Subnetting in Computer NetworksIn this tutorial, we will learn about Subnetting in Computer Networks Subject. First and foremost, the most crucial concept we are going to learn today is that while studying the subject of computer networks is subnetting. The most crucial idea known as Subnetting will help to lessen or disperse the pressure that the networks' heavy load causes. Let's now quickly go through the idea of subnetting for everyone. Now, let us know the definition of Subnetting. But before going into the Subnetting concept let us know the overview of the concept named Subnetting in Computer Networks. Subnetting is a part of Network Layer. The duty of the network layer is to divide the received message into separate components and activities. The Network layer can be called as the heart of Computer Networks. Basic idea of the ConceptFinding a network and delivering data to it was simpler when the IP (Internet Protocol) system was initially implemented since there were fewer individuals online. Sending a data packet to the desired machine in a network is getting more and more challenging these days due to the rise in internet users. Network performance becomes a major issue once a network is large enough to serve an enterprise. In order to divide larger networks logically (firewalls, etc.) or physically (for example), an organization can employ IP subnets (smaller broadcast domains, etc.). To put it another way, routers base their routing choices on subnets. We shall learn more about these ideas in this post. Introduction to SubnettingSubnetting is a combination of two words i.e. Sub and Netting. Here Sub word means Substitute and netting word means Network. The Substitute Network created for a function to happen is known as Subnetting. Here, Substitute Network does not mean a new network is created. A full piece of network is broken into small pieces and each piece a different is assigned. Subnet is the name given to piece of the broken network or can also be called as the Substitute network is known as Subnet. Subnets are the legal small parts of IP (Internet Protocol) Addressing process Subnetting should be done in such a way that network does not gets affected. This means that we can divide the network into different parts but all when put together should perform the same task when done before splitting in to small parts. Subnets reduce the need for traffic to use unnecessary routes, which speeds up the network. To help with the lack of IP addresses on the internet, subnets were developed Subnetting is a technique for creating logical sub-networks from a single physical network (subnets). A company can grow its network via subnetting without asking for a new network number from its ISP. Subnetting hides network complexity while assisting in the reduction of network traffic. Here, a network which is unique has to provide its services to many Local Area Networks i.e. (LAN). So, for this reason Subnetting is extensively used. Do you know what these little subnets are? As we all know, subnetting divides networks into them. A subnet is a smaller network, also referred to as a sub network. An IP network is logically divided into several smaller network components by subnets. A subnet is used to divide a large network into a number of smaller, linked networks, which helps to minimize traffic. Subnets reduce the need for traffic to use unnecessary routes, which speeds up the network. To help with the lack of IP addresses on the internet, subnets were developed. A rapid, effective, and reliable computer network is what subnetting is meant to create. Network traffic must find more effective routes as they become larger and more complicated. If all network traffic used the same path and moved through the system at once, bottlenecks and congestion would form, creating sluggish and inefficient backlogs. You may reduce the number of routers that network traffic must transit through by setting up a subnet. In order to make traffic go the shortest distance feasible inside a bigger network, an engineer will effectively create smaller mini routes. Purpose of Subnetting in Computer Networks
By removing the need for extra routers, subnetting makes network traffic simpler. This makes sure the data being transmitted can get to its destination as fast as possible, eliminating or avoiding any potential diversions that may slow it down.
By isolating or removing vulnerable network regions and making it harder for intruders to move through a company's network, subnetting helps the network managers in reducing network-wide risks.
Each class has a finite amount of possible host allocations; for instance, networks with more than 254 devices require a Class B allocation. Assume that you are a network administrator. Now, you have a task of allocating 150 hosts among three physical networks in three distinct cities for a Class B or C network. If so, we must either ask for additional address blocks for each network or split the single big network into small parts named subnets so that we could utilize a single address block across a number of physical networks. We will learn about this concept deeper in the upcoming topics.
Placing all of the computers on the same subnet can assist minimize network traffic if a significant amount of an organization's traffic is intended to be shared routinely among a number of devices. Without a subnet, all computers and servers on the network would be able to see data packets from every other machine.
The main network is divided into smaller subnets through the process of subnetting, and the goal of these smaller, linked networks is to split the large network into a collection of smaller, less-busy networks. Subnets reduce the need for traffic to use unnecessary routes, which speeds up the network.
An IP address is split into its network address and host address via subnetting. The split address may then be further divided into units using the subnet mask approach, and those units can be assigned to different network devices. 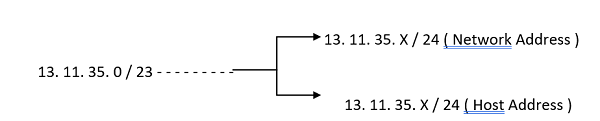
Here, X refers to the Host ID. This is the only thing which gets changed in the Internet Protocol Address Now, we are going to learn how these subnets provide the different addresses to different devices and also the process of subnetting in computer networks. So, by this example we would easily understand the working of the Subnet. We are going to learn how Subnets are formed for Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) Addressing. The IPv4 Addressing has five different classes. They are:
The total number of Internet Protocol Addresses (IP Address) gives the total number of Subnets that can be formed by using a network.
The number of usable IP Addresses that can be created is The total number of IP Addresses creatable = 2 The total number of Host ID Bits - 2. Class A Network can have 224 - 2 Class B Network can have 216 - 2 Class C Network can have 28 - 2 Class D and Class E do not contribute for IP Address creation. Class D is used for multicasting purpose Class E is used for Address Range Calculator They are saved for future purposes.
SubnettingWe have arrived at the subject at hand, Subnetting, thanks to the problem of IP address waste. By taking bits from the Host ID section of the address, subnetting enables the creation of smaller networks (sub networks; subnets) within of a larger network. With the help of those borrowed bits, we can build more networks with a reduced overall size. A Subnet is created from the bits taken from the Host ID. To understand about this concept let take an example of a network this belongs to class C. 
Our goal is to create to build a network. The capacity of each network must be Thirty (30) Devices. We have three networks of type Class C Network based on IPv4 Addressing. Each Class C Network can provide Two Hundred and Fifty Four (254) Internet Protocol Addresses. The Capacity of each device which we require is very less than the Capacity which we require. So, now we divide the four networks based on the requirement. Let us see how this division happens. We have four Class C Networks of imaginary Internet Protocol (IP) Addresses like:
We know that each network can produce 254 IP Addresses alone. This means four networks can produce 254 * 4 = 1016 (Thousand and Sixteen ) Internet Protocol Addresses can be formed. But what we require is only thirty Internet Protocol Addresses from each Network. This means we only need hundred and Twenty (120) IP Addresses only. This means 1016 - 120 = 896 Eight Hundred and Ninety-Six Addresses created are wasted. So, we need to use the Host ID bits wisely. So, by some calculation we will get to know that if we take 5 bits from each network we will be able to get 30 IP Addresses from each Network. The formula for number of IP Addresses is: The total number of IP Addresses creatable = 2 The total number of Host ID Bits - 2. So, now we will consider 5 Host ID Bits. 25 - 2 = 30 Internet Protocol Addresses from each Network. So, by considering we can create 30 Usable IP Addresses from each Class C Network. So, now we have 3 more Host ID Bits left over unused. We also have different ways in using these remaining bits. Other Ways are:
First method is usually chosen because creation of two different subnets causes wastage of IP Addresses. Let me explain this problem with the help of the above example. Example:
The network belongs to Class C Network which has 8 Host ID Bits.
In the above first created Subnet we have only used 30 IP Addresses only. In the newly created Subnet we have created only 6 IP Addresses only. This means we have used the full potential of the Class C Network. We might have used the whole 8 bits. But, this is considered as wastage of resources. This is called wastage because we have now a capacity of 36 IP Addresses to be created. But, the actual capacity of the Class C is 254 IP Addresses. This means 254 - 36 = 218 IP Addresses are wasted now because of this Host ID Bits Division. So, it is better to save the remaining Host ID Bits for future purpose rather than dividing it for these kind of resource wasting purpose. Working of Subnets in Computer NetworksSubnetting, as we all know, separates the network into small subnets. While each subnet permits communication between the devices connected to it, subnets are connected together by routers. The network technology being utilized and the connectivity requirements define the size of a subnet. Each organization is responsible for selecting the number and size of the subnets it produces, within the constraints of the address space available for its use.
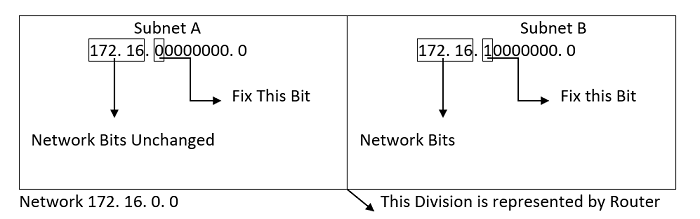
We need a subnet mask to identify a subnet, which is created by substituting the number "1" for each Network ID bit and the amount of bits we reserve for Host ID to create the subnet. A data packet from the internet is intended to be forwarded to the specified subnet network using the subnet mask. A part of an address should be used as the Subnet ID is also specified by the subnet mask. In order to apply the subnet mask to the whole network address, a binary AND operation is utilized. When performing an AND operation, it is assumed that the result will be "true" if both inputs are. If not, "false" is presented. This is only possible when both bits are 1. The Subnet ID results from this. The Subnet ID is used by routers to choose the best route among the sub - networks. 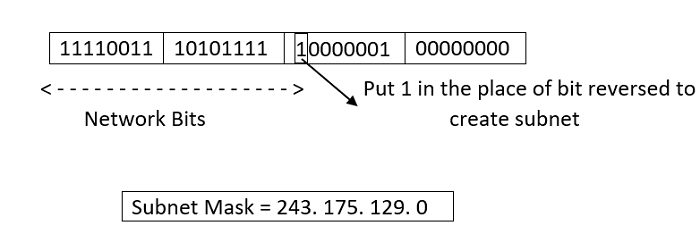
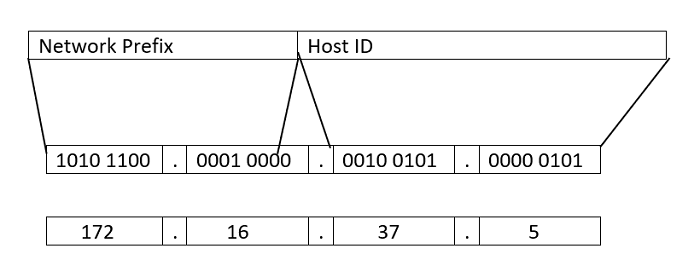
Advantages of Subnetting
Disadvantages of Subnetting
This is all about Subnetting Concept in the subject named Computer Networks.
Next Topic#
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









