C++ Tutorial
C++ Control Statement
C++ Functions
C++ Arrays
C++ Pointers
C++ Object Class
C++ Inheritance
C++ Polymorphism
C++ Abstraction
C++ Namespaces
C++ Strings
C++ Exceptions
C++ Templates
Signal Handling
C++ File & Stream
C++ Misc
C++ STL Tutorial
C++ Iterators
C++ Programs
MCQ
Interview Question
C++ Exception HandlingException Handling in C++ is a process to handle runtime errors. We perform exception handling so the normal flow of the application can be maintained even after runtime errors. In C++, exception is an event or object which is thrown at runtime. All exceptions are derived from std::exception class. It is a runtime error which can be handled. If we don't handle the exception, it prints exception message and terminates the program. AdvantageIt maintains the normal flow of the application. In such case, rest of the code is executed even after exception. C++ Exception ClassesIn C++ standard exceptions are defined in <exception> class that we can use inside our programs. The arrangement of parent-child class hierarchy is shown below: 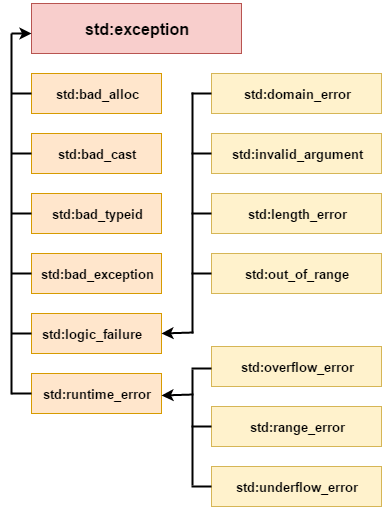
All the exception classes in C++ are derived from std::exception class. Let's see the list of C++ common exception classes.
C++ Exception Handling KeywordsIn C++, we use 3 keywords to perform exception handling:
Moreover, we can create user-defined exception which we will learn in next chapters.
Next TopicC++ try/catch
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









