10BASE-T10BASE-T Ethernet, also called as "10BASE-T," is a fundamental networking standard that has long been the foundation of local area networks (LANs). 10BASE-T enables a data transmission rate of 10 Mbps and was created to give a dependable and affordable method of connecting computers and other devices together inside a local network. Characteristics of 10 Base-T
WorkingCommunication in a 10BASE-T Ethernet network is supported by central hubs or switches placed in a star topology and twisted pair copper connections.
A central hub or switch with a specific function is at the heart of the network's data administration. While switches operate intelligently by sending data solely to their intended destination, hubs transmit incoming data to all connected devices, improving overall network efficiency. Its reputation as a foundational technology in the world of local area networks (LANs) is cemented by the ability of devices inside a 10BASE-T Ethernet network to establish dependable connections thanks to the cooperation of hardware and protocols. 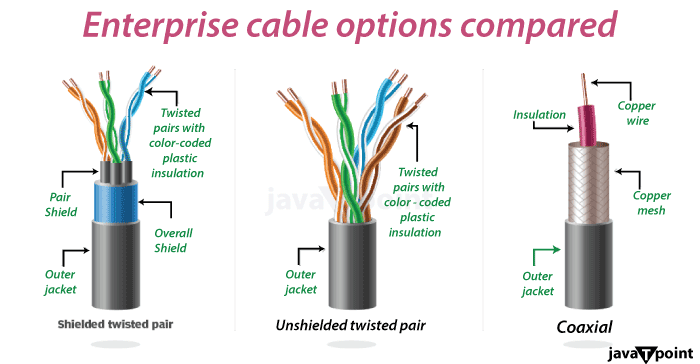
Advantages
The star design of a 10BASE-T network makes it very easy to incorporate, relocate, or adjust devices within the network. You can easily move or change a device by disconnecting it from one port on the hub and plugging it back in as needed.
The fault tolerance of a 10BASE-T network is one of its main benefits. The network's nodes (devices) are each connected to a central hub or switch by a dedicated connection. Because of this architecture, the likelihood that the entire network will be affected if one node has an issue or fails is significantly reduced. The central hub includes a "partitioning" feature that is integrated into it and can identify problems on any of its ports. The hub or switch can isolate a port if a fault is discovered on that port, cutting off the affected node from the rest of the network.
The fact that 10BASE-T uses an Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cable is a significant additional benefit. As a result of UTP cable's extensive use in networking and telecommunications applications, many buildings already have it pre-wired. Even if UTP was not initially used for wiring, it is frequently chosen to be installed over other cable types. The benefit of UTP cables is that they are adaptable and can handle various network kinds and applications.
A 10BASE-T network's star-wired design and the hub's segmentation features simplify troubleshooting. Technicians can resolve network issues by methodically removing each node from the hub one at a time until the network stabilises or recovers. Disadvantages
Compared to other cable types, such as coaxial or shielded twisted pair (STP) cables, 10BASE-T networks' unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables are more prone to electrical noise and interference.
When it comes to cable length, 10BASE-T Ethernet has a noticeable restriction. The maximum distance between the network's central hub/switch and a node (device) is 100 metres. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









