What are Communication NetworksWhat is a Communication Network?An organization can effectively communicate information by implementing a pattern or form called a communication network. The established system known as the communication network allows messages to flow within an organization in one or more directions, depending on the needs of the organization. Formal and informal communication can be broadly divided into two categories. Various communication networks can be put into place based on their efficacy, depending on the kind of communication, the size and nature of the organization, and other factors. It is challenging to create an efficient communication network in large organizations. The primary communication network in these kinds of organization's is split up into numerous smaller networks that remain connected to the main network in order to maximize efficiency. The communication network is useful in assessing the accuracy, speed, and smoothness of the messages that are sent throughout the organization. Different Types of Communication Network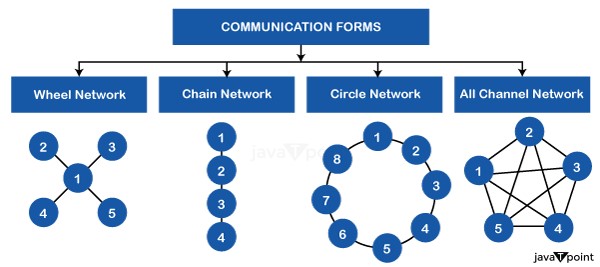
Communication networks can be classified into four categories: wheel, chain, circle, and all-channel networks. Wheel ConnectionThe organization's leader serves as the focal point for gathering and sharing information among all members within the wheel communication network. Information in the wheel network comes from the top-level manager. He offers information both inside and outside the company. He informs subordinates within the organization and obtains the necessary data from them as well. Chain subordinates are not allowed to speak with each other in this network system in order to share official information. In a similar vein, the manager gets all the external information. It is faster and suitable for simple, routine types of work. It is, nonetheless, the most authoritarian kind of network. To summarize, a top-level manager in the wheel network is the information source; he gathers, produces, and distributes information to every organizational mechanism. Key Components and Structure The primary person occupying a central role in the network is known as the central hub. They are linked to every other member and act as the main hub for coordination and communication.
Benefits and Drawbacks Benefits
The wheel network's hierarchical structure offers a clear chain of command concerning reporting relationships and authority. Drawbacks
Examples of Wheel Network
The wheel network works well in scenarios requiring precise guidance and command, like in hierarchical organizations or when a central authority figure is required. But when the central hub is absent, it might not be the best situation. Star NetworkA communication network structure called the "Star Network" is one in which a single person, usually a manager or supervisor, serves as the focal point for information sharing within the company. All channels of communication in this network go through the central hub, and other members speak with the hub directly instead of with one another. The hub serves as a primary point of contact, coordination, and decision-making. Key Elements and Structure
Benefits and Drawbacks Benefits
Drawbacks
Examples of Start Network
The star network helps with centralized control, effective information flow, and a clear chain of command in organizational communication. However, before putting into practice a star network structure, organizations should think about the nature of their communication needs and any potential trade-offs. Chain NetworkThe chain network appears to be a hierarchical structure within an organization. It is the official chain of communication in its vertical, upward, and downward forms. A person can only communicate with his direct superior and subordinate in this communication network. Information about an organization is conveyed in this structure in a chain from the upper level to the lower levels, as well as from the lower levels to the higher levels. All organizations with a well-defined structure of authority and responsibility among their members are likely to have this kind of network. To put it briefly, a chain network is a vertical communication system where an individual can only speak with his direct supervisor and subordinate. Key Components and Structure
Benefits and drawbacks Benefits
Drawbacks
Circular NetworkIt is a circle network in a horizontal or sideways configuration. A user can converse with someone to his right or left in this network, but not with any other group member. There are more channels available on such a network. To put it briefly, a circle network is a horizontal communication system where a person can only speak with those who are directly to his or her right or left. For instance, during a meeting, a participant may speak with the person to his left or right. Similar to this, a production manager in an official organization would speak with the manager of marketing or finance to obtain official information. All-Channel NetworkAll members of all channel networks are able to communicate with all other members without official limitations. It is a casual kind of networking where participants can freely share their thoughts, opinions, and recommendations with one another. Members of this communication structure are free to communicate without limitations or boundaries. Information can be shared among group members with greater freedom. The group's leader does not have extraordinary authority over the other members of the group. As a result, the term "open communication network" applies to it. Vertical NetworkA vertical network is a network structure in which the majority of communication channels move up and down the organizational hierarchy. It highlights the official line of command and adheres to the reporting lines inside the organizational structure. Information is mainly shared between superiors and subordinates, or between subordinates and superiors, in accordance with the organizational hierarchy. Key Components and Structure Those holding senior positions in the organizational hierarchy, such as executives, directors, or top-level managers, are referred to as higher-level managers.
Benefits and Drawbacks Benefits
Drawbacks
Examples of Vertical Network
Importance of Communication NetworksThe transmission and flow of messages between people or groups are controlled by a communication network. Here are the top five justifications for the significance of communication networks in the workplace: Effective Information Flow The effective and timely flow of information throughout the organization is guaranteed by communication networks. Clear channels and protocols allow messages to be sent promptly and accurately, giving staff members access to the data they require to carry out their jobs well. Enhanced Cooperation Teams and employees work together more when they use communication networks. In order to promote a culture of collaboration and synergy, they offer organized channels for exchanging concepts, expertise, and criticism. Employee collaboration improves problem-solving, creativity, and productivity when there is smooth communication between team members. Decreased uncertainty and misunderstanding Minimizing ambiguity and misunderstanding is facilitated by clear communication networks. Organizations can guarantee accurate and thorough information transmission by clearly outlining roles and responsibilities and designating specific channels for communication. As a result, there is less chance of miscommunication, misunderstanding, and mistakes in tasks or projects. Better worker satisfaction and engagement More engagement and satisfaction among employees is a result of effective communication networks. Motivated, productive, and content with their work are more likely to be found in employees who feel informed, involved, and connected in the communication processes. A thoughtfully constructed network promotes candid communication, involvement, and acknowledgment of staff members' work. Conformity to corporate objectives For team and individual efforts to be in line with organizational objectives, communication networks are ideal. They assist in ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goals by offering a clear framework for exchanging goals, objectives, and progress reports. Achieving goals is facilitated by this alignment, which also improves overall organizational effectiveness.
Next TopicInitialization Vector
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









