The list of animalsLiving creatures are called animals. Animals and plants both require food and water to survive in this world. Animals, on the other hand, nourish themselves by consuming plants or other animals, as opposed to plants, which produce their food. Because of their bodies, they can move in response to their environment. Animals are also able to find food, mates, and safe places with the help of their senses and mobility. There are lots of different animals on the planet. Throughout the planet, animals can be found in various habitats, from cold Polar Regions to scorching deserts. They can be found both on land and in the ocean. In terms of size and structure, they're incredibly diverse. A total of more than 7 million animal species have been described, including more than 1.5 million insect species. A single animal might be as small as 8.5 micrometers (0.00033 inches) or as large as 33.6 meters (110 ft). From a scientific point of view, zoology is the study of animals. Scientists classify creatures into two basic categories; vertebrates are animals with a backbone and invertebrates are animals without a backbone. Invertebrates make up about 95% of all creatures. Etymology"Animal" is derived from the Latin word animalis, which means "breathing", "soul", or "living being". All members of the Animalia kingdom are included in the biological definition. When referring to non-human creatures, the term animal is often used in everyday speech. CharacteristicsAnimals have various distinguishing traits that distinguish them from other living creatures. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. Animals are heterotrophic, meaning they feed on organic material and digest it internally, unlike plants and algae, which make their nutrition. Animals, with only a few exceptions, breathe aerobically. During a minimal part of their life cycle, all animals can move from one place to another but some animals, like sponges, corals, mussels, and barnacles, become non-motile during down the lane. Evolutionary animal typesThey can be divided into distinct varieties based on their food preferences, habitats, size, reproduction, and body structure, among other factors. The list of their types is given below; Types of Animals Based on their food preferences, size, habitats and body structure
Explanation of the above animal types1. Sponges
These are multicellular organisms that are primarily found in maritime environments. Because the cells do not form a tissue, they do not have organs. Each cell in the body lives on its own, yet the body as a whole remains in place. They have a column-shaped body structure. 2. Coelenterates
These creatures are far more advanced than sponges. They have a mouth and a tube-like body. They even have swimming tentacles (appendages). In pursuit of food and shelter, they migrate from one location to the next. 3. Worms
These are the most common types of creatures. They can be found as both regular living creatures and parasites on higher animals. Their bodies are thread-like or tape-like. They are distinctively long and thin in their body structure. They show various shapes and sizes, such as earthworms. 4. Arthropods
Arthropods are a type of arthropod (insects). These are animals with joints in their legs. The insect is a frequent name for them. Some of them are herbivorous, while others are predatory. They are also parasites that infect other animals with diseases. They are one of the most distinct animal groups on earth. Houseflies, mosquitoes, spiders, butterflies, and other insects are common examples of arthropods. 5. Echinoderms
It is a group of creatures that includes starfish. They can only be found in the seas and oceans. We come across invertebrate animals till we reach echinoderms. The evolution of vertebrate creatures continues from there. 6. Fishes
These are the organisms that most people are familiar with. Found Mostly in both freshwater and marine hostile. They have gills for breathing and fins for swimming. They reproduce by laying eggs and giving birth. A large number of people living around the coastal areas are dependent on fish for their food, nutrition and earnings. 7. Amphibians
These animals may live on land and in water, as their name implies. Frogs, in particular, belong to this category of animals. They are herbivores as well as predators. Poisonous snakes, lizards, and fierce crocodiles are examples of reptiles that are amphibians. Take a look at reptilian traits. Except for tortoises, they are usually carnivores. They can live both on land and water. 8. Birds
Birds are animals that have the unique ability to fly. Because of their powerful forelimbs, birds can fly for miles together. Warm-blooded creatures are derived from these animals and mammals. They maintain a constant body temperature despite of the weather outside. They are carnivores, but they may also eat plant matter. They reproduce by laying eggs and giving birth to offspring. 9. Mammals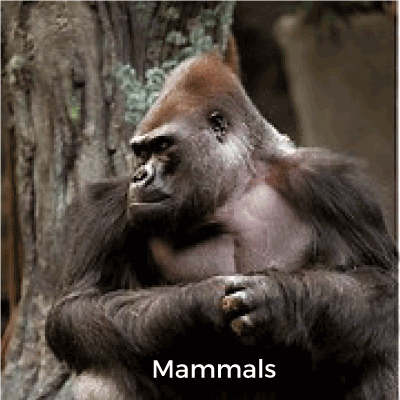
Of all the creatures, these are the most evolved. They give birth to their children directly. They give milk from their mammary glands to the babies. Mammals are those animals with whom people feel more comfortable. Dogs, cats, rabbits, and even pigs are more popular animals among humans. Surprisingly, Mammalia is not the largest animal classification. Mammalian species number is around 4,000, but insect species number is over 900,000. Drinking mother's milk is a distinguishing characteristic of mammals. Warm-blooded vertebrates make up the whole Mammalia class. Although most mammals are fuzzy two- or four-legged land dwellers, there are also flying mammals (bats) and swimming mammals (otters and seals). Classifications of animals based on other factors1. Based on the vertebral columni) Vertebrates: Animals with a vertebral column are known as vertebral column animals or vertebrates. The spinal cord is housed in this vertebral column, which aids in its connection to the brain. It also has chambers where the spinal nerves link to the rest of the body. All mammals, birds, and reptiles are examples of vertebrates. ii) Invertebrates: There is no spinal column in these animals. They have flexible body shapes due to the lack of a spinal column, for example, snails, earthworms, insects, and so on. 2. Based on the temperature of the bodyBecause of their metabolic activities, all creatures have a body temperature. But the animals have different ways of controlling their body temperature, accordingly, they can be of the following two types; i) Endotherms: Endotherms have a constant body temperature regardless of the outside temperature. As part of the metabolic process, they generate heat energy in their bodies. Endotherms are also known as homeotherms because they maintain a steady body temperature. These animals have a homeostatic mechanism that maintains a consistent body temperature regardless of external temperatures. Inability to regulate body temperature will result in death. A wide range of animals, including mammals and birds, are included in this group of creatures. ii) Ectotherms: It means that the external environment in which they live will make an impact on their body temperature. They can adjust or change their body temperature as per the outside temperature. Fish and reptiles are examples of amphibians (such as frogs). Poikilotherms are another name for some of them. So, their body temperature varies without affecting their health. Snails, lizards and snakes are also examples of ectotherms. 3. Based on the respiratory systemBy breathing, animals take in oxygen in the atmosphere and utilize it for energy production by oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria. It's important to note that animals' respiratory systems fluctuate depending on their habitat and body size and respiratory organs. Types of Respiratory organs involved in the respiration in different animals are as follows; i) Lungs: Lungs are the respiratory organs of larger creatures such as mammals, birds, and reptiles. They inhale and exhale air with the help of their lungs. It is through this mechanism that oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged from the blood into the air. ii) Gills: These are the water-breathing organs that are essential for aquatic life. Crustaceans have gill structures. Gills can be found in amphibians as early as the larval stage. Thus, even tadpoles can develop them. iii) Tracheae and Spiracle: Organs for breathing in insects are the spiracles and the tracheae. The spiracles are open to the outside, and air enters the tracheae via the spiracles. The air enters the tissues immediately through the tracheal passages. iv) Skin and body surface: In all animals, the skin serves as a protective layer that covers and protects the body's surface. Almost all of it is impenetrable. Only a small number of animals have skin that aids with respiration. In eels, roughly 60 percent of the oxygen they take in is taken in through their skin. Through the skin, carbon dioxide leaves the body of frogs. The capillaries on the skin of earthworms allow for the exchange of air. Animals like jellyfish, on the other hand, do not have respiratory organs. They absorb gas from the surrounding water. The list of some of the common and popular animals is given below;
Next TopicList of China Products in India
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









