Glycolic AcidGlycolic acid is the smallest alpha-hydroxy acid. It also goes with the name hydroxyacetic acid. Its chemical formula is CH2OHCOOH or C2H4O3. It is a 2-hydroxy monocarboxylic acid wherein the methyl group is hydroxylated. 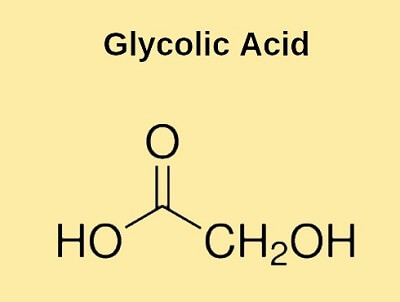
It is produced when glycol is made to undergo oxidation with dilute nitric acid. It is mainly used in various skin-care products that improve the texture and health of skin. It is obtained from sugarcane, sugar beets, cantaloupe and unripe grapes. Physical Properties of Glycolic acid
Why is Glycolic Acid good for skin?It is widely used in skin care products owing to its ability to penetrate the skin. It is used as a chemical-peel by dermatologists and other people. It helps improve various skin conditions such as hyperpigmentation, acne, wrinkles, etc. When applied, it reacts with the outermost dead layer (the Stratum Corneum) of the skin and exfoliates it and thus improves skin glow and also aids the reflection of light by the skin. It weakens the binding ability of lipids that hold the dead skin cells together. Thus, the outer skin tend to dissolve, which reveals the underlying skin. History of Glycolic AcidThe term glycolic acid was given by Auguste Laurent (French chemist) in 1848. Glycolic acid for the first time prepared in 1851 by Adolph Strecker (German chemist) and Nikolai Nikolaevich Sokolov (Russian chemist). To obtain it, they treated hippuric acid with nitric acid and nitrogen dioxide that formed an ester of benzoic acid and glycolic acid, which was called 'benzoglycolic acid' by them. The ester was then boiled with sulphuric acid to form benzoic acid and glycolic acid. Preparation of Glycolic AcidIt can be prepared either by a biochemical enzymatic reaction or by chemical synthesis wherein sodium hydroxide reacts with chloroacetic acid and then undergo re-acidification. In the biochemical enzymatic method it produces fewer impurities, requires less energy and leaves less co-product. Uses of Glycolic AcidApart from benefiting skin, it offers lots of other uses, some of which are as follows:
Mechanism of ActionThere are two proposed mechanisms of glycolic acid action: i) The first mechanism states that glycolic acid stimulates the epidermis to produce new cells by causing slight sub-clinical irritation. ii) As per the second mechanism, this acid weakens the intercellular bonds between corneocytes.
Next TopicLipoic Acid
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










