Pronoun SentencesNouns play an important role in our sentences. They play a vital role as subjects and objects. However, sometimes or in fact more often there are situations when nouns should be avoided, or there are scenarios when a noun does not fit correctly in the statement. Have you ever thought in such a case noun turn to which part of speech for help or substitution whenever they are in need of it? It is the pronouns, which are a perfect substitution for them. What are Pronouns?Pronouns are very vital part of speech, as well as using these correctly will immensely improve your verbal or writing form. These have the ability to do all the tasks and roles of nouns, but many of these are shorter and more dynamic. Pronoun allow us to make comments like "I am pleased of myself" or "You can ask for assistance." In an English sentence, a pronoun is a word that takes the form of a noun. It can appear in a statement where a noun already exists or to inhibit the noun from being repeated in the statement. A pronoun is a word or statement that is used to substitute the nouns or noun phrases known as the pronoun's antecedent. 
Pronoun(s) are short phrases which can perform all the tasks/ responsibilities of a noun and are one of the sentence formation elements. Common pronouns include he, she, you, me, I, we, us, this, them, and that. A pronoun indeed serves as a subject, direct object, indirect object, prepositional object, and so on, and have the ability to represent persons, places, animals, or objects. Here is the list of the most common pronoun These include; He/ She It You/ They I We Who Him Them Whoever Anyone Something Nobody and so on Types of PronounsThere are various types of Pronouns. The most common ones are; Personal Pronouns- These refer to a person or persons speaking or writing ( which are generally the first person), the person or individuals being talked to (which are the second person), or another individual or items (which implies to the third person). Like nouns, personal pronoun can be the subjects or the object of verb or preposition: "She liked him, yet he regards her." Possessive Pronouns: These are employed for referring to the items or the individuals that own or possess something. The frequently employed possessive pronouns are mine, yours, her, his, it, ours, and their. The most prevalent possessive pronouns are mine and yours. Demonstrative Pronouns: There are mainly 4 demonstrative pronouns-this, that, these, and those-that distinguish the certain individual or the item being referred from other people, groupings, or things; they are interchangeable with the demonstrative adjective. Relative pronouns give a subordinate clause, which is a phrase component that includes both a subject and a verb and hence cannot stand separately. The frequently employed relative pronoun include- that, which, who, whom, what, and whose. Reflexive Pronouns: These refer back to the subjects or issue of a statement or clause. These are formed by pre-fixation of the personal pronoun or possessive adjective along the terms like -self or -selves, such as himself, myself, ourself, and itself. 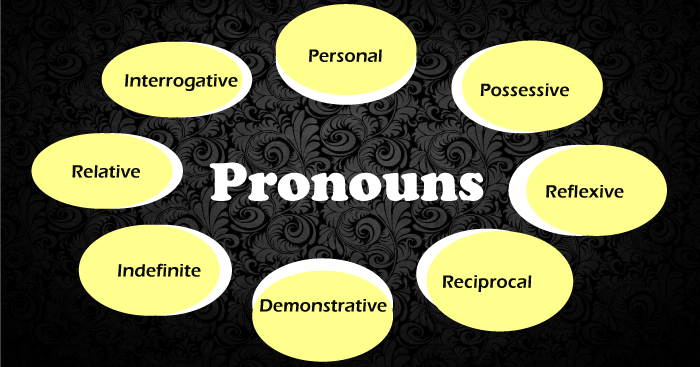
Interrogative pronouns - What, which, who, whom, and whose are some of the interrogative pronouns that begin queries, in reply to that a noun usually replies, as in "Which one do you advise?" Indefinite Pronoun: Everyone, either, none, and anything are instances of this pronoun that do not imply to a particular individual or item. As a result, some instances of this type of pronoun include everybody, either, none, and whatever do not refer to a specific individual or the object, but instead to the not known individuals or the items. Reciprocal Pronouns: This is a pronoun that conveys a reciprocal relationship. In simpler words, reciprocal pronouns refer to the instances in which someone or something does something to another and receives the same behavior in return. Let us have a look at few pronoun sentences; Andy and Bushra assisted each other. The Rhinos huddled together to guard one another. Emphatic Pronouns: To stress the subject, emphatic pronouns are used. These highlights the subject(s) by coming back to it to showcase that the subject performs the actions. So in general, the subject could be the noun or the pronoun. Thus these are also titled as the Intensive Pronouns. The emphatic pronouns include terms like myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves. Let us have a look at few pronoun sentences;
Distributive Pronouns: Distributive pronouns are pronouns that disseminate the consequences of a verb on more than one person or object at a time. These pronouns focus on particular team members or participants. They have relationships with various nouns, not as a group but as individuals. Each, either, and neither are distributive pronouns. Let us have a look at few pronoun sentences; Either of you can catch this ball. What they advised didn't sit well with either of us. The instructor spoke with each of our parents individually. An object pronoun is a phrase that substitutes the nouns in a phrase or statement. The noun it substitutes cannot be the subject of the statement. It can also be used in place of an object noun, which is a noun that has obtained verbal action. Objective pronouns are another name for object pronouns. Object pronouns are pronouns that perform an action in a sentence. These include terms like- are me, you, he, her, us, them, and whom. Let us have a look at few pronoun sentences; Don't stare at me! This voucher is for you. As per her, we are early. I speak to them every day. Here are a some instances of pronoun sentences with pronouns in them. The pronouns have been highlighted in the following sentences for easy recognition. Pronoun Sentences are as follow;
These pronoun sentences are perfect for understanding and grasping the concept. 
Next TopicTypes of Adverb
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









