IPTV (Internet Protocol Television)IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) is a system that uses the Internet Protocol (IP) network to provide television programming and multimedia services. IPTV uses the internet to deliver media material to the viewer's device in a more interactive and on-demand manner than traditional broadcast television (satellite or cable TV), which depends on set schedules and channels. IPTV enables interactive elements that extend beyond the passive viewing experience of conventional television. Users may typically pause, rewind, or fast-forward live television, giving them more control over their watching experience. Some IPTV systems additionally include interactive program guides, personalized content, and suggestions based on viewing history. A service provider is often responsible for providing and distributing IPTV services. This can include an Internet Service Provider (ISP), a telecommunications corporation, or a specialized IPTV service provider. These organizations utilize IP networks to distribute television shows and other video material to viewers. An IPTV service can provide both live television and on-demand video material. Live TV is given in real-time, comparable to traditional cable or satellite TV. However, on-demand material allows customers to watch certain programs, movies, or series when they choose. 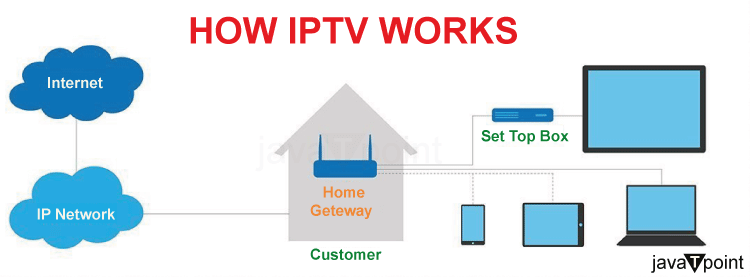
History of IPTVThe name IPTV first appeared in 1995 when Precept Software created a system for broadcasting audio and video information over IP networks utilizing RTP(Real-time Transport Protocol) and RTCP(Real-time Transport Control Protocol) protocols. Kingston Communications, situated in the United Kingdom, introduced one of the earliest IPTV services via DSL in 1999; then, in 2001, they pioneered Video-on-Demand (VoD), a game-changing service throughout the world. In 2005, a North American company launched high-definition television channels using IPTV. By 2010, Asian and European nations have developed VoD services in partnership with internet service providers, introducing DVR capabilities through set-top boxes. These milestones highlight IPTV's progression from its early beginnings to a full platform that includes live TV, on-demand programming, and sophisticated features, influencing the present landscape of television consumption. Working
IPTV material is often supplied over a controlled or specialized network, such as a Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) connection. This is in contrast with the public internet. Using a private network allows network operators to have more control over video traffic, ensuring quality of service, uptime, bandwidth, and dependability. This degree of control is critical for providing consumers with a smooth, high-quality viewing experience.
Traditional television distribution involves broadcasting all programs concurrently in a multicast mode. IPTV programming is transmitted in a unicast manner, which means that the user's device receives just one program at a time. This provides for a more personalized experience because the material is stored on the internet service provider's network until the user picks a certain program.
When a viewer switches channels in an IPTV service, the provider's server sends a fresh feed straight to the user. This is similar to how cable television works when changing channels triggers the transmission of a fresh program. Set-top boxes and other customer premises equipment, such as wifi routers, are commonly used in IPTV deployments.
IPTV typically uses IP multicasting for live television broadcasts. IP multicasting is a communication mechanism in which data is delivered from a single sender to numerous receivers. It is useful for concurrently distributing material to several consumers. IPv4-based live television broadcasts typically employ the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP), whereas IPv6 networks use Multicast Listener Discovery.
IPTV systems frequently employ the Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) to deliver on-demand content. RTSP is a network control protocol intended for use in entertainment and communication systems that employ streaming video. It allows consumers to access material on demand. IPTV ArchitectureDepending on the service provider's network architecture, two types of IPTV architecture can be considered for IPTV deployment: centralized and dispersed. The centralized architectural paradigm is a straightforward and manageable option. All media material is kept on centralized servers. Hence, a full content distribution system is unnecessary. Centralized architecture is typically beneficial for a network with a limited VOD service deployment, appropriate core and edge bandwidth, and an effective content delivery network (CDN). Although dispersed architecture includes intrinsic system management capabilities and benefits in bandwidth utilization, it is less scalable than the centralized approach. These characteristics are crucial for operating a bigger server network. Operators planning to install a large system should consider incorporating a distributed architectural model from the outset. Intelligent and sophisticated content distribution solutions are required in a distributed architecture to improve the effective delivery of multimedia content via the service provider's network. Types of IPTV
Advantages of IPTV
Disadvantages of IPTV
In brief, IPTV plays nice in places with ok internet to get admission to. So, when you have a reliable net connection and an HDMI-enabled TV that could hook up to wifi (if vital), you have to pass for it. Market lengthThe African and European markets have emerged as the most important in terms of subscribers, with a predicted popularity of a couple of thousand million and a projected fee of USD 90 billion by 2025. The global name for IPTV services is growing at 30-35 percent each year price. SK Telecom, Orange SK, Cisco Systems, Huawei Technologies, AT&T Inc., Matrix Stream Technologies, and Verizon Communication Inc. are the foremost IPTV carriers working inside the worldwide market. The high call for custom-designed TV programming is using the IPTV enterprise enlargement. The incorporation of on-name for advertising and marketing with content material is another key function that speeds up the organization in this industry and generates income and advertising. With the fast growth of high-velocity broadband Internet connections in the course of the dominion, India is now the largest increasing marketplace for Internet Protocol TV. This upward thrust has grown the Internet Protocol TV marketplace length to more than $ hundred million in sales. In India, it changed into, to start, launched in some locations through MTNL, BSNL, and Reliance JIO. However, it quickly gained recognition and became referred to as for. In 2015, Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited debuted 4G services in India, which include voice-over LTE and diverse net offerings. The JIOTV carrier, which permits you to watch live TV, suggested cricket, and DVR changed into delivered in 2016. Along with JIOTV, Reliance JIO has released different offerings for its visitors, together with JIO CINEMA, which allows them to look at on-call modern-day movies and net collections; JIO Saavan, which lets them pay attention to tunes online and offline in diverse languages; Jio Money Wallet, which allows them to make online payments, recharge their telephones and pay bills, and masses of more. Devices Compatible with IPTV ServicesThe unique name or kind of device one can perform may additionally range based totally on the IPTV company you're using. However, IPTV offerings are regularly compatible with a wide type of devices, which encompass:
Top IPTV Service ProvidersWith time, numerous first-rate IPTV companies have emerged, offering a few extremely good offerings. The pinnacle IPTV issuer companies for 2024 are:
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









