Natural AlternativesNatural alternatives of building materials are those that are used less frequently than resources like wood or iron, such as rocks or Adobe. Natural Alternative materials have a wide range of useful applications in fields including environmentally friendly engineering and architecture. The major goal of employing such materials is to increase the effectiveness and flexibility of the buildings while reducing the negative consequences that our built environment might have on Earth. 
Alternative natural materials have been around for a while, although historically only in extremely basic forms or as components of a specific substance. For instance, Earth has been utilised as a building material for home walls for thousands of years. Much more recently, in the 1920s, the American government advocated the use of rammed Earth as a fire-resistant building technique for farmhouses. Adobe is a different, more typical example. The Southwest United States and numerous Spanish-speaking nations are known for their adobe dwellings. Although straw bale construction is a relatively recent idea, there is evidence that dwellings were built from straw on African plains as early as the Paleolithic period. Alternative natural materials, especially their uses, have become increasingly prevalent lately. In reaction to global warming and climate change, green and sustainable concepts placed more emphasis on the materials and construction techniques used to construct our houses and cities. The use of alternative natural materials in place of traditional natural materials or man-made products that significantly rely on natural resources has gained popularity as environmentally aware actions have become more prevalent. MaterialsRock
A fantastic substitute for traditional materials that include chemicals that might be detrimental to people, animals, or the environment is rock. Rocks are excellent thermal insulators and have considerable thermal mass. These qualities make stone an excellent choice since it helps to maintain a relatively consistent indoor temperature, which reduces the need for air conditioning and other cooling equipment. Reject stone (stone fragments that cannot be utilised for another purpose), limestone, and flagstone are examples of the types of rocks that can be used. Straw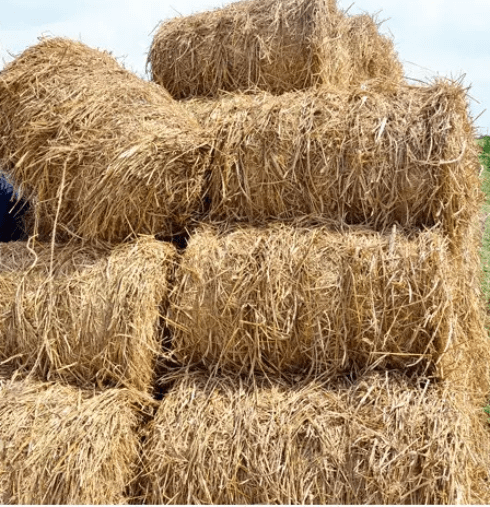
Walls may be built using straw bales rather than plasterboard. In a conventional post-and-beam building, where a wood frame supports the home, straw offers great insulation and fire protection. Because no oxygen can get through the walls, fire cannot spread, and there is no danger of combustion. These straw walls are approximately 75% more energy efficient than conventional plasterboard. Bamboo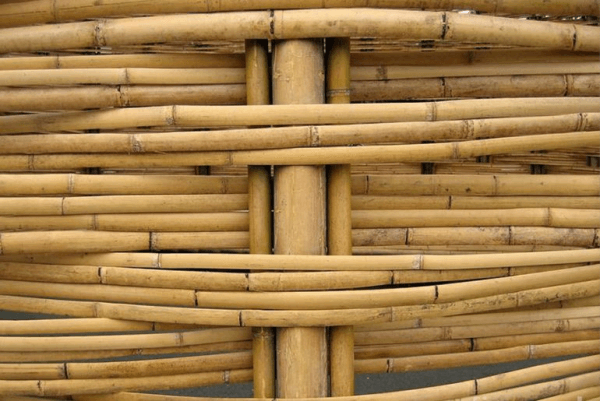
Bamboo is utilised in Asian nations to construct buildings like bridges and houses. Bamboo is an abundant resource because it grows exceedingly quickly, is surprisingly robust, and is somewhat flexible. Although joining corners together might be challenging, bamboo is incredibly robust and makes up for the challenges that may arise during construction. Cordwood
Small pieces of leftover firewood and other materials are combined to create cordwood. These little wood pieces may be joined together with ease to create a structure that, like stone, has excellent insulation and thermal mass. Without using a tonne of timber, cordwood gives buildings the rustic appearance of log cabins. Stones can be used to fill in the walls, or cordwood alone can be used to construct a full structure. Rammed Earth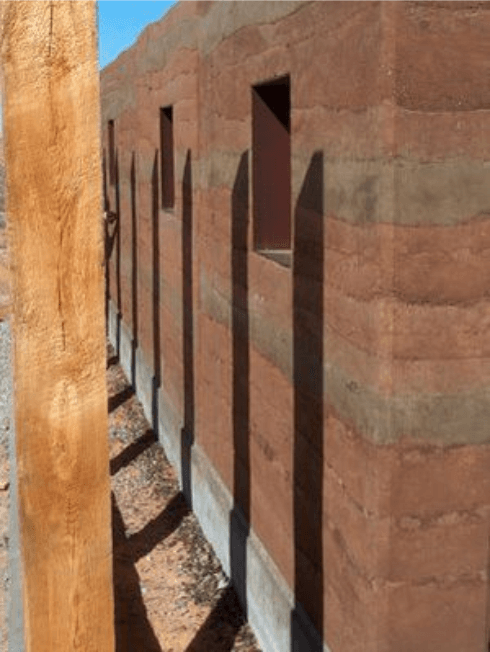
Concrete and brick may be substituted with rammed Earth since it is a material that is readily accessible. To create a sturdy wall packing composed of Earth, stones, and sticks, the soil is crammed firmly into wall moulds, which are forced together and solidified. Additionally, rammed Earth has a large thermal mass, which results in significant energy savings. It was also utilised in constructing the Great Wall of China because it is extremely waterproof and robust. Earth-sheltered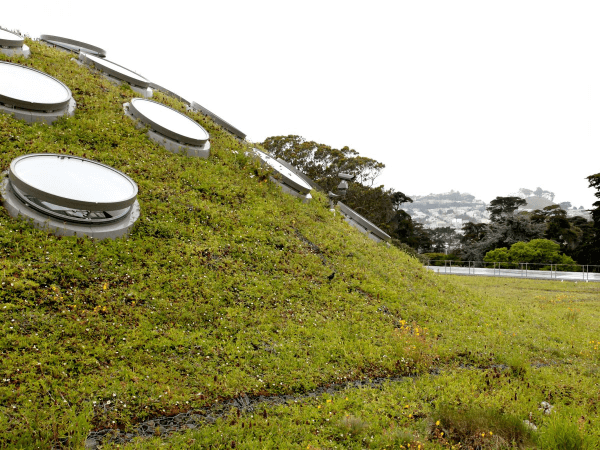
Buildings using the unusual construction method known as "earth sheltering" have at least one side entirely made of Earth, whether it is a clay wall, a grass roof, or both. As a result of the challenges presented by utilising excessive amounts of power in such a home, this unusual design often has a lot of windows. As a result, the cost of lighting is decreased, improving the home's energy efficiency. Papercrete
A fascinating and relatively new substance that works well in place of concrete is called papercrete. Shredded paper, sand, and cement are combined to create papercrete, which hardens into a substance resembling brick. Buildings made of papercrete have excellent insulation and are also fire and termite resistant. Papercrete is extremely affordable, typically costing around $0.35 per square foot. Adobe
An age-old method called Adobe is inexpensive, simple to use, and perfect for hot situations. Sand, clay, and water are combined, then poured into a mould and let to dry in the sun. It becomes extremely durable and heat-resistant after drying. Adobe provides great insulation throughout the summer to lower energy expenses by not allowing much heat to pass through to the inside of the building. Despite being a fantastic heat insulator, this clay combination is not very watertight and can be hazardous in earthquake-prone locations due to its propensity to shatter readily. Sawdust
For usage in wall construction, sawdust works well when mixed with cement or clay. These barriers end up being quite strong and efficiently reuse any trees that might need to be removed from the construction site. The wood chips in the walls absorb moisture and assist prevent cracking during freeze/thaw cycles depending on the type of sawdust used (hardwood is preferable). Sawdust may be mixed with water and then frozen to create pykrete, a substance that is durable and less prone to melting than conventional ice. ExamplesAlthough this is a more recent technology, several buildings have already used these materials in addition to other strategies to become more environmentally friendly.
Next TopicRobinhood Alternatives
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









