Functions, Advantages and Disadvantages of the Physical Layer
In this networking article, we will cover the functions, advantages and disadvantages of physical layer. We will also cover the topologies and components used in the physical layer.
What is Physical Layer?
In computer networking, there is a seven-layer model called the OSI model. The physical layer is the OSI model's first or base layer. The layer deals with the physical connection responsible for facilitating networks in the computer. It is related to the physical connections that connect different devices to form a network. The layer can be implemented by a chipset known as a PHY chip.
It acts as a medium to communicate and share files between different devices in a network. It provides an electrical, mechanical, or physical means to transmit messages or resources in the network. The physical layers specify various properties of these physical connections. It specifies the properties and shape of the connecting materials. It also determines the type of electrical connections and the frequencies used for transmission. It also specifies the line of code used to transmit the data similar to the low-level parameters by the physical layers.
Functions performed by Physical Layer
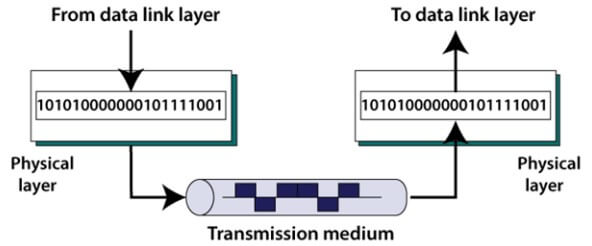
The physical layer in the OSI model determines the medium by which the stream of raw bits of data will be transmitted through a physical wire or connection between the different nodes in the network
The stream of bits of data is combined to form codes or symbols converted into a physical signal. This signal is transmitted through the transmission medium. The transmission medium can be any wire connecting the nodes in the network.
The layer also includes the electronic circuit technologies responsible for transmitting the data over a network. It acts as the fundamental layer that underlines the higher-level functions in the network. These functions can be implemented using various hardware technologies with numerous hardware components that may vary in characteristics.
In the OSI model of computer networks, the task of the physical layer is to translate the logical communications requests forwarded by the data link layer and make it suitable for hardware-specific operations such as receiving and sending these signals.
The physical layer is responsible for generating the logical data packets. These data packets carry the information from the data link layer that is shared between different nodes in the computer network.
Advantages of the Physical Layer
The physical layer deals with the physical aspect of the network. The major functions performed by the physical layer are as follows:
- The data is transmitted in the physical layer bit by bit or symbol by symbol over a physical transmission medium.
- The physical layer also gives a standardized interface to the transmission medium. It specifies the mechanical specifications of the physical connections in the networks. The specifications include the physical capabilities of the wires and cables, such as the length of the cable. It also specifies the electrical specifications of the transmitting line, signal level, and impedance.
- The layer is also responsible for determining the electromagnetic compatibility of the medium. It includes the frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum and its range. It also specifies the signal strength and the bandwidth for the transmission.
- The cables that are used to connect the nodes in the networks. Based on the above properties defined by the physical layer, these cables vary too. They can be either electrical or optical. They are only sometimes physical as they can be wireless communication links such as radio signals or free space optical communication.
- Line coding is performed to convert the data into electrical signals. These electrical signals can be modulated on a different carrier wave. The flow of data is managed at the bit level. The process of managing the data at the bit level is known as bit synchronization. It is performed in synchronous serial communication and for control in asynchronous communication. It also enables sharing the transmission medium among multiple nodes in the network by using simple circuits or multiplexing.
- Some complex MAC protocols enable users to share the transmission medium among different nodes. These protocols implement carrier sense and collision detection. It also uses signal processing techniques such as equalization and pulse shaping to increase the reliability and efficiency of the data transmission in the network.
- The layer also determines the rate by which the data is transmitted from one node to another in the network. The rate is known as the data rate and can be different for different notes in the network.
- It also is responsible for performing the synchronization of bits. It has a clock that manages both the sender and receiver by synchronizing the data at the bit level.
- It also helps in deciding the direction for transferring the data. The data can be transferred in one or both directions.
- It determines the physical topology of the network. The topology of the network can be defined as the arrangement of the nodes in the network. It is determined by the network's pattern in which the nodes or devices are connected. The various types of physical topology are bus, mesh, star, and ring.
- It also helps in transmission by providing a physical medium to facilitate transmission. It also takes the decisions associated with the interface of the medium.
- It provides two types of configurations for data transmission. They can either be point-to-point that transmit data from one node to another or multi-point configurations that send the data to multiple nodes simultaneously.
- It also provides an interface between the devices such as personal computers and other nodes in the network.
- It also has a protocol for data units in bits.
- Many important devices that are essential components in the network work in the physical layer. These devices are hubs, ethernet, etc.
- The physical layer in the OSI model falls under the Hardware layer; therefore, it is responsible for handling the physical components of the networks. It is responsible for establishing and processing the connection between these network components.
- This layer is also responsible for another important process in the communication process, which is modulation. It is the process by which the data is converted into radio waves by adding it to an electrical or optical signal and making it suitable for transmission through the medium.
- It also acts as a switching mechanism where the data packets can be transferred from one port in the device to another port in a different device. The transmitting port is the sender port, and the receiving port is the destination port.
Disadvantages of Physical Layer
- Sequential Delivery of Data: Though the physical layer tries to send the data to the receiving node in sequential order, it does not have any error control or flow control; therefore, there are chances that the data might be lost, duplicated, or modified.
- Fault Detection: There is no mechanism to solve any fault in the physical layer; therefore, it informs the data link layer in case of any fault in the physical layer.
- Terminating the Physical Connection: when the user wants to disconnect, the physical layer disconnects the entire connection by deactivating the physical link between the nodes in the network.
- Synchronization: The physical layer is incapable of performing character and frame synchronization performed by the data link layer.
Physical Topologies: Advantage and Disadvantage
It can be referred to as the geographical representation of the nodes in the network. There are four common types of physical topology in the network. The four topologies are as follows:
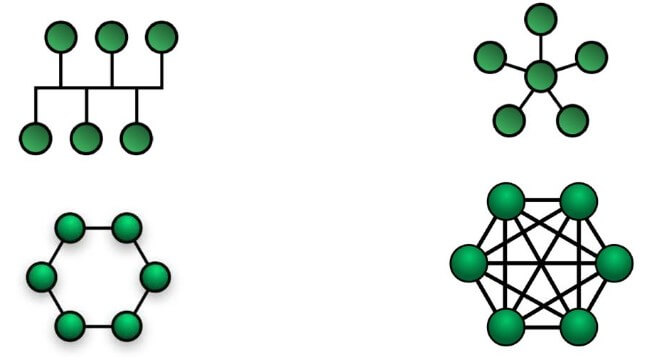
- Bus Topology: In a bus topology, all the devices in the network are connected through a common cable. The common cable is known as the backbone cable of the network. The connection between the nodes and the cable is made with the help of tap and drop lines. It is cheaper than the mesh and star topology. It isn't easy to reinstall or reconnect the nodes in the topology.
- Star Topology: In this topology, all the nodes in the network have a dedicated point-to-point connection with a central component that acts as a controller in the network. The central device is a hub. It is easier to set up the nodes in star topology than in mesh topology. This topology lacks fault tolerance. The entire network is dependent on the central component. If it fails, then the entire network will fail.
- Ring topology: In this topology, the nodes in the network are connected circularly using repeaters. Since it is a circular arrangement similar to a ring, it is known as a ring topology. It is only possible for a node to transmit the data to another node if the node has a token. A node must have a token to transmit the data using the network. It is the responsibility of the monitor to place the token in the ring topology.
- Mesh Topology:In this type of topology, each node in the network is connected to every other node. This means that there is a dedicated point-to-point connection between every device in the network. It is secure as every two devices have a separate connection in this topology, but it is costly and complex to install.
Types of Configuration in Physical Layer
- Point-to-Point Configuration: Each device has a one-to-one link between the nodes fully dedicated to transmitting the data between those two devices.
- Multi-Point configuration: In this configuration, there is no dedicated connection; rather, all the network nodes are connected using a single line. All the devices use the same link to transmit the data to each other.
Mode of Transmission Medium
There are three types of modes of transmission medium based on the direction the information can be transmitted in the network. These networks are as follows:
- Simplex Mode: This mode is used between two nodes where only one node can transmit the data while the other node can only receive the data. For instance, the input sends from the keyboard to the system. Television and radio broadcasting are also implemented in simplex mode.
- Half Duplex: in this mode, both devices can transmit and receive data in the network, but only one device can transmit the data at a time; that is, it is not possible for both devices to simultaneously transmit the data using this method of transmission. For example, walkie-talkies and police radios.
- Full Duplex Mode: This Mode of transmission allows both the nodes connected in the network to transmit and receive data simultaneously. For example, chatting applications, voice calls, and video conferences. Nowadays, this mode of transmission is the most used.
Physical Components used in Implementing Physical Layer

PHY
PHY is an abbreviation used for the physical layer. It is an electronic component in the system that is used as an integrated circuit in the system's motherboard. PHY is an essential IC to implement the functions of the physical layer in the OSI model in a network interface controller.
The circuit establishes a connection with a link layer device known as MAC. MAC stands for medium access control. This enables the user to connect the MAC with the physical medium, such as optical fibers or copper cables. A PHY device consists of a physical coding sublayer and medium-depend layer functionality.
A PHY chip is used with a modular transceiver in fiber optic communication to form the PMA sublayer in the network model.
Ethernet PHY
It is the component in the OSI model that runs at the physical layer of the network model. The component is used to implement the physical layer portion for the Ethernet connection. The function of the Ethernet PHY is to provide analog signal physical access to the physical medium or the link. Ethernet PHY is mostly interfaced with a media-independent interface. It is placed on a MAC chip in the microcontroller or another system that can perform and manage the higher-layer functions in the system.
The primary function of the Ethernet PHY chip is to implement the hardware send and receive function of Ethernet frames. It acts as an interface between the higher layer in the system and the analog domain of the ethernet line module. The link layer is the next higher layer in the OSI model, and the data domain is digital. Thus it acts as a bridge between digital and analog data.
The PHY is only sometimes responsible for managing the MAC addressing. The data link layer performs the MAC addressing. Similarly, the network interface card performs the BootROM and Wake on LAN functions.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









