Types of Wireless Transmission MediaWhen we talk about a Headset or Earphones, there are wired regular earphones that we physically connect to our phones, and there are wireless Bluetooth headsets that we connect via Bluetooth. Transmission via Bluetooth is one of the simplest and most prominent examples of wireless transmission media. Wireless data transmission is also called "Unguided Transmission" or "Unbounded Transmission" because of the absence of physical boundaries. When we turn on the Bluetooth on our phone and connect a headset, our phone and the device communicate with each other using ultra high-frequency Radio waves-one of the wireless transmission media. This tutorial explains about three major wireless transmission media in details with examples around us. 1. Infrared TransmissionIR or Infrared radiation is a part of electromagnetic radiation. These rays have a wavelength greater than visible light, making them invisible to the human eye. We cannot see Infrared light but feel the rays in the form of heat. Frequency range: 300 GHz to 400 THz. When we look at a fire, we can feel the heat from it and see it because it emits visible light and Infrared energy. The human body also emits heat but only in the form of Infrared light. Instruments such as night-vision goggles and Infrared cameras can capture Infrared light. Sun is the biggest source of Infrared radiation. Hence, it causes a lot of interference in Infrared communication. One most important point about Infrared rays is that these rays cannot penetrate through walls. Hence, the applications of Infrared rays lie within a contained space. So, how does the data transfer take place using this Infrared light? Let us apply for Infrared data transfer and see how it is happening. The most used application is the "TV Remote control". When we press a button on the remote, how is it changing the channel on the TV? 
An Infrared Light emitting diode is embedded into the TV remote and an IR detector is inserted into the TV. This detector converts the Infrared light signal from the remote and converts it into an electrical signal. Hence, the remote acts as a transmitter and the TV as a receiver.  
All the buttons on a TV remote are connected to a microprocessor which generates a unique binary code for each button pressed. All these codes will be of the same length. The LED flashes on and off according to the generated pattern of the pressed button. The detector on the TV will be pre-programmed to interpret the binary codes and perform the requested actions. These binary codes vary from company to company and device to device, which is why we can't control a TV with a remote that doesn't belong to it. Although, a universal remote has all the codes programmed into it, which is why it can control any TV. 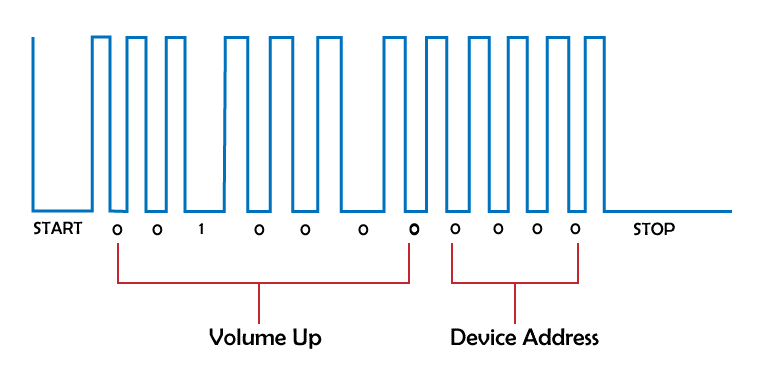
If there is some object between your remote and the TV, the detector on the TV might not be able to get the Infrared rays from the remote as these rays can't penetrate through objects. New technology led to various changes in Remote control, like using Radio waves instead of Infrared, mobile apps, voice control, etc. Other Applications of Infrared transmissions:
Advantages of Infrared communication:
Disadvantages of Infrared communication:
2. Radio wavesLike Infrared radiation, Radio waves are also a part of electromagnetic radiation. These waves have the longest wavelengths, from 1mm to 100km in the spectrum. The name itself has Radio. A Radio is one of the thousands of wireless technologies that use Radio waves for communication. A Radio is the simplest example of Radio wave communication. Other examples include RADAR, Satellite communications, Bluetooth headsets, TV Broadcasts, GPS Signals, etc. Frequency range: 300GHz to 3kHz. Like in Infrared communication, there will be a Radio wave transmitter and a receiver. All the Radios today use continuous sine waves to transmit information, as almost every single person on the planet uses these waves in one form or another. The information can be from audio, video, sound, and textual data. Suppose a person is using Radio, sine waves are transmitted from it, and if another person uses a TV, it also broadcasts sine waves. How are these signals separated and identified? Every single Radio signal will have a different frequency for the sine waves. A Radio station is an equipment installation with one or more transmitters or receivers. This is the flow: Transmitter (Sender's side): The information in any form is encoded into sine waves and is transmitted into the air by radiating the waves through an Antenna. Receiver (Destination): The Antenna on the receiver's side captures the Radio waves and decodes the information from the sine waves. To transmit Radio signals, there is a need for a transmitting antenna on the transmitter's side and a receiving antenna at the receiver's side. There is a concept to understand here:
Let us take an example of a sound wave. The frequency range a human ear can sense is 20Hz to 20kHz. If we try to transmit the Radio wave at the same frequency as the sound waves, the length of the antennas required will be in kilometers. It is not feasible. Here comes the concept of Modulation. We need the antenna height to be low, which means we need the Radio wave with high frequency. Hence, a signal with high frequency is taken, and its characteristics (amplitude or frequency, phase or pulse) are altered to store the information. After the modulation process, we'll get a high-frequency wave with all the data encoded into the wave. This wave is transmitted to the receiver Radio station, and demodulation is done to extract the blended data. Observe that there are FM Radios, AM Radios, and PM Radios based on the type of Modulation the Radio wave is going through to carry the information. Here is an example of Frequency Modulation: 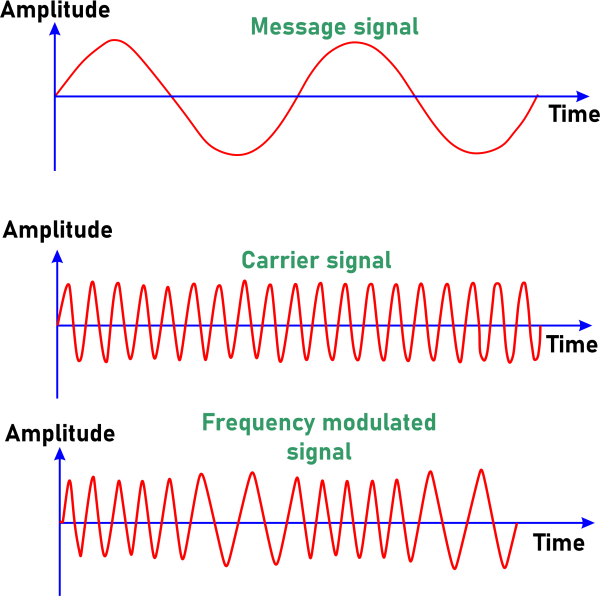
The first wave is the message the Transmitter wants to send. The next wave is a new signal with high frequency with no data in it. Now, the carrier signal is modified in terms of its frequency to carry the data in the message signal like a Morse code. This data will be demodulated to get back the message at the receiver's side. Advantages:
Disadvantages:
3. MicrowavesThese waves are also a part of electromagnetic radiation. The micro indicates that these waves have short wavelengths from 1 meter to 1 millimeter. These are high-frequency waves-> Frequency range: 300MHz to 300GHz. These waves fall between Radio waves and Infrared waves. These waves are used for point-to-point communication as it only transmits data in one direction. These can transmit all kinds of data, from audio to video. These waves can be used to transmit thermal energy too. 
Communication using Microwaves can be done only if the transmitting and receiving antennas are properly aligned- Line of sight transmission. Applications:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Next TopicBest Computer Networking Courses
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









