What is 1000 BASE-TIn the constantly changing field of networking technologies, maintaining a fast and reliable connection is extremely important. One technology that had a key role in achieving quicker data transfer speeds is 1000BASE-T, also referred to as Gigabit Ethernet. In this extensive manual, we will explore the details of 1000BASE-T, its technical specifications, and its importance in the networking industry. What is 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet)?1000BASE-T is a Gigabit Ethernet standard, where 'Gigabit' refers to a 1,000 megabits per second (Mbps) data transfer rate. What sets 1000BASE-T apart is its reliance on copper cables, specifically four pairs of Category 5 (Cat5) unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, to achieve this remarkable data rate. This technology can be seamlessly integrated into data centres for server interconnections, network switch uplinks, and even directly connected to desktop computers. One of its most significant advantages is its ability to utilize existing copper cabling, eliminating the need for costly rewiring with optical fibre or newer-generation cables. You may encounter various names for 1000BASE-T, such as Gigabit Ethernet, 1000BaseT, GbE, 1 GigE, or simply Gigabit. It operates at Layer 1 of the Open Systems Interconnection model, which is the physical layer responsible for the physical medium through which data is transmitted. Evolution of Ethernet SpeedsTo appreciate the significance of 1000BASE-T, let's take a moment to reflect on the Ethernet speed roadmap. This technology emerged as a successor to older Ethernet standards, including Ethernet (10BASE-T, 10 Mbps) and Fast Ethernet (100BASE-T, 100 Mbps), swiftly establishing itself as the de facto standard for networking equipment. 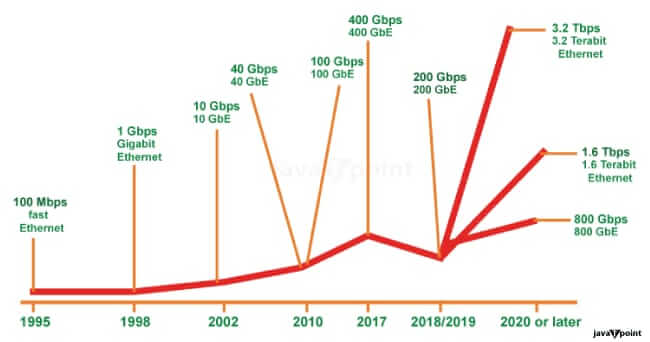
Almost all modern networking equipment supports 1000BASE-T, making it suitable for most common applications. It finds applications in general server interconnects and endpoint client connections. While it serves the access layer well, some backbone applications may demand even faster standards. However, for most home and business equipment produced in the last decade, Gigabit Ethernet is a ubiquitous feature. Specifications of 1000BASE-TThe Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) introduced the 1000BASE-T standard in 1999 under the designation IEEE 802.3ab. This standard is meticulously defined, and its specifications are as follows:
Automatic Medium-Dependent Interface CrossoverA notable feature of Gigabit Ethernet, including 1000BASE-T, is the Automatic Medium-Dependent Interface Crossover. This functionality allows Gigabit ports to automatically negotiate the transmit and receive twisted pairs within the cable. As a result, crossover cables are not required, and dedicated upload ports on switches become largely redundant. The physical medium attachment sublayer can even correct for nonstandard or reversed cabling, enhancing the convenience of deployment. Interoperability and Upgrade PathsAnother significant advantage of 1000BASE-T is its compatibility with faster standards. Both 2.5GBASE-T (2.5 Gbps) and 5GBASE-T (5 Gbps) Ethernet can utilize the same Cat5e and Cat6 cables as Gigabit Ethernet. Even the extremely fast 10GBASE-T (10 Gbps) is feasible over Cat6e cables. These standards are interoperable and can be auto-negotiated, enabling straightforward upgrade paths. This means that businesses and users can continue using their existing wiring infrastructure while increasing available bandwidth with relatively minor upgrades. Other Gigabit Ethernet StandardsWhile 1000BASE-T is a dominant Gigabit Ethernet standard, there are other variations that utilize different cable types. These can be broadly categorized into copper wire Gigabit Ethernet and fibre optic Gigabit Ethernet:
Applications of 1000BASE-TUnderstanding the practical applications of 1000BASE-T is essential in appreciating its significance. This high-speed Ethernet standard finds its place in various scenarios: 1. Data Centers Data centres are the heart of modern businesses, serving as hubs for data storage, processing, and distribution. In these critical environments, 1000BASE-T is often used for fast server switching and interconnections. Its ability to handle rapid data transfers ensures seamless operations in data-intensive applications. 2. Network Switch Uplinks Network switches are essential components in networking infrastructure, and they rely on high-speed connections for efficient data routing. 1000BASE-T serves as an ideal choice for network switch uplinks, ensuring that data flows smoothly through the network. 3. Desktop Computers For desktop computers and workstations, 1000BASE-T offers lightning-fast network connectivity. Whether it's downloading large files, streaming high-definition content, or participating in video conferencing, this standard ensures that users experience minimal lag and rapid data access. 4. Broadband Applications Broadband applications have a significant impact on every aspect of our life in the current digital era. In order to give high-speed internet access to households and companies, 1000BASE-T is essential. This technology enables smooth video streaming, online gaming, and web surfing. Advantages of 1000BASE-TThe widespread adoption of 1000BASE-T can be attributed to several key advantages: 1. Compatibility with Existing Cabling One of the most significant advantages of 1000BASE-T is its ability to work with existing copper cabling infrastructure. This compatibility eliminates the need for costly rewiring with optical fibre or newer-generation cables, making it a cost-effective choice for many organizations. Hence, one of the key advantages of 1000BASE-T is its compatibility with readily available cables, which were already in use for various applications. It utilizes four twisted pairs for full-duplex communication, enabling simultaneous transmit and receive operations. While Cat5 cable is the minimum standard required, it is compatible with newer standards such as Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6e, and Cat8. 2. Impressive Speed 1000BASE-T ensures that data travels across the network quickly and effectively because of its blistering 1 Gbps data transmission rate. For applications that require quick data access, such as video streaming, online gaming, and huge file transfers, this speed is essential. 3. Interoperability Organizations have flexibility and scalability because of the standard's interchange with faster Ethernet standards, including 2.5GBASE-T, 5GBASE-T, and 10GBASE-T. While progressively upgrading to meet changing bandwidth requirements, they may make use of their current infrastructure. 4. Affordable Equipment: Switches and network interface cards (NICs) for 1000BASE-T systems are frequently affordable. Because of its low cost, a wide spectrum of firms, from tiny businesses to huge corporations, may use it. 5. Efficiency in Energy: 1000BASE-T typically uses less electricity than certain higher-speed Ethernet protocols. Organizations may save energy as a result of this, especially in settings with lots of networked devices. ConclusionIn the world of networking, 1000BASE-T stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of faster data transfer rates and seamless connectivity. Its compatibility with existing copper cabling, impressive speed, and interoperability with faster standards make it a go-to choice for a wide range of applications. 1000BASE-T is a pillar of contemporary networking as technology develops, guaranteeing that our data moves through copper cables at the speed of light. With its lengthy history and ongoing importance, 1000BASE-T has clearly made a lasting impression on the networking industry and is in a position to have a big impact on how data transmission is developed in the future. Therefore, remember that 1000BASE-T is continuously operating in the background to enable you to enjoy lightning-fast internet speeds or perfect data transfers the next time you do so. Gigabit Ethernet standards like 1000BASE-T continue to be the foundation of our linked world as we advance in the digital era, allowing us to reach new levels of speed and connection that were previously unthinkable.
Next Topic10BASE-T
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









