Homophones Examples
Homophones are words or sentences that sound too alike to distinguish them. They are also regarded as widely confused words because the phonetic similarity frequently causes undeniable confusion.

What Exactly Is a Homophone?
The Greek words homos (same) and phn (utterance) combine to form homophones or phonetically homogenous words.
They are collections of words with the same or equivalent sounding spellings, origins, and meanings. These share only a phonetic resemblance despite being utterly distinct in essence and meaning.
Types of Homophones
Homophones are terms that sound the same yet have distinct meanings and spellings. Learning homophones is an important component of acquiring the English language, as it helps with vocabulary development and spelling.
There are various kinds of Homophones, these include;
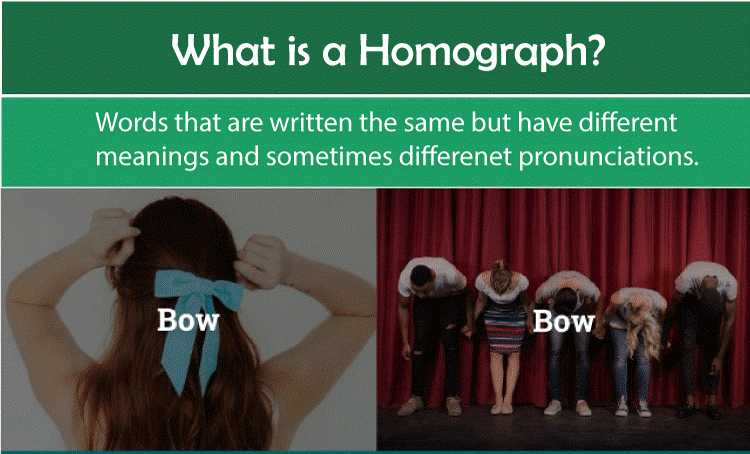
Homograph
This refers to the pair of words that have identical spelling but varying meanings, irrespective of the fact they sound alike or not.
e.g.-
- Bat - An animal or ;
- Bat - A wooden tool to hit the ball in cricket/ sports.
Heterograph
This implies to words that have different spelling and meanings but the same pronunciation.
For instance
- Weak - someone who has less physical strength.
- Week- Seven days a month.
Heteronym
This refers to the words that are different in meaning but have the same spelling but vary in sound.
- Lead - a metal that is dark grey in color.
- Lead- This Means guiding someone on the path.
Oronym
This refers to the words that are pronounced alike and have the same phonetics but vary in meaning as well as spelling. For instance
- I scream - We scream, I scream, we all scream ice- cream.
- Ice- cream- Jina loves eating ice cream in winter.
Pseudo Homophone
This implies to the words have the same pronunciation, but one of the words in the pair is incorrect and used by mistake instead of the correct word.
For instance;
- Groan- A sound that expresses pain.
- Grone - Wrong and incorrect word with incorrect spelling.
Synophone
This implies to words that are similar in sound and meaning but different in spelling and have the difference of just one phoneme.
For instance;
- Effect- Outcome or the result.
- Affect- Having a negative influence.
Some common Homophone Pairs
The following are some common instances of homophones comprising words utilized in a sentence:
- Brake/break: When I was training my kid to drive, I warned her that he'd break the vehicle's rearview mirror if he didn't touch the brake at the right time.
- Cell and sell- If you sell illegal things, you will be caught and placed in a jail cell.
- Cent/ scent- I will not spend a single cent on a fragrance bottle until I am certain that I adore the scent.
- Die/ dye: You could die if you consumed a bottle of clothing dye by mistake.
- Flour/flower: Flour is required to make a flower-shaped pastry.
- For/ four: I bought four new footwear pairs for my forthcoming trip.
- Heel/heal: If the heel of your footwear breaks, you may fall. Your wounds will, nevertheless, heal with time.
- Hear/ Here: I desired to sit here so that I could hear the vocalist without being distracted.
- Hour/ our: I have one hour until our meeting with the property agent.
- Idle/idol: Sitting idle often leads to boredom but listening to your favorite idol's songs often instills enthusiasm and energy.
- Knight/ night: The knight is on his journey to the palace, but traveling at night is quite risky.
- Not/Knot: I'm not sure how she learned to secure the Knot for that necklace.
- Poor/pour: Every evening, I pour beverages in a bar. I am poor since I have numerous debts and little funds.
- Right/ write: There is no right or wrong approach to writing a wonderful book.
- Sea/see: I adore waking up at my shoreline cottage to see the sea.
- Sole/soul: My fave pair of sneakers requires a new sole. Running is beneficial to my soul.
- Sun/ Son- My son is thirteen years old. He enjoys spending time outdoors in the sun, especially in winter.
- Steal/steel: Somebody who robs a car has committed an offense, although automobile parts are composed of steel.
- Tail/ Tale: My dog was chasing his tail madly while I narrated a fairy tale to my kids.
- Weather/ whether: I'm not sure whether I should bring a sweater or not. Today's weather appears to be uncertain.
Homophones Examples That Are Frequently Misunderstood
In the English language, there are so many homophones that almost everybody gets confused at some time. Among the frequently misunderstood homophones are:
- Accept/except: The verb accept signifies to take or receive. Except is a preposition or conjunction that can signify but or exclude.
- Affect/effect: In most circumstances, affect is a verb that expresses influence. The result of an activity or change is a noun (in most circumstances).
- Compliment/complement: To compliment somebody or something implies to say something positive about them. A complement is something that improves or fulfills something else.
- Then/than: Then is a flexible word that can be used as an adverb, noun, or adjective to express the sequence of events. You could use than as a subordinating conjunction to compare things.
- To/too: When utilized with a verb, to can be either a preposition or an infinitive. Too is a preposition or a synonym for also.
- You're/your: You're is an abbreviation for you are. Your is a personal pronoun.
- Bearing versus baring: The verb baring implies "to bare," whereas the verb bearing implies "to bear. "
- Boulder vs. Bolder: Bolder means more daring, and boulder means more rock.
- Canon vs. Cannon: Canon refers to a recognized concept or rule, whereas cannon refers to a large gun.
- Cite vs. sight vs. site: In most circumstances, the site refers to a specific area, sight relates to vision, and cite pertains to something that is included in a report.
- Creak vs. creek: Creak refers to a noise, whereas creek refers to a little stream of water.
- Hole versus whole: A hole is an opening in anything, while a whole indicates complete.
- Insight vs. incite: Incitement means to agitate, but insight is the ability of seeing someone's or something's true essence.
- It's vs. its: It's a fusion of "it" and "is," and its is the possessive form of it.
- Peak vs. peek vs. pique: Peak denotes maximal height, peek denotes seeing, and pique piques your curiosity.
- Rain vs. reign vs. reign: Rain is falling water from the skies, the reign is a temporal period, and rein is a leather band.
- Real versus reel: A reel is an object that holds film or string, whereas a real is an item that is authentic.
- Role vs. role: A role is a character that you play, whereas a roll can refer to both the activity of rolling and a carb-loaded snack.
- Sole vs. soul: The sole refers to the foot, but the soul is more spiritual.
- Stationery vs. stationary: Stationery refers to paper and envelopes; stationery implies staying in one place.
- Steel versus steal: Steel is a metal, and to steal entails taking anything without consent.
- Tale vs. tail: A tale is a narrative; a tail accompanies you.
- They're vs. they're no: They're is a shortened version of "they" and "are," and their is the possessive pronoun of they.
- Waist vs. waste: The waist is your midsection, whereas waste is anything you discard or misuse.
- Wear vs. where: Where is a location, and wear is to put something on.
- Yore vs. you're vs. your: Yore denotes the past; you're is a shortened form of "you" and "are,"; and your implies to the possessive form of you.
Examples of Homophones in Sentences
Each sentence has a pair of homophones that have been highlighted for easy recognition.
- Visitors are not allowed to speak aloud in the museum.
- The house maid made the dinner.
- Let us have chicken meat as we meet for barbeque.
- When serving the glass of rye, the waiter smiled wryly.
- Will the professor offer me a special role since I'm on the honorable roll ?
- The essay review of the fresh revue was not very nice.
- On the tropical isle, the newlywed walked down the beach aisle.
- If you tumbled through a pane of glass, you'd be in a lot of pain.
- When I spilled the water pail, I got pale.
- They tasted a pair of pears.
- The amount of Television ads adds quite so much time to a sporting event.
- Write in the right manner.
- Was it you gazing at the ewe underneath the yew, or was it the other way around ?
- I can clearly see the sea.
- If the sailboat is not tied down, it will drift away with the tide.
- The coffee bean has been sown.
- That wood would suffice.
- A nose understands that a scent sent from a flower in rows and tiers can attract tears of happiness.
- A bored ordinary pilot boarded the plane.
- He ate eight chappatis since he was hungry since morning.
There are hundreds of Homophones. However, it is impossible to list all of them. So these are some of the most common ones used in regular life. Hopefully, these examples will help you understand the concept of Homophones.
|


 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









