Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
Synchronous Optical Network, or SONET. A communication protocol called SONET was created by Bellcore and is used to send a lot of data over relatively long distances using optical fibre. Multiple digital data streams are transmitted simultaneously over the optical fibre with SONET.
Key Ideas
- Bellcore developed
- North American usage
- established by ANSI (American National Standards Institute).
- SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy), which is utilised in Europe and Japan, is comparable.
Why is SONET referred to as a synchronised network?
Across the entire network, the timing of signal and equipment transmission is controlled by a single clock (the Primary Reference Clock, or PRC).
SONET Network Constituents
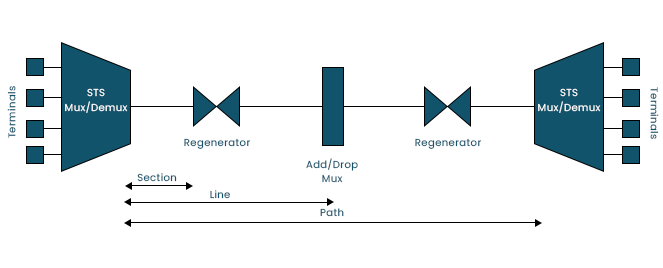
Multiplexer STS:
- performs signal multiplexing.
- optical signal from electrical signal is converted.
Demultiplexer STS:
- performs signal demultiplexing.
- optical signal to electrical signal conversion.
Regenerator:
- It is a repeater that regenerates (increases the strength of) optical signals.
Drop/Add Multiplexer:
- It enables the addition of signals from various sources to a particular path or the removal of a signal.
Why is SONET employed?
An electrical signal is changed into an optical signal by SONET so that it can travel farther.
Connections to SONET
- Section: The portion of the network that connects two nearby devices.
- Line: A section of the network that links two nearby multiplexers.
- Path: The network's end-to-end section.
Layers of SONET:
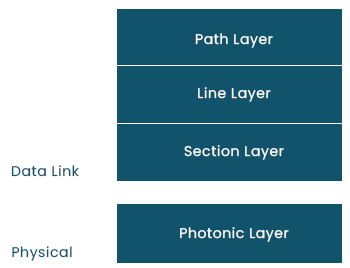
There are four functional layers in SONET:
1. Step Layer:
- It is in charge of transferring signals from their optical source to their optical destination.
- Providing path layer functions is STS Mux/Demux.
2. The Line Layer
- It is in charge of signal transmission across a real line.
- Add/Drop Mux and STS Mux/Demux both offer Line layer functions.
3. Stacking Section:
- It is in charge of signal transmission across a physical region.
- Each network device performs section layer functions.
4. Optical Layer:
- It corresponds to the OSI model's physical layer.
- It includes the optical fibre channel's physical specifications (light is present when 1 and not present when 0).
Benefits of SONET
- transmits information over long distances
- very little electromagnetic interference
- greater data rates
- Broad Bandwidth
SONET's drawbacks include:
- No standard that is compatible.
- SONET mux services are necessary for tributary services.
- Low cost and efficient for few channels.
- The SONET/SDH network management system is inadequate for managing and using the DWDM technique.
- At higher capacities, bandwidth efficiency is a problem.
- There must be more overhead.
| 

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










