Active and Passive Voice RulesActive and Passive is an essential subject in English Grammar and holds significant value in English speaking and writing. The statements in English can be presented in both active and passive voice. The active voice is the direct form, whereas the passive voice is the indirect form. In English, the verb expresses the subject, whether an object or a person, who has done something or who is doing something. A sentence that commences with either the subjects or objects to categorize if the statement is Active or has a Passive voice. 
What Exactly Is the Voice of the Verb?The verb voices express if the subject of the sentence has done or received the activity. English Grammar comprises of two kinds of voices:
Active voice exists whenever an activity completed by the subject is conveyed via the action words or word. An active voice is used whenever a stronger connection and clearness between the subjects and the action words are essential. Passive voice exists whenever the subject acquires the activity conveyed by the action verbs. When the performer of the activity is unspecified, and the emphasis of the phrase is on the action or the task instead of the subject, passive voice is used. Types of Voices of VerbVerbs have two kinds of voices: active and passive. Active Voice: An active voice is used whenever a verb indicates a subject's action. Whenever a more direct relationship and clearness between the subject and the verb is necessary, the active voice is utilized. Example of Active Voice:
Passive voice is used when the subject is the recipient of the actions conveyed by the verb. Whenever the person of the act or activity is unknown, and the attention of the statement is on the activity rather than the topic, passive voice is utilized. Examples of Passive Voice:
Rules For Active and Passive Voice For Sentence ConversionsLet us explore some samples of active and passive voice sentences prior to going into the rules of active-passive voice. Instances of Active and Passive Voice ConversionRiya penned a message. (The example has the Subject along the Verb and the Object) A message was penned by Riya. (Object) + (auxiliary verb) + (past participle) + (by subject). Elizabeth prepares the meal. (The example has the Subject along the Verb and the Object ) The meal is prepared by Elizabeth. (Object) + (auxiliary verb) + (past participle) + (by subject ) Principles Of Active/Passive ConversionI. The active verb's object becomes the passive verb's subject . II. The subject present in the active form of the statement will take the place of the object in the passive statement (or is dropped). The verb's finite form is converted to the past participle or third verb form . III. The passive object is preceded by the preposition "by. " 
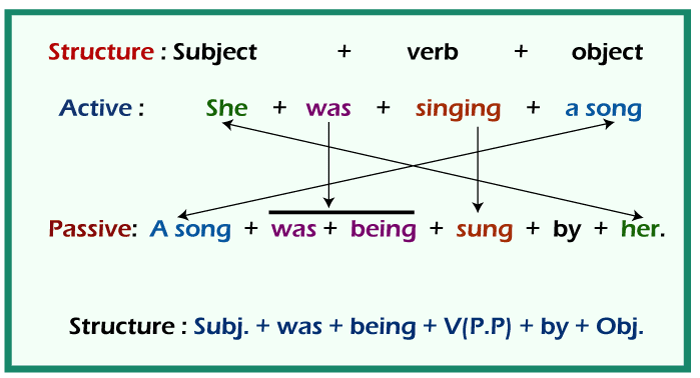
Active and Passive Voice RulesRule 1: To change an active statement to passive voice, locate the (S+V+O) Subject, Verb, and Object . Example: She drives a bike. (She is the subject, the verb is 'drives', and the object is the bike. ) 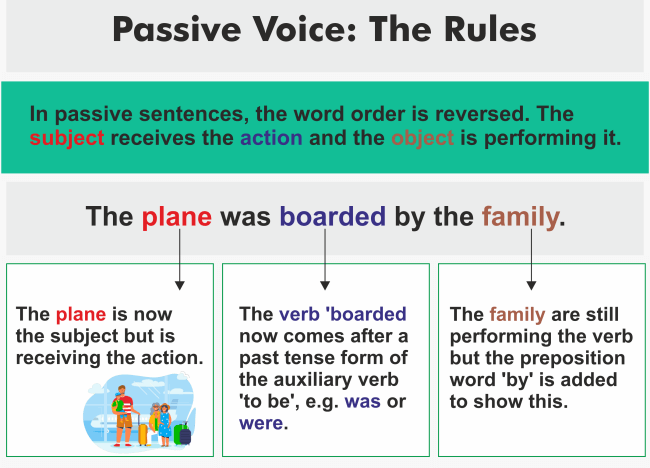
Rule 2: Interchange the objects and the subjects so that the objects of the active sentences become the subjects of the passive sentences . Example: Active Voice: Mary knits a scarf. (Mary is the subject, Knits is the verb, and scarf is the object. ) Passive Voice: A scarf is knitted by Mary. (The object scarf is swapped with the subject Mary. ) 
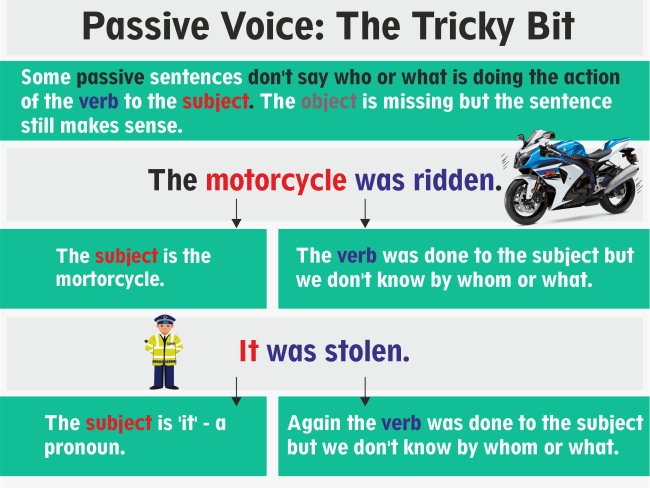
Rule 3: The subjects are not always utilized in passive voice, i.e. the subjects in passive voice can be omitted if the sentences lacking it convey a substantial sense . Example:
Rule 4: In the active voice, convert the base verbs to the past participles, i.e. third form verbs in the passive statements, i.e. prefixed by (By, With, to, etc.). In passive voice statement, base verb is rarely used . Example: Active voice: She arranges a feast . Passive voice: The feast is arranged by her . Active voice: She remembers him . Passive voice: He is remembered by her . Active voice: Smoothie fills the flask . Passive voice: The flask is filled with the smoothie . 
Rule 5: When an active voice statement is converted to a passive voice sentence, the pronoun utilized in the sentence transforms in the following way .
Rule 6: Utilize the appropriate auxiliary or assisting verbs (is, am, are, was, etc.). Each tense has a different set of guidelines for the use of auxiliary verbs in passive voice phrases . Example:
Rules for Converting from Passive to Active VoiceTo change the sentences from passive to active voice, remember the following guidelines :
Now let us have a look at the rules of Voices on the basis of Tenses Voices On the Basis of TensesSimple Present TenseActive voice - subject + verb +object Passive voice - object + am/ is/are + Verb +by+ subject Example - Active-I watch the tv every weekend . Passive-Tv is watched by me every weekend . Active- He enjoys travelling . Passive- Travelling is enjoyed by him . Present Continuous TenseActive voice - subject +am/is / are +Verb+ing +object Passive voice - object+ am/ is/are +being + Verb+by+ subject Example - Active- He is providing for the needy . Passive- The needy are being provided by him . Present Perfect TenseActive voice - subject +has/have + Verb +object Passive voice - object+ has /have +been + Verb +by+ subject Example - Active- Rimi has made the organizer . Passive- The organizer has been made by Rishi . Active- Kate has managed her team well . Passive- Her team has been managed well by Kate . Simple Past TenseActive voice - subject + verb +object Passive voice - object+ was/were + Verb +by+ subject Example - Active- She made an agreement . Passive- An agreement was made by her . Active- Piyush resolved all the queries appropriately . Passive- All the queries were appropriately resolved by Piyush . Past Continuous TenseActive voice - subject + was/were+ Verb +ing +object Passive voice - object + was/were + being+ Verb +by + subject Example - Active- He was peeping into the room . Passive- The room was being peeped into by him . Past Perfect TenseActive voice - subject + had+ verb +object Passive voice - object+ had + been+ Verb +by+ subject Example - Active- A driver had estimated such an incident . Passive- Such an incident had been estimated by a driver . Simple Future TenseActive voice- Subject + will/shall+ verb + object Passive voice- Object +will/shall+ be +Verb+ by +subject. Example- Active- Your team member will interrogate you . Passive- You will be interrogated by your team member . Future Perfect TenseActive voice - subject + will/shall+ have +Verb +object Passive voice- Object +will/subject +have +been +Verb +by +subject Active voice- The owner will have given some concessions . Passive voice - Some concessions will have given by the owner . Active voice- Billions of offices will have vacated their workplaces due to the epidemic . Passive voice - Workplaces will have been vacated by billions of offices due to the epidemic . Imperative SentenceImperative sentences are those that communicate demands, requests, orders, recommendations, etc. With or without an object, the passive version of an imperative sentence is introduced. Passive form (With object) - Let + object +be + past participle . Passive form (Without object) - In case Statements starts with 'You are ordered/advised/ suggested?……. etc. For example- Active - Cash vouchers on time . Passive - You are suggested to take cash vouchers on time . Active voice - Let us rehearse here . Passive voice- We may be permitted to rehearse here . Interrogative SentenceInterrogative sentences are those that pose an inquiry. There are two sorts of interrogative phrases in voice: those that contain words from the W family and those that do not. If "who" is employed in the active voice, the passive form should be "By whom." When using the active voice without the word "who," the assisting verb comes before the object since the statement is an interrogative. For instance, Active Voice- Who advises him ? Passive Voice- By whom is he advised ? Active Voice-Are you organizing the interview ? Passive Voice- Is the interview being organized by you ?
Next TopicActive and Passive Voice Worksheet
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









