List of Banks in IndiaWhat is Bank?A bank is a type of financial institution that allows the public to deposit and borrow money. The functions of banks are governed by legislation. Different countries have different laws for the establishment and working of a bank. People who work at a bank are known as bank employees. Certain banks deal directly with the public, while other banks handle investments and international currency trading. The word bank is derived from the Italian word banca, which means a bench or a counter. A bank is not only a safe place to deposit money but also a reliable place to take loans that are repaid to the bank with interest later. For example, obtaining a mortgage to purchase a home or apartment. Banks can also invest the money they have from deposit accounts in businesses to increase their profits. In most nations, the government sets the rules for banks through legislation. The amount of money released at any time is adjusted by a central bank (such as the Bank of England). It is a determinant in a country's economy, and the government is in charge of major choices. The Indian Banking SystemBanking was initially introduced to India in the first part of the 18th century. The General Bank of India, which is created in 1786, was the country's first bank. The State Bank of India, originally known as The Bank of Bengal, was founded in Kolkata in 1806. The Reserve Bank of India supervises all banks in India. All Indian banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India or RBI. In 1935, this governing body had the responsibility of formally regulating Indian banks. The Reserve Bank of India has been designated as the country's official Central Banking Authority, overseeing the country's banking sector. In India, there are two sorts of banks: public sector banks and private sector banks. A bank often offers the following services:
Furthermore, banking sector offers a variety of services such as personal banking, corporate banking, investment banking, private banking, transaction banking, insurance, consumer lending, trade finance, and other related services. In India, banks are categorized into four types:A strong banking system is critical because it assures public wealth, access to low-cost loans, economic growth, rural development, and worldwide reach. India has a large number of banks that are categorized into numerous types. But the best part is that they are all RBI-licensed, which means they are safe and reliable. The four types of banks in India are as follows; 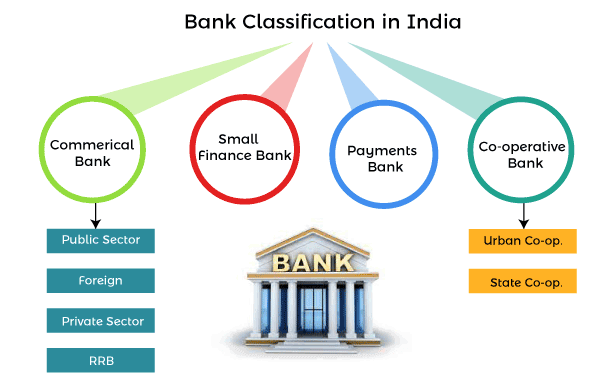
Brief Explanation about these four banks:1. Commercial bank: A commercial bank is a financial institution that accepts public deposits and lends money for profitable consumption and investment. Also, a large bank's section that interacts with companies or large/middle-sized organizations might be referred to as a corporate bank to distinguish it from retail banking and investment banking. Commercial banks are divided into two types: private sector banks and public sector banks. Primary functions
i) Public sector banking The banking activities of a specific type of commercial bank are referred to as public sector banking. The exact meaning of this statement varies depending on the country or region of the world in which it is used. Public-sector banks are those owned or operated by national governments in general. Some countries use this sort of banking more than others, but "public sector banking" is common in many regions where state control is still prevalent. ii) Private sector banking- Private sector banks are ones in which private individuals or private corporations possess a significant portion of the bank's equity. A big portion of these banks' shares are traded on the stock market, and anyone can purchase a significant portion of these banks' shares on the stock market. Even while these banks adhere to the standards of the country's central bank, they are free to develop their financial strategies for their consumers. Private sector banks in India fall into two categories: old and modern.
2. Small Finance Bank: Small finance banks are a type of specialist bank in India. Banks with a small finance bank license can offer basic banking services such as deposit acceptance and lending. Tiny business units, small and marginal farmers, micro and small firms, and unorganized sector organizations are among the areas of the economy that other banks do not currently handle. Objectives of small finance bank: The objectives of setting up small finance banks will be to improve financial inclusion by: i) Providing savings vehicles primarily to unserved and underserved segments of the population, and promoting financial inclusion in general. ii) Financing to small business units, small and marginal farmers, micro and small industries, and other unorganized sector organizations via high-tech, low-cost operations. 3. Payments banks: A payments bank is comparable to any other bank, except that it operates on a smaller scale and does not take on any credit risk. In other words, it can perform the majority of banking functions but cannot make loans or issue credit cards. It can accept demand deposits of up to Rs 1 lakh, remittances, mobile payments/transfers/purchases, and other banking services such as ATM/debit cards, net banking, and third-party cash transfers. 4. Cooperative Banks: Cooperative Banks are a type of bank that is owned and operated by its members. The term "cooperative" comes from the Latin word "cooperat" or "cooperate," which means "worked together." It means that people band together and help each other out since they have similar interests. Similarly, cooperative banks are associations of people who have a shared belief and get together to collaborate. A cooperative bank is one of the financial entities that belong to its members, who are also the bank's owners and clients. Cooperative banks are further classified into two types: i) State Cooperative Banks: A state cooperative bank is a federation of the cooperative central bank that serves as the custodian of the cooperative banking structure in the state. Its funds are derived from the Reserve Bank of India's social capital, deposits, loans, and overdrafts. State-owned cooperative banks provide money to cooperative central banks and primary companies rather than to farmers directly. ii) Urban Co-operative Bank: Although not formally defined, the term Urban Co-operative Banks (UCB) refers to primary cooperative banks in urban and semi-urban areas. Until 1996, these banks could only lend money for non-agricultural uses. This distinction is no longer met nowadays. Traditionally, these banks concentrated on communities, towns, and workplace organizations. They mostly lend to small borrowers and enterprises. Its operating environment has grown significantly in recent years. The Goal of Cooperative Banks
Other Bank types:i) Foreign bank: Foreign banks have their origins in another country and provide services to people in that country. In simple terms, foreign banks in India are banks whose headquarters are located in another nation but whose functions are managed from India. It must also adhere to the norms and obligations of both the Host and Parent countries. Foreign banks' functions Foreign banks are not often from the host country, but as previously stated, they must adhere to the host country's legislation. If an international bank wishes to begin operations, it may do so in any of two ways.
ii) Rural Regional Bank After the nationalization of banks in India in 1969, the banking system began to improve. Our Indian government owns RRB-Regional Rural Bank, a commercial bank. Regional Rural Bank has contributed to the growth of our Indian economy. The Regional Rural Bank was established to help India's rural areas thrive. Functions of Regional Rural Banks:Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are local-level banking operations in all Indian states. They were established to provide basic banking and financial services, particularly to the country's rural areas. On the other hand, Regional Rural Bank may have branches established up for urban operations, and their service area may also encompass metropolitan regions. The objectives of Regional Rural Banks.
So, here is the list of Banks in India. It will assist you in gaining an understanding of their performance and dependability. List of all public sector banks in India
List of private sector banks in India
List of regional rural banks in India
List of foreign banks in India
List of small finance banks in India
List of payment banks in India
List of State Co-operative banks in India
List of Urban Co-operative Banks in India
Next TopicList of Outdoor Games
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









