Soil Pollution EssaySoil Pollution is soil contamination with chemicals and toxic substances that risk human health. It is a severe environmental problem that has a long-lasting impact on human health. When humans get exposed to highly benzene-contaminated soil, it poses the risk of humans getting affected by the leukemia crisis. It is worth knowing that all dirt has some compound with a little element of toxicity. However, such concentration of effluents in the ground is minimal and poses a minimum threat to the environment. When a poisonous substance is mixed in soil in massive amounts, then the soil is polluted and will cause tremendous damage to a living organism. 
Some of the contributing factors to this problem are:
Pollutants That are Contaminating the SoilXenobiotics: These pollutants are the most hazardous. They are not present in nature but are created due to human intervention. The word has a Greek origin, and 'Xenos' means foreigner and Bios (life). They are also known as carcinogens. Some of the major pollutants that are present in the soil are:
Various types of pollutants that are present in the polluted soil are:

These are organic compounds, and they have:
The name is PAH, i.e., Polycyclic Aromatic Carbons, which includes phenalene, naphthalene, and anthracene. Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon will give rise to different forms of cancer. These organic compounds can cause cardiovascular diseases in human beings. The source of PAHs could be credited to vehicle emissions, coke(coal), extraction of shale oil, and cigarette smoke. Pesticides Pesticides are used in soil to disinfect, kill, or resist pests. Primarily used pesticides in agriculture are:
An unintended sprinkling of pesticides in the field is called pesticide drift, an extreme cause of concern and degrades soil and water quality. Contaminants that are available in pesticides are: Insecticides
Fungicides
Herbicides
Such chemicals pose high threats to human health and have a long-lasting environmental impact. Such chemical directly damages the central nervous system and rise to disease like congenital disabilities and immune systems disease. Process of Causing Soil PollutionSoil Pollution is primarily classified in two ways:
Anthropogenic Soil Pollution Most of the cases that have come to scientists are anthropogenic in nature. A lot of human activities contribute to this problem. Some of the processes are:
Other pollutants include e-waste, coal ash, and nuclear waste. Negative Results of Soil Pollution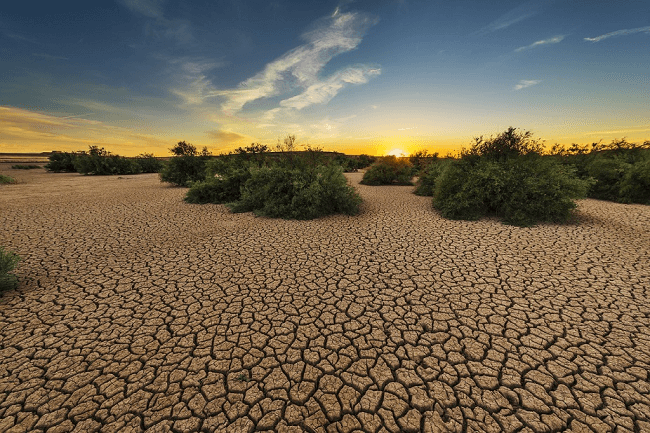
Soil PollutionSoil Pollution has negative consequences on human beings, plants, and animals. Children are more vulnerable to diseases, which pose an immense risk to them. Effects on Plants and AnimalsDegradation of soil is closely associated with loss of nutrients in the soil. In case of the unavailability of nutrients present in the soil, the plant does not thrive. Inorganic aluminium-contaminated soils hurt plants. This form of contamination has the probability of increasing the salinity of the soil. The salinity of the soil makes it unfavorable for the plants to grow. Plants that thrive on polluted soil possess a high quantity of pollutants, and the whole process is called bioaccumulation. These plant that has grown in a contaminated atmosphere is consumed by the herbivores and get directly emitted into the food chain. It would lead to the extinction and loss of some animals. Some pollutants can reach the top level of the food chain and enter a human being. Effects on Human Beings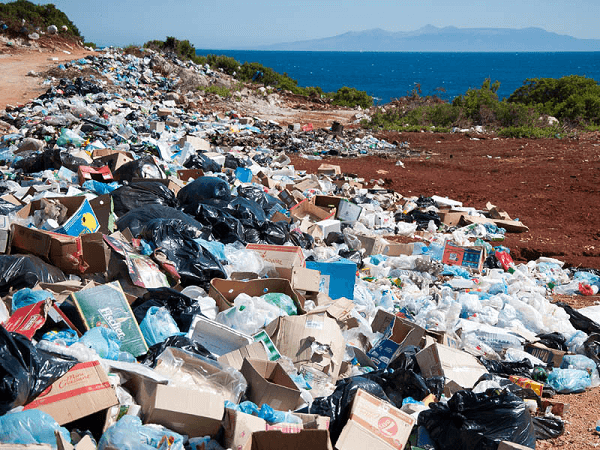
Soil Pollutants are present in all three mediums: liquid, solid, and gas. It makes a suitable way to reach the human body. They could reach through inhaling contaminated soil dust and direct skin contact. Short-period effects that can be seen after humans get exposed to contaminated soil include:
Lots of long-term diseases are directly connected to soil pollution, and such disease is:
It is interesting to know that contaminants like industrial solvents and petroleum hydrocarbon are directly connected to a congenital disorder. Side-Effects on Environment Ecosystem
Ways to Control Soil PollutionPrevention of soil pollution is a challenging task for the Government and society. It is a very complex issue and involves a multifaceted approach. The issue is getting bigger with each passing day, and concrete, viable and visible action needs to be taken. We are seeing the side effects of soil erosion worldwide, and the world needs to be more conscious of the problem. Some listed methods to prevent soil pollution are:
Government Role in Preventing Soil ErosionSoil pollution cannot be prevented without support and intervention from the Government. The problem of soil erosion directly affects the food security of the nation. The food security issue is the top priority of any government. The Government is compelled to take initiatives in this direction. Central Government supported the plans
Desertification and Land degradation atlas was launched to compare the situation between 2016 and (2003-05) and (2011-2013). The Government prepared National Action Programme for fighting desertification. Along with innumerable mega outreach events, the Government conducted seminars and programs to create awareness among the people. NGOs Working for Land Pollution
Government-Backed Institute Working for Land Pollution
Frequently Asked Questions on Soil PollutionQues: What is the importance of the soil? Ans: Water filtering, plant development, and Human nourishment depend on the soil. Soil helps regulate climate and houses more carbon than all of the world's forests combined. Human Survival entirely depends on the health of the soil. Ques: What are the ways to control soil pollution? Ans: Some of the well-known ways to control pollution are:
Ques: What is Soil Conservation? Ans: It is a combination of practices used to protect the soil from degradation, treat it as a living ecosystem, and return to the use of organic matter on a continued basis. Ques: What are the good reasons to practice soil conservation? Ans: Some of the good reasons to practice soil conservation are:
Ques: What are the techniques of soil conservation? Ans: Some of the well-known soil conservation techniques are:
Ques: What are the major pollutants of the soil? Ans: Some of the major pollutants of the soil are heavy metals such as lead and mercury, pharmaceuticals such as antibiotics used for livestock management, inorganic and organic solvent, and hydrocarbons. Ques: What are the consequences of soil pollution? Ans: Some of the dangerous consequences of soil pollution are:
Ques: What are some facts related to soil pollution? Ans: Some of the unknown facts related to soil pollution are:
Ques: What are the different types of soil? Ans: Different types of soil present are:
Ques: Which soil is most fertile? Ans: The most fruitful and fertile soil is porous loamy soil. In this soil, clay, silt, and sand are available in equal amounts. The soil is rich in organic content and can hold water. It offers a nutrient-rich environment to the soil. Ques: What is land degradation? How does it happen? Ans: It is the loss of soil quality due to biological, physical, and chemical factors. Some visible features of the degraded soil are alkalinity, organic matter loss, and reduction in soil fertility. Ques: Lists soil deposits found in India. Ans: Eight soil deposits are found in India, and they are:
Ques: What is Zero Budget Natural Farming? Ans: The term Zero Budget Natural Farming means raising crops without the use of pesticides or any other external materials, and the word zero refers to zero cost involved in the production of all crops Ques: What are the principles involved in Zero Budget Natural Farming? Ans: Principals involved in the Zero Budget Natural Farming are:
Ques: Which states follow the Zero Budget Natural Farming model (ZBNF)? Ans: Some of the states that are following the ZBNF model are:
Ques: Is Zero Budget Natural Farming practical? Ans: This method looks simple, doable, and easy. However, there are fundamental challenges, and even if farmers get input freely present in nature, farmers have to spend on labor and transportation.
Next TopicStress and Its Effects on Youth Essay
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









