Write the Names and Formulas of 10 SaltsSalt:Salt is a chemical compound formed from the combination of negatively and positively charged particles called anions and cations respectively. Salts are crystalline and often the result of acid and base reaction. This reaction between acid and base is known as a neutralization reaction; the resultant salt has a neutral pH, i.e., ph=7 Example: HCl + NaOH ----→ NaCl + H2O In the above reaction, hydrochloric acid (HCL) reacts with Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH), a base; the resultant or product obtained is a neutral compound, sodium chloride, commonly known as common salt. 
Classification of Salts:Salts are classified into two categories 1) Based on pH and type of ion: -
2) Based on nature: -
1. Normal/Ordinary Salt: The salt formed by a reaction between acid and base is called regular salt. A most familiar example of ordinary salt is sodium chloride or table salt. 2. Acid Salt: The salt formed from the partial hydrogen atom replacement are known as acidic salts. Acidic salts produce an acidic solution when dissolved in solvent. Magnesium Hydroxide is an example of acidic salt. 3. Base Salt: A reaction between weak acid and strong base forms base salt. Base salt is also known as alkaline salt. Example, Sodium Carbonate. 4. Double Salt: Salt obtained by combining two different salts is known as double salt. Double salt contains more than one cation or more than one anion. For example, Potash Alum [K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O]. 5. Anhydrous Salt: Salt, which exists in dry form are known as anhydrous salt. All water molecules are removed from this kind of salt. Usually, these salts cannot incorporate water molecules, but a few of them may be able to incorporate water molecules; therefore, their water molecules are removed by heating. Table Salt is an example of anhydrous salt. 6. Hydrated Salt: Hydrated salt exist in crystalline state and are loosely attached to water molecules. Unlike anhydrous salts which cannot incorporate water molecules, hydrated salts can incorporate water molecules within them, for example, Copper Sulfate (CuSO4.5H20) Names and Formulas of 10 Salts:1. Calcium sulfate (CaSO4.2H2O) Common name- Gypsum Use- Used as fertilizer, the main constituent of drywall, chalk, etc. 2. Magnesium sulphate (MgSO4.7H2O) Common name- Epsom salt Use- For treating convulsions during pregnancy 3. Calcium chloride (CaCl2.6H2O) Common name- Dow flake Use- Production of activated charcoal 4. Sodium tetraborate decahydrate (Na3B4O7.10H2O) Common name- Borax Use- AC cleaner 5. Ferrous sulphate (FeSO4.7H2O) Common name- Green vitriol 
Use- Treats and prevents deficiency of anemia 6. Sodium sulphate (Na2SO4.10H2O) Common name- Glauber's salt Use- Manufacturing of detergents 7. Calcium sulphate semi-hydrate (CaSO4.1/2H2O) Common name- Plaster of Paris Use- Architectural, sculpture application 
8. Calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2] Common name- lime saltpetre Use- Water treatment, fertilizer 9. Copper II sulphite pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O) Common name- Bluestone Use- Fungicide, root killer herbicide 10. Sodium carbonate decahydrate (NaCO3.10H2O) Common name- Washing soda Use- Solvent to remove the stain Properties of Salts:
Occurrence:Common salt occurs at the earth's surface in the following form-
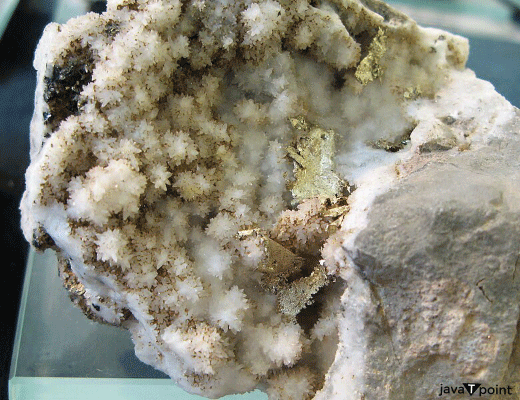

Around 3.5 pounds of salt is present in ocean water. Saline springs have relatively smaller quantities of salt. Beds of rock salt are the most abundant source of common salt. In some places such as dry lakes bottom and glacial deposits minute salt crystals occurs disseminated in porous soil. Although the original source of common salt are rocks. During weathering of rocks new minerals are produced among which are the soluble salts like sodium chloride, calcium sulphate etc. Effect of Salt on Human HealthSalt has a vital effect on human life and bodily function. Excessive salt intake damage bone health. Both sodium and chlorine are essential elements that maintain cellular rebalance and blood sugar levels. Sodium deficiency affects the brain and cannot send necessary electrical impulses to the rest of your body. The right amount of salt consumption is significant. Both excess and deficiency are unhealthy for our bodies. Higher salt intake and increased blood pressure cause hypertension, which may cause fatigue, weakness, and confusion. Therefore, everyone should maintain the proper salt balance in their diet. Our kidney helps to regulate the sodium level in our body. The excess sodium is removed through sweating and urination. Sodium also plays a vital role in nerve and muscle function and helps our body maintain average fluid balance. 
Conclusion:In conclusion, salts are ionic compounds without net charge. When dissolved in water, salt is an electrolyte that can conduct electricity. Salt also plays an essential role in the human body. Their deficiency can cause diseases like thyroid, and when consumed in excess, they dehydrate the human body.
Next TopicCrystalline and Amorphous Solids
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










