List of cell organellesThe cell is a basic functional and structural unit of living creatures and is considered the smallest life form. The human body is comprised of trillion of cells, and they provide structure to the body, absorb nutrients from the food, change these nutrients into energy, and help in performing all the specific functions. An organelle inside the cell is a specific subunit that plays a distinct role in the cell's functioning. Organelles are encompassed inside their lipid bilayers or are boundless by membranes. Cell organelles are the cell's internal organs that are involved in carrying out numerous vital functions such as protein synthesis, reproduction, energy production, maintaining the shape of the cell, transportation of substances inside and outside of the cell, and the cell's movement. Here is a list of cell organelles described below: 1. Plasma Membrane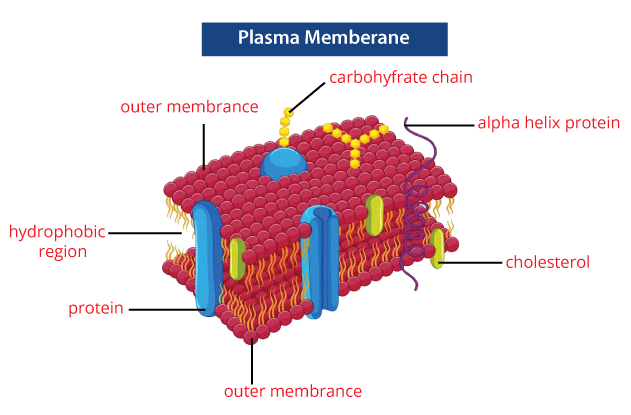
The plasma membranes are also called Cytoplasmic membranes or cell membranes and are present in both animal and plant cells. It is made up of proteins and lipids, and it is the selectively permeable membrane as it permits the entry of selective substances inside and outside of the cell as per its necessity. In animal cells, the cell membrane gives shape and protects the internal constituents of the cell, and based on its structure, it is considered the fluid mosaic model, and as explained by the fluid mosaic model, the plasma membranes are subcellular and formed by a lipid bilayer in which the molecules of protein are enclosed. 2. Cytoplasm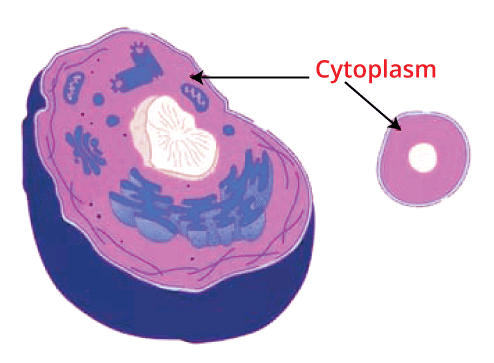
The cytoplasm is a jelly-like material present between the cell membrane and nucleus and exists in both animal and plant cells. It is composed of inorganic and organic compounds and water. The cytoplasm is one of the important parts of the cell, as all the cell organelles are embedded in it, and all these cell organelles possess enzymes that are generally important to carry out the metabolic activity occurring inside the cell and are the site where most of the chemical reactions take place inside a cell. 3. Nucleus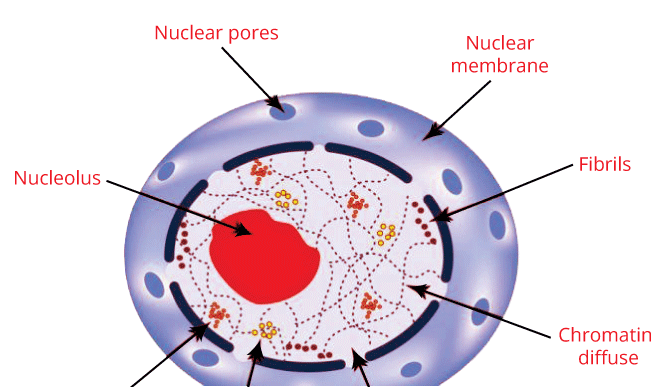
The nucleus is present in all eukaryotic cells, and it is a double membraned organelle and the largest organelle. It acts as the storehouse of the cell's DNA and is the control center of cellular activities. The nucleus is dark, round in structure, and surrounded by a nuclear membrane, and a nuclear membrane is a porous membrane like a cell membrane and creates a wall between the nucleus and cytoplasm. The nucleolus, tiny spherical bodies are present inside the nucleus. It contains a very crucial structure called chromosomes. Chromosomes are thin, a thread-like structure that carries other essential structures termed genes. Gene is a hereditary material in organisms. It helps offspring to inherit the traits of their parents. Therefore, the characters and functions of cells in one's body are controlled by the nucleus only. The nucleus's primary role is to monitor cellular activities such as metabolism and growth by using genetic information possessed by DNA. The nucleus contains nucleoli that are accountable for the synthesis of RNA and protein. 4. MicrobodiesMicrobodies are tiny, membrane-bound, and vesicular organelles present in both animal and plant cells. They consist of several proteins and enzymes that are only visible under the electronic microscope. As microbodies are found in the cytoplasm, so they are known as cytosomes, and Peroxisomes and Glyoxysomes are the types of microbodies. (i) Peroxisomes-
They are found in eukaryotic cells and have a membrane, and they are involved in several oxidative processes, catabolism of D-amino acids, polyamines and bile acids, and lipid metabolism. Enzymes such as catalase and peroxide convert peroxides into water which is the reactive oxygen species produced during the process. Photorespiration in plants occurs in peroxisomes. (ii) Glyoxysomes-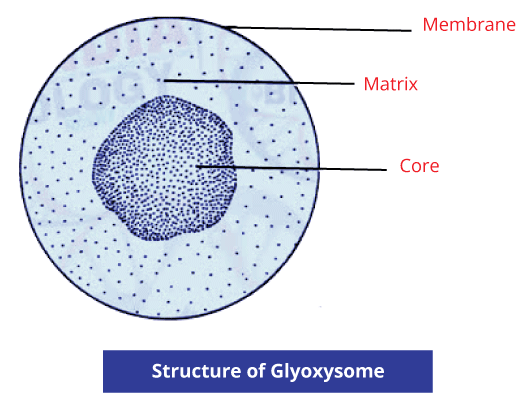
These are the specialized peroxisomes, and they are found in fungi and plants and are common in the germinating seeds in their fat-storing tissues. Their primary function is to convert fatty acids into carbohydrates. 5. Cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton exists in all living cells, especially in the eukaryotic cells, and it is the constant networking of proteinaceous and filamentous formations that run in every part of the cytoplasm, from the nucleus to the plasma membrane. The cytoskeleton web consists of various types of proteins that divide speedily or dissimulate as per the need of cells. The primary role of the cytoskeleton includes giving shape, and mechanical resistance to the cell in case of deformation, the contracting capability of the filament aids in locomotion during cytokinesis. 6. Cilia and Flagella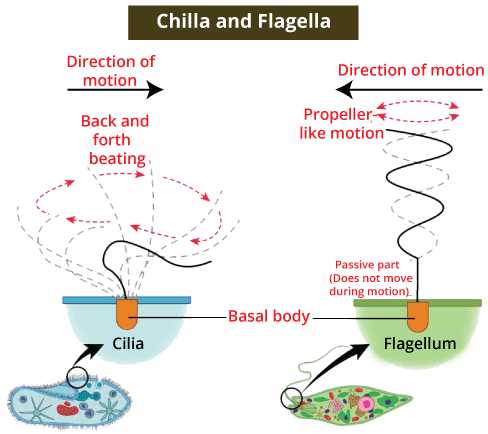
Flagella are somewhat bigger and help in the movement of cells. Structurally, the eukaryotic flagellum is different from its prokaryotic fellow. On the other hand, Cilia are tiny structures and hair-like projections found outside the cell wall, and it functions as oars to either move the cell or the extracellular fluid. Axoneme, the core of cilia and flagella, consists of nine sets of microtubules and a set of central microtubules moving collaterally to the centerline. The central tubules are associated with a bridge and are enclosed by a central sheath, and there are nine radial spokes, and through each radial spoke, one of the outermost microtubular pairs is joined to the central sheath. A centriole-like structure through which cilia and flagella arise is termed basal bodies. 7. Centrosome and Centrioles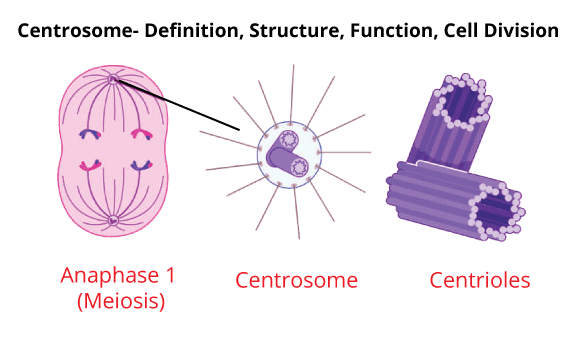
Two commonly perpendicular formations called centrioles makes centrosome organelle. Fibrils are a pair of interconnected triplets, and each centriole consists of 9 equitably arranged outermost fibrils of tubulin protein. The central portion of the centrioles is proteinaceous and is called the hub, and this hub joins the outer fibrils through a radial spoke made up of proteins. Spindle fibres during cell division emerge from the centrioles from the basal bodies of both Flagella and Cilia. 8. Vacuoles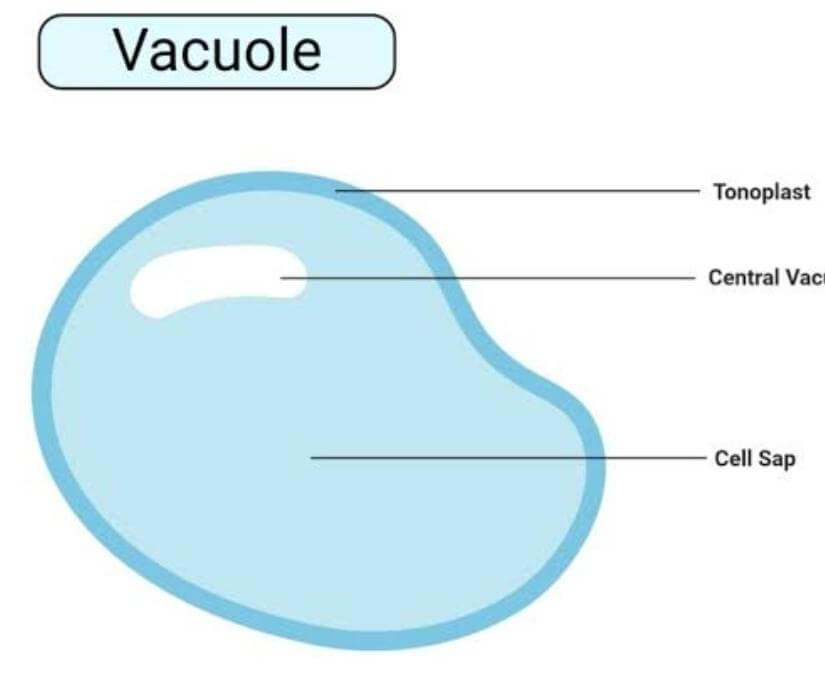
Vacuoles are the fluid-filled organelles surrounded by the membrane. They don't have any definite shape and are the storage bubbles present in cells. Vacuole stores a range of nutrients and food needed for the survival of cells. Additionally, it also stores waste products that are sooner or later thrown out by the vacuole, so the other cells get protected from contamination. The plant and animal cells differ in number and size of vacuoles; as compared to animals, plant cells contain larger vacuoles. 9. Endoplasmic Reticulum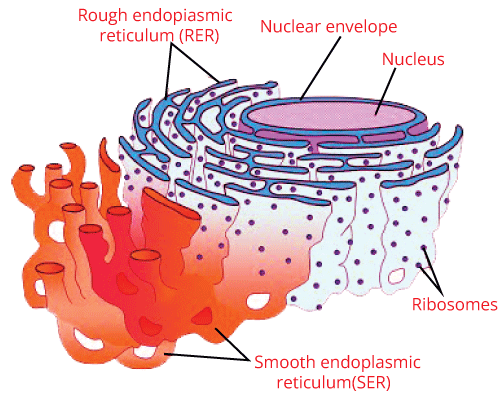
The Endoplasmic reticulum is a matrix of the fluid-filled membranous canal which act as the transport system of the cell. It is involved in transferring substances in every part of the cell. Endoplasmic reticulum is further classified into two types, and these two types of reticulum are described below: (i) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum- They are linked with the production of steroids and lipids and are the reason behind the detoxification of cells. They are also the storage organelle. (ii) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum- They are found all over the cell and participate in the production of protein. They are composed of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae. 10. Mitochondria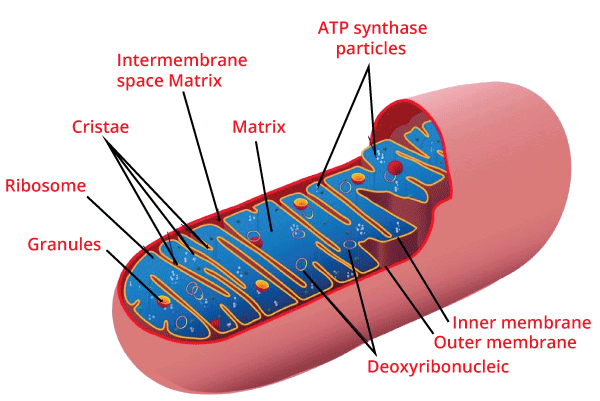
Mitochondria are called the "Powerhouse of the cell", and they produce energy-rich molecules for the cell. The mitochondrial genome is inherited maternally in various organisms, and Mitochondria is present in mostly all eukaryotic cells and is a sausage-shaped and double membrane-bound organelle. The double membranes separate its lumen into two different watery sections. The internal section is known as the "matrix," which is folded into cristae whereas on the other hand, the outer membrane creates a continual border with the cytoplasm. They generally differ in their size and are present either oval or round in shape. Aerobic respiration takes place in mitochondria, and it builds energy in the form of ATP and aids in the conversion of the molecules. For example, glucose is converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Mitochondria possess their own circular DNA, RNA molecules, some other molecules that aid in the process of protein synthesis, and the 70s ribosomes. 11. PlastidsPlastids are large organelles that contain pigment and are enclosed by the membrane. According to the type of pigments present in the plastids, they are categorized into three types which are described below: (i) Chromoplast-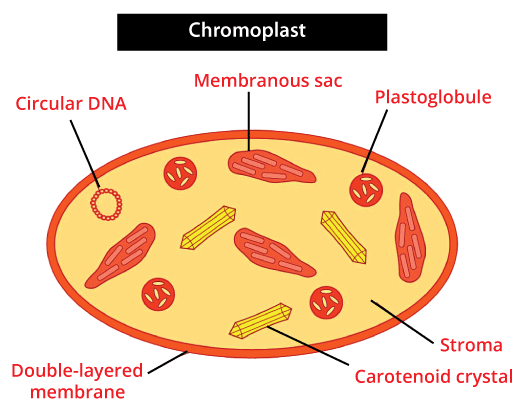
The chromoplasts consist of fat-soluble carotenoid pigments such as carotene, xanthophylls, etc., that give plants their distinctive color- orange, yellow, red, etc. (ii) Chloroplast-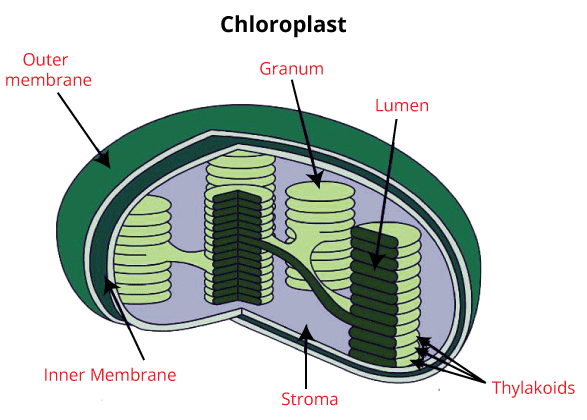
Chloroplasts are double membrane-bound organelles that generally differ in shape, like discord, discovered, spherical, oval, and ribbon found in mesophyll cells of leaves, and these pigments trap the light energy required for photosynthesis. The internal membrane surrounds a space known as the stroma. Thyllakoids, flat disc-like formations, are organized in a stacked manner like a pile of coins, and each pile is named granum (plural: grana), and Thyllakoids of distinct grana is joined via flat membranous tubules called stromal lamella. The stroma of chloroplast consists of DNA, enzymes responsible for proteins and carbohydrates synthesis, and 70s ribosomes. (iii) Leucoplasts-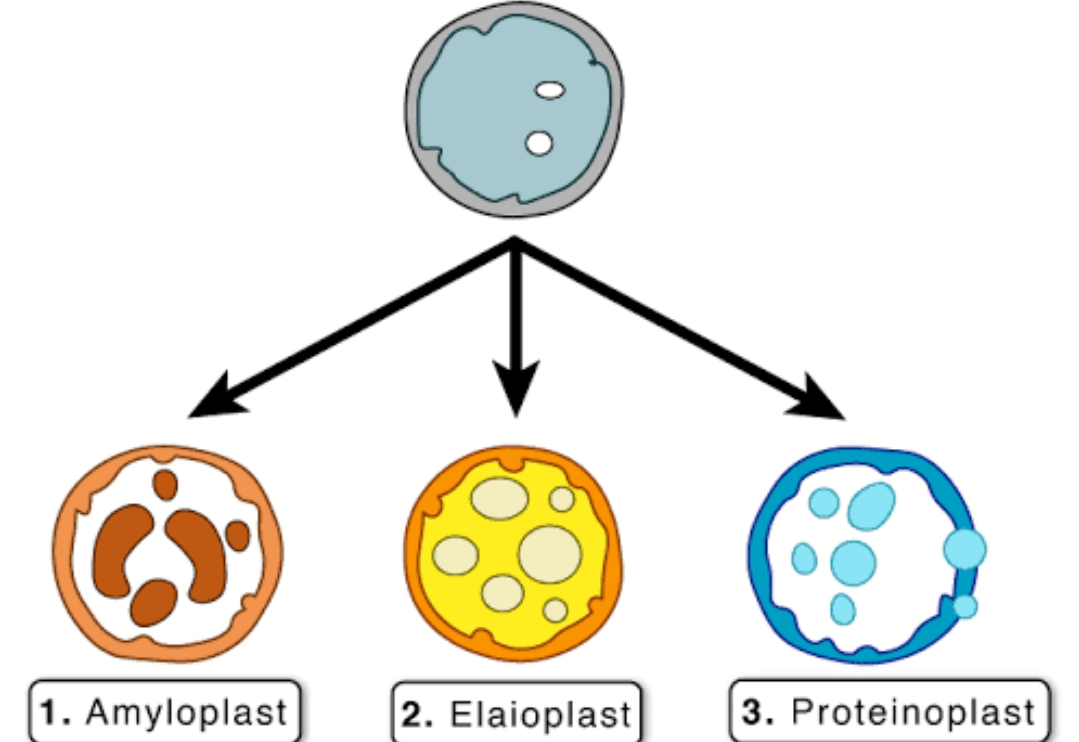
These are the colorless plastids that keep a stock of nutrients, and one of its three types, Aleuroplast, stores proteins, whereas elaioplast stores fats and oils, and amyloplast stores carbohydrates such as starch in potatoes. 12. Golgi Apparatus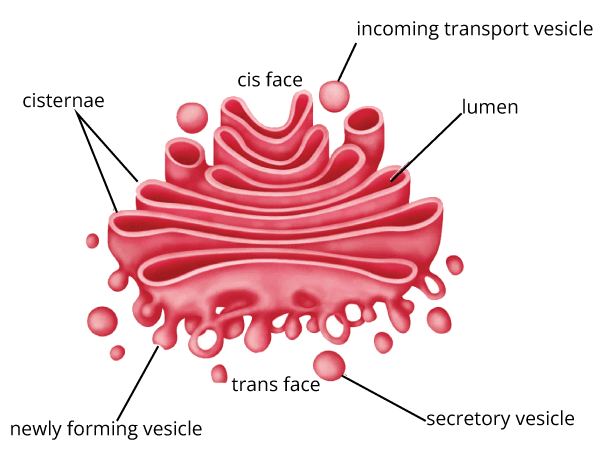
Golgi Apparatus is also called Golgi Complex and is a membrane-bound organelle comprised of a sequence of flat, stacked bags known as cisternae. Golgi Apparatus is basically involved in the transportation, modification, and packaging of lipids and proteins to aimed locations, and it is present in both plant and animal cells and is found inside the cytoplasm of the cell. 13. Ribosome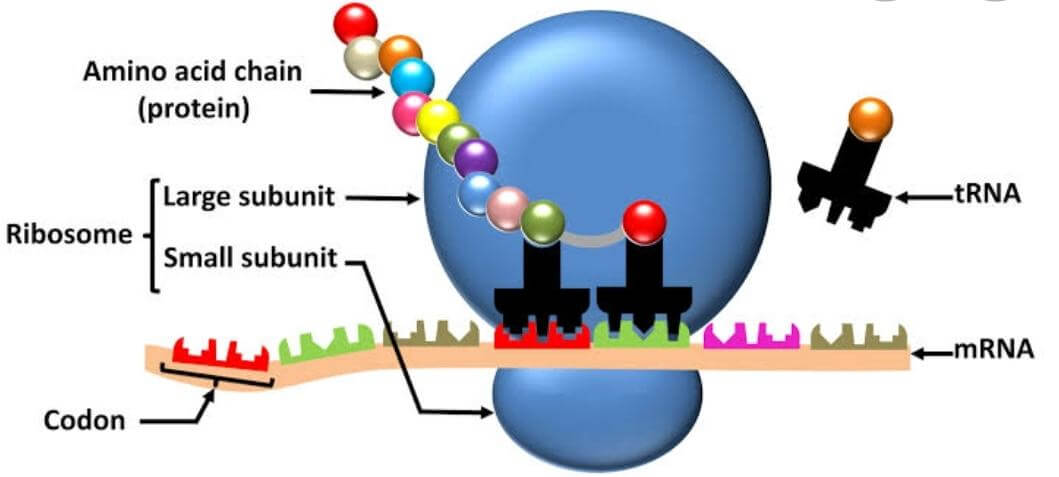
Ribosomes are tiny particles that do not have a membrane and are the crucial Cytoplasmic Organelles present in mutual association with the endoplasmic reticulum, and they are found in a large number of cells and mostly consist of 1/3rd of protein and 2/3rd of RNA. They are termed the 80s (present in eukaryotes) and the 70s (present in prokaryotes). S is the Swedberg's Unit that refers to the size and density. Both 70s and 80s type of ribosomes are made up from two different types of subunits. Ribosomes are surrounded inside the endoplasmic reticulum or are easily detected in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomes are constituted of two components, ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA, and the basic function of the ribosomes involves the process of protein synthesis in all living cells, which assures their survival. 14. Lysosomes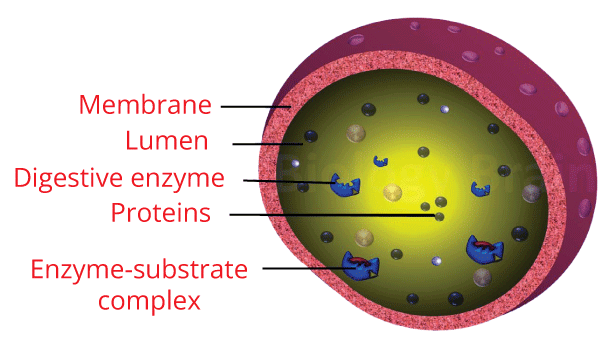
Lysosomes are essential membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells, and the area within the membrane is named the Lumen (A Lumen consists of hydrolytic enzymes and other cellular debris, and these hydrolytic enzymes have the ability to break down various biomolecules). Lysosomes act as the waste discarding formations of the cell, and they process the unwanted materials and deteriorate them, both outside the cell and waste elements present inside the cell. The digestive enzymes sometimes end up doing damage to the lysosomes themselves, and this causes the cell to die; this is named autolysis, where "auto" means "self" and "lysis" means "the decomposition of the cell by the demolition of its cell membrane." Therefore, lysosomes are also called "Suicidal Bags." ConclusionA cell has several elements called organelles, and each performs a specialized function. All of these cell organelles work collectively to ensure the cell functions adequately, assuring the survival of an organism, and if an organelle does not function properly, the cell suffers and could die.
Next TopicList of Indoor Plants
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









