named Nathan Borenstein at a company called Bell Communications. MIME is an e-mail extension protocol, i.e., it does not operate independently, but it helps to extend the capabilities of e-mail in collaboration with other protocols such as SMTP. Since MIME was able to transfer only text written file in a limited size English language with the help of the internet. At present, it is used by almost all e-mail related service companies such as Gmail, Yahoo-mail, Hotmail. Need of MIME ProtocolMIME protocol is used to transfer e-mail in the computer network for the following reasons:
MIME HeaderMIME adds five additional fields to the header portion of the actual e-mail to extend the properties of the simple email protocol. These fields are as follows:
1. MIME Version It defines the version of the MIME protocol. This header usually has a parameter value 1.0, indicating that the message is formatted using MIME. 2. Content Type It describes the type and subtype of information to be sent in the message. These messages can be of many types such as Text, Image, Audio, Video, and they also have many subtypes such that the subtype of the image can be png or jpeg. Similarly, the subtype of Video can be WEBM, MP4 etc. 3. Content Type Encoding In this field, it is told which method has been used to convert mail information into ASCII or Binary number, such as 7-bit encoding, 8-bit encoding, etc. 4. Content Id In this field, a unique "Content Id" number is appended to all email messages so that they can be uniquely identified. 5. Content description This field contains a brief description of the content within the email. This means that information about whatever is being sent in the mail is clearly in the "Content Description". This field also provides the information of name, creation date, and modification date of the file. Example of Content description
Content-Description: attachment; filename = javatpoint.jpeg;
modification-date = "Wed, 12 Feb 1997 16:29:51 -0500"; Working diagram of MIME Protocol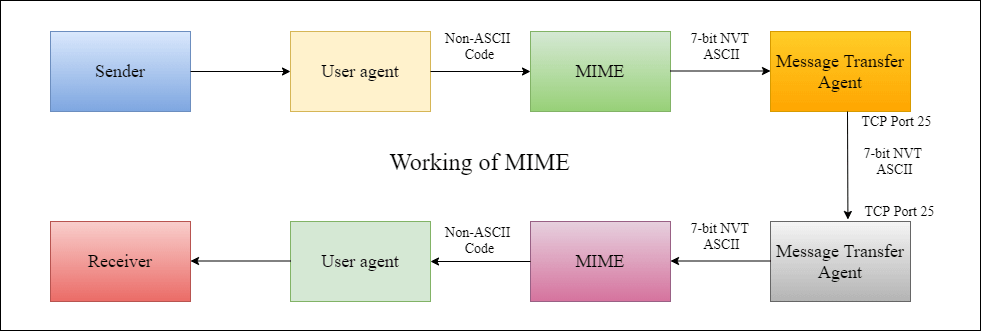
Features of MIME Protocol
Advantage of the MIMEThe MIME protocol has the following advantages:
Next TopicIP address
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










