ARP Packet FormatThe address resolution protocol (ARP) uses a basic message format that contains either address resolution request or address resolution response. The ARP message size depends on the address size of the link layer and the network layer. The message header describes the network type used at each layer and the address size of each layer. The message header is complete with the help of the operation code, which is 1 for request and 2 for the response. The payload of the packet has four addresses, these are:
The Packet format of the Address Resolution Protocol is shown in the figure: 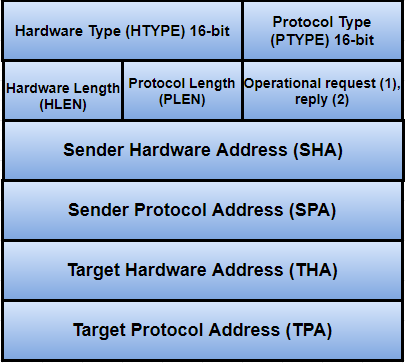
HTYPE (Hardware Type) - The size of the hardware type field is 16 bit. This field defines the network type that the local network needs to transmit the ARP message. There are some typical values for this field, which are given below:
PTYPE (Protocol Type) - The protocol type is a 16-bit field used to specify the type of protocol. Note: ARP can be used with any higher-level protocol such as IPv4, IPv6, etc.HLEN (Hardware Length) - The size of the hardware length field is 8-bit. This field specifies the length of the physical address in bytes. Example: For this, the address length of Ethernet is 6. PLEN (Protocol Length) - The size of the protocol length field is 8-bit long. It defines the length of the IP address in bytes. OPER (Operation) - It is a 16-bit field that determines the type of ARP packet. There are two types of ARP packets, i.e., ARP request and ARP Reply. In the given table, the first two values are used for the ARP request and reply. The values for the other ARP frame format such as RARP, DRARP, etc. are also specified in this table.
SHA (Sender Hardware Address) - This field specifies the physical address of the sender, and the length of this field is not fixed. SPA (Sender Protocol Address) - This field is used to determine the logical address of the sender, and the length of this field is not fixed. THA (Target Hardware Address) - The target hardware address specifies the physical address of the target. It is a variable-length field. For the ARP request packet, this field contains all zeros because the sender does not know the physical address of the receiver. Note: The default target hardware address is zero.TPA (Target Protocol Address) - This field determines the logical address of the target. TPA is a variable-length field.
Next TopicARP Table
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










