MAN in Computer Networks
Introduction of MAN
MAN is the short form of Metropolitan Area Network, which is a computer network typically used to connect computers in a metropolitan area (large geographical area) such as a city or university. It is basically a larger version of LAN. A single private or public company mainly operates it.
It is bigger than a LAN (Local Area Network) and smaller than a WAN (Wide Area Network). It is used to expand over a larger area, such as an entire city. It covers a range of up to 50 km and uses telecommunication media within the city.
It connects various LANs using local exchange carriers such as fiber optics. For example, it may connect branch offices to head offices through metropolitan area networks within the same city. It uses local exchange carriers that facilitate connection between the branch and head offices.
The metropolitan area uses switches or hubs to establish a LAN and routers or bridges to connect to other LANs. Local Area Network consists of computers that can communicate with other Local Area Network computers with the help of a metropolitan area network that uses routers for the interconnection of multiple LANs.
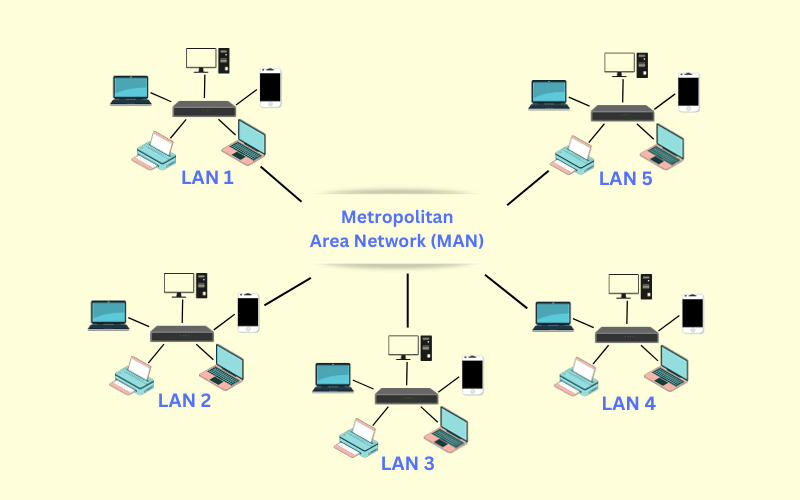
It is commonly used on large companies or school campuses with multiple buildings. It serves as a high-speed network to permit the sharing of regional resources. The most common examples of MAN are cable TV networks and telephone company networks.
Metropolitan Area Network commonly uses fiber optic cables to share high-speed data between devices on different LANs.
History of the Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs)
- In the 1980s, LANs became popular and widely used within organizations. It is used by the devices available within a single building for communication purposes. Its limitation is that it can cover a small area not suitable for connecting devices over long distances.
- In the late 1970s, ARPANET started to evolve, which is used to connect multiple institutions. It has served as an early prototype for MANs. ARPANET could connect multiple institutions, but its limitations are that it can cover a limited geographical area and does not provide global coverage. The data transmission rate it provides could have been faster.
- To overcome the limitations of LANs and ARPANET, a network called Metropolitan Area Networks was developed, which are used to connect devices at longer distances and are able to transmit data at high speed.
- In the 1980s, fiber optics technology started to emerge, which allows the transmission of data at high speed. Fiber optics became a key component in the development of metropolitan area networks.
- In the 1990s, fiber optics networks were deployed within metropolitan areas to provide high-speed data transmission over longer distances.
- In the 2000s, Ethernet-based MANs came, which provided high-speed data transmission and considered the cost-effective solution.
- In the 2000s, WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) technology was developed that provides wireless connectivity within MANs.
- At present, 5G wireless technology and other emerging technologies are used within MANs, providing high-speed data communication.
Working on the Metropolitan Area Network
- Network components that are used to set up metropolitan area networks are fiber-optic cables, switches, routers, etc. These components are used throughout metropolitan areas for connection.
- Fiber optics are considered the backbone of MANs and are mostly used to set up MANs using fiber optics as they provide high-speed data communication.
- Various nodes in MAN connect organizations or institutions to the network. The technologies that are used to connect organizations or institutions to the MAN are fiber optics, Ethernet, WiMAX, etc.
- Devices like routers or switches are used in the MAN. Routers find the best route to travel data from one LAN to another. Switches efficiently direct data to the appropriate devices on the local network.
- Telecommunication companies, internet service providers (ISPs), and network service providers often operate and manage MANs to offer connectivity services to businesses.
- MANs come with built-in security measures like encryption and intrusion detection systems to safeguard data during transit. Management tools are utilized to monitor and troubleshoot issues to ensure optimal network performance.
- A well-designed MAN is scalable to accommodate growing data traffic and new network connections.
- End-users, such as businesses, institutions, and residents, can connect their devices to the MAN using appropriate network interfaces and devices such as routers or modems.
Characteristics of MAN
| Parameter |
MAN |
| Full Form |
Metropolitan Area Network |
| Technology |
CDDI (Copper Distributed Data Interface), FDDI (Fibre Distributed Data Interface), ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) |
| Range |
5 to 50 km |
| Transmission speed |
Average |
| Area |
Within the city |
| Ownership |
Private or public |
| Maintenance |
Difficult |
| Error rate and cost |
High |
Advantages of Metropolitan Area Network
The advantages of Metropolitan Area Networks are as follows:
- It uses technologies such as fiber optics, Ethernet, or wireless connections to provide high-speed data transmission.
- Data speeds can reach up to 1000Mbps based on the technology used in the metropolitan area networks.
- MANs cover a significant metropolitan area, making them suitable for connecting multiple locations, such as businesses, educational institutions, government offices, and data centers, within the same city or region.
- It is designed to be scalable, which means that new locations and users can be effortlessly added to the network without significant disruption.
- It can offer cost-effective solutions for high-speed connectivity. They are especially useful for businesses and institutions that require reliable and fast communications across a city.
- It allows you to send local emails fast and free.
- Users can share their Internet connection with the MAN installation.
- It has a higher level of security than WAN.
- It is less expensive to establish a connection using MAN compared to WAN.
Disadvantages of Metropolitan Area Networks
The disadvantages of Metropolitan Area Networks are as follows:
- MAN requires high initial costs to set up because fiber-optic cables and other networking equipment can be expensive.
- MAN requires highly technical people to set up.
- It requires regular maintenance to provide the best performance.
- As compared to LAN, MAN is more complex to implement.
- As the geographical area in MAN increases, it is at risk of being attacked by hackers; hence, more security measures are followed to protect against intruders.
- It is hard to make the system safe from hackers.
- It becomes very difficult to manage if the size and number of LANs increase.
- Its reach is limited to a 50-kilometer area, so organizations located beyond the metropolitan area require a WAN connection.
Applications of Metropolitan Area Networks
Applications of Metropolitan Area Networks are as follows:
- Internet Access: MAN provides high-speed Internet that allows the sharing of large amounts of data in a short time.
- Resource sharing: MAN helps in sharing devices like computers, printers, etc., among multiple LANs.
- Educational Institutions: MAN is used to connect institutions and schools in the metropolitan area, which helps in providing online educational resources.
- Health services: MAN helps share medical data between health facilities.
- Smart City: MAN helps in building smart cities by connecting various devices required across the city to make the city smart.
- Financial services: MAN connects the branches and ATMs to the central banking network.
- Video Conferencing: MAN provides high-quality video conferencing that helps organizations collaborate remotely with different locations.
- Media and Broadcasting: MAN allows the distribution of content such as radio, television broadcasts, etc.
Conclusion
In this article, you understood the MAN in computer networks. MAN, i.e., Metropolitan Area Network, serves as high-speed data communication between different entities within a metropolitan area. It provides the connectivity needed for businesses and institutions to access online resources, communicate, and share data efficiently across a metropolitan area.
You have learned the characteristics of MAN, the working on MAN, the advantages of MAN, the disadvantages of MAN, and the applications of MAN.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









