Lactic AcidLactic acid is an organic acid. It has a white color in solid state and is soluble in water. It is a carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is C3H6O6, which in extended form is CH3CH(OH)COOH. It is an alpha hydroxy acid and a common ingredient in generic skin care products. Lactic acid is also known as milk acid. It is a byproduct of anaerobic respiration, a process in which energy is produced by cells without using oxygen. Further, it is produced by bacteria in yogurt and in our guts. It is also found in the blood, deposited by muscle and red blood cells. It is also an important chemical compound as it takes part in various biochemical reactions. Chemical Formula of Lactic AcidThe chemical formula of lactic acid is C3H6O3. Lactic acid contains a carbon atom to which a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a carboxylic group (-COOH) is bonded along with a methyl group (-CH3). The hydroxyl group is present adjacent to the carboxyl group that makes it an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA). 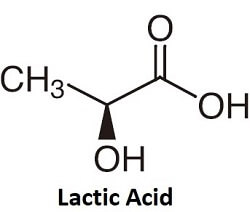
It is classified as an alpha-hydroxy acid as the hydroxyl group (-OH) and the carboxylic group (-COOH) are bonded to the same central carbon, which is chiral. The other two substituent groups include a hydrogen atom and a methyl group. So, two structures are there: L-(+)-Lactic acid and D-(-)-Lactic acid. Physical properties of lactic acid:
Chemical properties of lactic acid:It is a weak organic acid. However, it can react like stronger acids as the carboxylic acid group present in lactic acid tends to denote a hydrogen ion in the presence of organic as well inorganic bases. Uses of Lactic acid:
History of Lactic AcidLactic acid was isolated for the first time by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Jons Jacob Berzelius discovered in 1808 that lactic acid (L-lactate) is also formed in muscles during physical exertion. In 1873, Johannes Wislicenus established its structure. In 1856, Louis Pasteur introduced the role of Lactobacillus in the formation of lactic acid. The commercial production of lactic acid was started in 1895 by the German pharmacy: Boehringer Ingelheim. SourcesIt is mainly found in sour milk products like yogurt, kefir, leban, koumiss, cottage cheese, etc. The casein found in fermented milk is coagulated by lactic acid. What is a Lactic Acid Test?The test is performed to measure the level of lactic acid in your blood. Lactic acid is made by muscle tissue and red blood cells. Under normal circumstances, the level of lactic acid remains low in the blood. However, when the oxygen level decreases, the level of lactic acid tends to increase. The reason for the low level of oxygen can be one of the following:
A high level of lactic acid can lead to lactic acidosis, a life-threatening condition. So, a lactic acid test is used to diagnose lactic acidosis. It can also be used to check the oxygen supply to organs and tissues and to diagnose sepsis, which is caused by a bacterial infection. Further, if someone is suffering from meningitis, this test can be done to find out if it is caused by bacteria or a virus. Why one needs a lactic acid test?It is needed if someone has any of the following symptoms of lactic acidosis:
If someone is experiencing the symptoms of sepsis or meningitis, this test is also needed. The symptoms of sepsis are as follows:
The symptoms of meningitis are as follows:
How is the lactic acid test performed?The blood is taken from a vein or an artery by a health care professional. He or she uses a needle to take the blood from your arm. The blood is collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting while a needle is inserted. This procedure takes a few minutes: 3-5 minutes. You are not supposed to clench your fist as it may temporarily increase the level of lactic acid. Preparation of Lactic AcidThere are two methods that can be used for the production of lactic acid. i) Biotechnological method: In this method, lactic acid is produced on a large scale by the fermentation of carbohydrates such as glucose, corn syrups, etc., and also by the fermentation of nutrients like peptides and amino acids. This fermentation is done by a microorganism of the genus Lactobacillus. ii) Synthetic preparation: In this method, lactic acid is formed from carbon monoxide and acetaldehyde in an acid solution at a temperature of 130 to 200 degrees Celsius. Why do muscles produce lactic acid?Lactic acid is formed and accumulated in the muscles when the demand for energy increases and oxygen level in the body is low or not sufficient to fulfill the increased demand for energy. For example, during an intense exercise or physical work or due to infection or disease. Our body prefers to produce energy through aerobic methods, which means by using oxygen. But during strenuous exercise such as running, weight lifting, etc., our body needs faster production of energy that may not be possible with the available level of oxygen. So, in such cases, the muscles prefer to generate energy anaerobically (without using oxygen or in the absence of oxygen). This energy is produced from glucose through glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into a substance called pyruvate. When the oxygen level is high, pyruvate follows the aerobic pathway to be further broken down to produce more energy. However, during limited oxygen, our body temporarily converts pyruvate into lactate which continues the breakdown of glucose or energy production. The muscles can perform this anaerobic energy production at a high rate for a few minutes (1-3 minutes), which leads to the accumulation of lactate. Once you slow down, and oxygen is sufficient, lactate reverts back to pyruvate and thus body restores aerobic metabolism and allows the body to recover from the strenuous workout. This is the reason that people often have levels of lactic acid during or after strenuous exercise. This increased level of lactic acid due to exercise is called hyperlactatemia. It is the accumulated lactic acid that makes muscles feel sore or tired. How to prevent exercise-induced hyperlactatemiaThere are many ways to prevent the production of lactic acid while exercising, as follows:
Next TopicNitric Acid
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









