PronounOverviewEach day, you utilize pronouns. In reality, even if you do not really know what pronouns are, you still utilize them-and we have now used pronouns 4 times in this phrase only. 
A pronoun is a word that is utilized to imply to another term or in replacement of noun. If your audience actually already recognizes the nouns you're addressing to, you use pronouns to replace them. For example, one can say, "I have a cat." She's black and white" You don't need to specify that you are describing your cat in the following sentence since you mentioned him after the first. However, connecting "I have a cat" with "black and white" is grammatically wrong... therefore, using the pronoun "she has, or she's," you make the sentence "black and white" into a full sentence: He is black and white (referring to the cat's color). Pronouns do much more than transform phrases into statements. They give context, clarify the meaning of your phrases, and alter how we interpret people and things. Keep on reading to gain knowledge of several uses of pronouns or how to utilize them to form sentences. There seems to be a lot to learn about pronouns, and even if you probably know a lot of it subconsciously, studying a comprehensive guide to pronoun uses and purposes (with examples!) will help you improve your English grammar and become a better writer. What is a Pronoun?A pronoun is a term that substitutes a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns relate to a noun that has already been stated or a noun that does not have to be specified. 
Pronouns are brief words that we use to replace other nouns in our writing and speech to make it speedier and more diversified. They are phrases like as: They I You Who Themselves Each other Pronoun is a tiny sub categorization of noun. Pronouns are differentiated with the fact that they can be utilized in substitution of other noun. For example, if you keep on repeating "Mary" over and over again while recounting a narrative about your niece Mary, the narrative will start to sound repetitious. As an example: Mary has always been interested in fashion. Mary stated that she wishes to attend design school. You may try to spice it up by alluding to Mary as "my niece" at times, but it makes it sound as though you're addressing to two separate individuals: Mary has always been interested in fashion. According to my aunt, Mary has expressed an interest in attending design school. Alternatively, you can address to Mary with the pronouns she and her: Mary has always been passionate about fashion. She stated that she wishes to attend design school. Pronouns can stand in for both proper and common noun. Some pronouns have strict limitations concerning when they can be employed, like never referring to an individual. Below, we describe all of the distinct categories and the limitations that go along with them. A pronoun (abbreviated pro) is a term or series of terms that can be used to replace nouns or even a noun phrase in linguistic and grammatical form. Pronouns have long been considered a part of speech, but due to the range of activities they fulfill cross-linguistically, some current theorists believe they do not create a single class. The plural and singular pronoun "you" is an instance of a pronoun. Personalized and possessive pronoun, reflexive pronoun, reciprocal pronoun, demonstrative pronoun, relative pronoun and interrogative pronoun, and indefinite pronoun are examples of sub categories of Pronoun. The usage of pronouns frequently involves anaphora, in which the pronoun's meaning is completely reliant on an antecedent, for instance, in the sentence. The poor young person looks as if he requires a jacket, the meaning of the pronoun he is reliant on its antecedent, that poor young man. "Pronominal" is the adjective related to "pronoun." A pronominal is a string of words that also functions as a pronoun. For instance, the expression (including the prop-word one) is a pronominal in, for instance- That's not someone I desired. Pronouns and GrammarPronouns are included among eight speech components in The Art of Grammar; a 2nd century BC Greek grammar treatise credited to Dionysius Thrax. There, the pronoun is defined as "a part of speech that can be substituted for nouns and is indicated for a person." Pronouns were still considered to be part of speech in Latin grammar (the Latin word being pronomen, wherein the English name - via Middle French - eventually derives), and so in the European tradition in broad. Pronouns are much less suitable to represent a single word class in much more current approaches to grammar due to the numerous varied syntactic functions that can perform. Types of PronounPersonal pronouns imply to an individual or people are speaking or writing (first person), the individual or persons being spoken to (second person), or other person or objects (third person). Personal pronouns, just like the noun, can be the subject or objects of the verbs or prepositions: "She adores him, but he respects her." The majority of personal pronouns have unique subject/ s and object/s types: 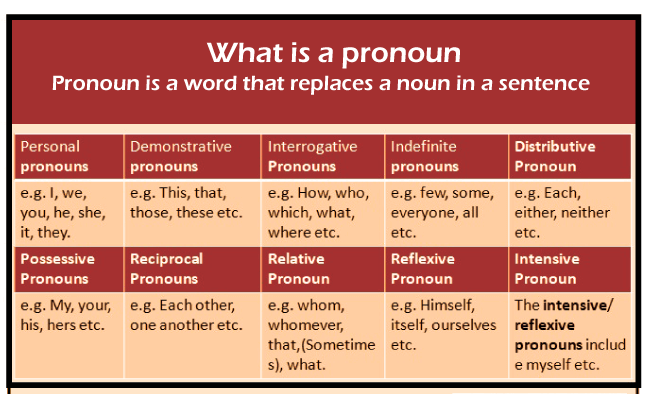
As a Subject 1st Person - I/we 2nd Person- You/You 3rd Person-He, she it/ They Whereas in the case of an object 1st Person- me/ us 2nd person- you/ you 3rd person- him, her, it/them There are several types of pronouns. Interrogative pronouns, namely what, which, who, whom, and whose, initiate inquiries to which a noun is a response, as in "Which one do you recommend?" Possessive pronouns relate to objects or people that somebody owns. Mine and yours are the most common possessive pronouns. Mine, yours, her, his, it, our, and there are the most common possessive pronoun. 
The four demonstrative pronouns - this, that, these, and those-separate the specific individual or an object being addressed to from other persons or groups or items; they are interchangeable with the demonstrative adjective. Relative pronouns provide a subordinate clause, which is a sentence component that comprises a subject and verb and therefore does not stand alone. That, which, who, whom, what, and whose are the most common relative pronouns. Reflexive pronouns relate back to the issue or the subject of a phrase or clause. They are produced by prefixing personal pronouns or possessive adjectives with -self or -selves, as in himself, myself, ourself, and itself. Indefinite pronoun like everyone, either, none, and something do not relate to a specific person or an item. So hence Indefinite pronouns, like everybody, either, none, and whatever, do not relate to a particular individual or thing, but rather to an unknown or unknown person or thing. When the grammar rules demand a subject, but no noun is actually alluded to, the words it then there can also be employed as pronouns. Both are typically used at the start of a phrase or clause, as in "It was almost lunchtime" and "There is still some dessert left." These are considered to as expletives on occasions. 
Examples of Pronoun in sentencesThe words that have been highlighted represent as Pronoun.
Next TopicTypes of Pronoun
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









