Subordinate ClauseThe subordinate clauses are a kind of clause that, while complementing the main or the primary clause of a sentence, cannot exist alone as a complete sentence and hence adds to the meaning of the entire sentence. A subordinate clause is sometimes known as a dependent clause since it needs the main clause to make sense. 
Whether you refer to this clause as subordinate or dependent, its purpose is obvious: It offers factual backing for the sentence's core idea. This primary clause will be self-sufficient; it can function as a complete sentence all by itself. We may all go for dairy products. This phrase stands alone as a clause. It has a subject and a verb, presenting a full unit of thought on its own. It conveys the idea in its entirety: All of us may go out and have dairy products (Horray! ) But perhaps this isn't the only point we want to make. We may all go for dairy products if I can find my handbag. If I can find my handbag significantly expands the sentence's meaning. There is a duty at hand. Therefore, it would be early to rejoice over our dairy product outing. First, we need to locate the handbag. If I can find my handbag is a subordinate sentence; it does not stand alone as a complete thought. Sentence fragments would be the result if they were written independently as a sentence. If I can find my handbag. - Incorrect When I locate my handbag, what will happen? A clause in your sentence is a subordinate clause if it places us in this kind of limbo when taken by itself. 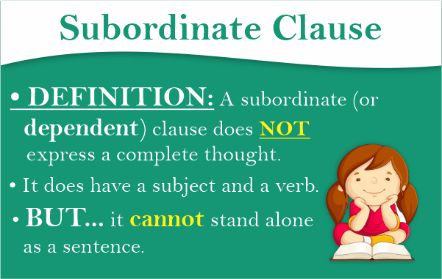
Words That Initiate Subordinate ClausesThe words for, as, since, therefore, hence, consequently, though, due to, provided that, because, unless, once, while, when, whenever, where, wherever, before, and after are subordinating conjunctions, which bind dependent clauses to independent ones. Additionally, they can start with relative pronouns such as that, which, who, whom, whatever, whoever, and whose. By looking for these words, you may tell you are working with a subordinate clause instead of the main clause. Important Things to Remember While Using The Subordinate ClausesYou might question how this knowledge can benefit you now that you know what a subordinate or dependent clause is. That has an easy solution. You'll be able to avoid hearing from the instructor or colleagues, "You should insert a comma there," or even better, "You shouldn't have placed a comma there." You can better arrange your thoughts and employ proper comma placement by understanding which phrases are main (independent) and which are subordinate (dependent). The best part is that it is really not that challenging. A comma follows a subordinate phrase at the start of a sentence. There is no comma to distinguish the primary clause from the dependent clause when it starts the sentence. If I can locate my handbag, we can all go for desserts. Incorrect We can all go for desserts if I can find my handbag. Incorrect If I can find my handbag, we can all go for desserts. Correct We can all go for desserts if I can find my handbag. Correct Placement Of Comma: Restrictive Vs. Non-Restrictive ClausesJust when a subordinate clause starts with a relative pronoun like that, which, who, when, where, or whose punctuation can become challenging. Fortunately, a relative clause can be used to describe this kind of subordinate clause. Restrictive and non-restrictive relative clauses are the two varieties. Essential clauses are another name for restrictive clauses. This is due to the fact that they are crucial to the understanding of the sentences in which they are used. Commas shouldn't separate essential parts of a statement. I enjoy seeing films that apply lots of visual effects. There shouldn't be a comma distinguishing the main sentence from the restrictive clause that makes extensive use of special effects. Since it is mandatory to the meaning of the statement, I like seeing films. Contrarily, non-restrictive clauses can be removed from a sentence without changing the meaning at its core. They must always be separated with commas in a sentence because they are optional. The example below shows that non-restrictive clauses frequently "interrupt" the main clause. In these cases, you should place a comma both prior to and after the clause. Watching Lord Of the rings, which has lots of visual effects, is my personal favorite. The main notion of the statement, "Watching Lord Of the rings is my personal favorite," is still true even without the non-restrictive clause, which has many visual effects. What Purpose Does a Subordinate Clause Serve?Adverbs, adjectives, and nouns can all be used as subordinate clauses. They enhance the overall meaning of a statement by supporting its primary clause. Additionally, subordinate sentences can be used to establish causality, temporal order, or a specific illustration of the idea. The purpose of this kind of clause is the same whether you refer to it as a subordinate or dependent clause: it adds details to support the sentence's primary event. 3 Kinds of Subordinate ClausesThe three types of subordinate clauses are direct objects, noun modifiers, and verb modifiers. These three subordinate clause kinds are listed below. 1. Noun clauses: A noun clause is a phrase in which a subordinate clause stands for the noun. Noun clauses often serve as direct objects or predicate nominatives and include both the subjects and the verbs. 2. Adjective clauses: These are subordinate clauses that offer additional information in a sentence. They are sometimes referred to as adjectival clauses or relative clauses. They are employed to alter a noun or noun phrase within a primary or independent sentence. A relative clause is often a dependent clause, which means it has a subject and verb but is not an independent or complete sentence. A relative pronoun, like "who," "whom," "which," "whose," or "that," or a relative adverb, such as "when," "where," or "why," are frequently used to initiate relative clauses in sentences. 3. Adverbial clauses: The relative adverbs "where," "when," and "why" offer details about a specific location, a specific period of time, or a particular cause. They serve a purpose in a statement by altering other words. An adjective clause with a relative adverb changes a noun or noun phrase. A relative adverb alters a verb when it starts an adverb clause. 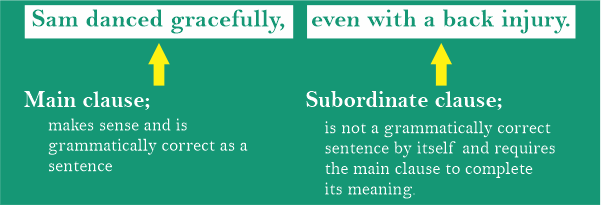
Examples of 3 Subordinate ClausesThe below-mentioned instances of subordinate clauses can help you understand the purpose of these parts of speech if you're having difficulties identifying them or simply want to enhance your sentence structure.
Examples of sentences with subordinate clauses There are subordinate clauses at the beginning, in the center, and at the ending of a sentence.
The subordinate clause in the first and third instances is "while the bull crammed noisily." In the second, the subordinate is "who was involved in hatching eggs." Additionally, you might have noticed that commas are used to demarcate subordinate clauses that fall in the midst of sentences. Such a subordinate clause is a sentence-included clause. Here are some additional instances of dependent clauses:
Next TopicSubordinate Clause Examples
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










