Guided Media
It is defined as the physical medium through which the signals are transmitted. It is also known as Bounded media.
Types Of Guided media:
Twisted pair:
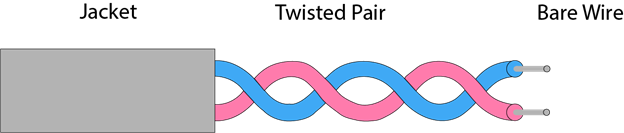
Twisted pair is a physical media made up of a pair of cables twisted with each other. A twisted pair cable is cheap as compared to other transmission media. Installation of the twisted pair cable is easy, and it is a lightweight cable. The frequency range for twisted pair cable is from 0 to 3.5KHz.
A twisted pair consists of two insulated copper wires arranged in a regular spiral pattern.
The degree of reduction in noise interference is determined by the number of turns per foot. Increasing the number of turns per foot decreases noise interference.
Types of Twisted pair:
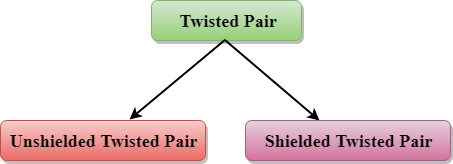
Unshielded Twisted Pair:
An unshielded twisted pair is widely used in telecommunication. Following are the categories of the unshielded twisted pair cable:
- Category 1: Category 1 is used for telephone lines that have low-speed data.
- Category 2: It can support upto 4Mbps.
- Category 3: It can support upto 16Mbps.
- Category 4: It can support upto 20Mbps. Therefore, it can be used for long-distance communication.
- Category 5: It can support upto 200Mbps.
Advantages Of Unshielded Twisted Pair:
- It is cheap.
- Installation of the unshielded twisted pair is easy.
- It can be used for high-speed LAN.
Disadvantage:
- This cable can only be used for shorter distances because of attenuation.
Shielded Twisted Pair
A shielded twisted pair is a cable that contains the mesh surrounding the wire that allows the higher transmission rate.
Characteristics Of Shielded Twisted Pair:
- The cost of the shielded twisted pair cable is not very high and not very low.
- An installation of STP is easy.
- It has higher capacity as compared to unshielded twisted pair cable.
- It has a higher attenuation.
- It is shielded that provides the higher data transmission rate.
Disadvantages
- It is more expensive as compared to UTP and coaxial cable.
- It has a higher attenuation rate.
Coaxial Cable
- Coaxial cable is very commonly used transmission media, for example, TV wire is usually a coaxial cable.
- The name of the cable is coaxial as it contains two conductors parallel to each other.
- It has a higher frequency as compared to Twisted pair cable.
- The inner conductor of the coaxial cable is made up of copper, and the outer conductor is made up of copper mesh. The middle core is made up of non-conductive cover that separates the inner conductor from the outer conductor.
- The middle core is responsible for the data transferring whereas the copper mesh prevents from the EMI(Electromagnetic interference).
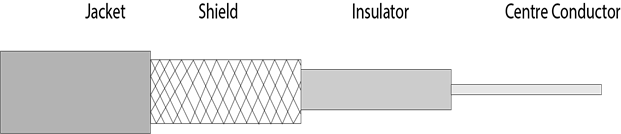
Coaxial cable is of two types:
- Baseband transmission: It is defined as the process of transmitting a single signal at high speed.
- Broadband transmission: It is defined as the process of transmitting multiple signals simultaneously.
Advantages Of Coaxial cable:
- The data can be transmitted at high speed.
- It has better shielding as compared to twisted pair cable.
- It provides higher bandwidth.
Disadvantages Of Coaxial cable:
- It is more expensive as compared to twisted pair cable.
- If any fault occurs in the cable causes the failure in the entire network.
Fibre Optic
- Fibre optic cable is a cable that uses electrical signals for communication.
- Fibre optic is a cable that holds the optical fibres coated in plastic that are used to send the data by pulses of light.
- The plastic coating protects the optical fibres from heat, cold, electromagnetic interference from other types of wiring.
- Fibre optics provide faster data transmission than copper wires.
Diagrammatic representation of fibre optic cable:
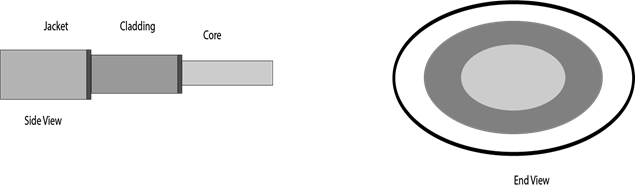
Basic elements of Fibre optic cable:
- Core: The optical fibre consists of a narrow strand of glass or plastic known as a core. A core is a light transmission area of the fibre. The more the area of the core, the more light will be transmitted into the fibre.
- Cladding: The concentric layer of glass is known as cladding. The main functionality of the cladding is to provide the lower refractive index at the core interface as to cause the reflection within the core so that the light waves are transmitted through the fibre.
- Jacket: The protective coating consisting of plastic is known as a jacket. The main purpose of a jacket is to preserve the fibre strength, absorb shock and extra fibre protection.
Following are the advantages of fibre optic cable over copper:
- Greater Bandwidth: The fibre optic cable provides more bandwidth as compared copper. Therefore, the fibre optic carries more data as compared to copper cable.
- Faster speed: Fibre optic cable carries the data in the form of light. This allows the fibre optic cable to carry the signals at a higher speed.
- Longer distances: The fibre optic cable carries the data at a longer distance as compared to copper cable.
- Better reliability: The fibre optic cable is more reliable than the copper cable as it is immune to any temperature changes while it can cause obstruct in the connectivity of copper cable.
- Thinner and Sturdier: Fibre optic cable is thinner and lighter in weight so it can withstand more pull pressure than copper cable.
| 



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









