Operating system based VirtualizationUsing an operating system A feature of an operating system known as virtualization allows for the existence of numerous separate user-space instances. Operating system-based virtualization is also referred to as virtualization during software installation. The host operating system is the one that it is installed over once it has already been running. In this form of virtualization, the user instals the virtualization software on his computer's operating system in the same way that he would any other programme, then makes use of the programme to run and create various virtual machines. Here, the user has direct access to any of the built-in virtual machines thanks to the virtualization software. Operating system virtualization may have an impact on hardware compatibility issues even when the hardware driver is not allotted to the virtualization software, as the host OS can provide hardware devices with the necessary support. Hardware IT resources that need specialised software to operate can be transformed into virtualized IT resources using virtualization software. Many OS-based services are available as organisational management and administration tools that can be used for the virtualization host management because the host OS is an entire operating system in and of itself. 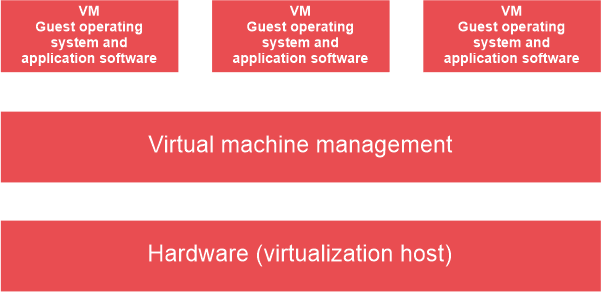
The following list of important operating system-based services is provided:
The following is a description of the principal operations of operating system-based virtualization:
Depending on the request made by the programme and the user account under which it is running, the operating system may be able to grant or deny access to these resources. These resources may also be hidden by the OS, which means that when they are computed by a computer programme, they are not included in the results of the enumeration. However, from the perspective of programming, the computer programme has engaged with those resources, and the operating system has controlled an action of engagement. It is possible to run programmes inside containers with operating-system virtualization or containerization, to which only a portion of these resources are allocated. Once running inside a container, a programme that is meant to understand the entire computer is limited to what it can see and assumes are the only resources available. Each operating system supports the formation of a number of containers, to each of which a portion of the computer's resources are allotted. Many computer programmes might be present in each container. These programmes might operate separately or concurrently, or even interact. Operating system-based virtualization may result in increased requirements and issues with performance overhead, including:
Next TopicContext based Access Control (CBAC)
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










