Difference Between Idioms and PhrasesWords alone do not provide or have a specific meaning. They are linked together to form sentences and then employed in such a way as to make them more captivating. Phrases and idioms are excellent examples of such tools. Both are often misconstrued and mistaken for one another, which is incorrect. 
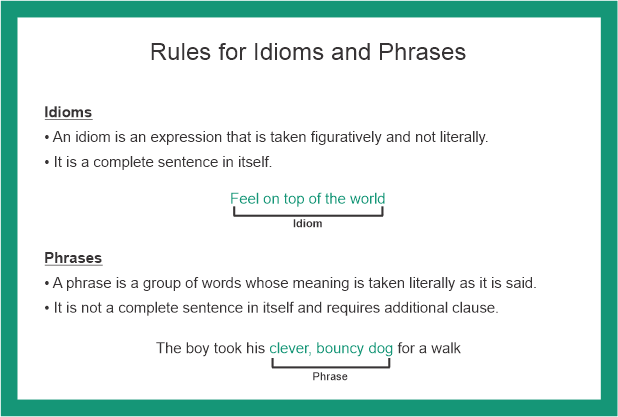
The English language employs phrases in statements as sentence-building elements. A phrase is defined as two or more words that are grammatically related and have meaning. A phrase is a short remark that has significance but cannot be used as a sentence on its own. A phrase is quite similar to an idiom, which is another language tool. Many people think these two tools are interchangeable. Idioms and phrases, on the other hand, are not interchangeable, and there are variances that will be discussed in this article. What Is an Idiom?Idiom: Definition Idioms are language tools used by writers to enhance the beauty of their writing. It is the usage of figures of speech to generate a meaning that differs from the meanings of the single words of the sentence. This is why non-natives and other English language learners struggle to understand the meaning of an idiom. For example, he is attempting to pull my leg does not imply what one is reading (i.e. its real meaning is way from the literal sense of words) because no one is grabbing the leg and tugging it. Rather, teasing is the literal sense of pulling my leg, which is not evident to those learning English. Likewise, if someone claims he is having difficulty keeping his head above water, this does not imply to indicate he is drowned or anything like that. He just means that he is finding it tough to keep things on track or handle a situation. The below-mentioned are some examples of idioms in which the dictionary definitions of individual words in the phrase do not add up to the phrase's meanings.
However, it is crucial to note that certain word combinations are not always utilized as idioms. They can also be used as simple sentences. The sentence pairs that follow show how the connotation of the phrases varies based on the circumstances. What is a Phrase?Phrases: Definition A phrase refers to the group of words that function as a conceptual unit. It serves as a part of a sentence's syntax in linguistic analysis. In general, though, individuals use a phrase to allude to statements with idiomatic meaning. Some instances are - all rights reserved, all of a sudden, lights, camera, action, fall in line, and so forth. These differ from idioms in that they are employed as sentences and are the conventional form of communicating a concept. Examples of Phrases: Tuesday became an awesome, wet evening. The phrase 'awesome, wet evening' refers to a rainy day. The phrase indicates the statement's literal meaning. So, to clarify the meaning, a phrase is a combination of words that are widely employed to convey anything through speech or writing. There are various types of phrases depending on where they appear in a sentence or the composition of the sentence. These phrases have different effects depending on where they are in a sentence. They can be thought of as follows: Noun phrase: It is a tiny set of words that includes a person, a location, or an object. For example, Preeti resides in a small building. Verb Phrase: A verb is used as a direct or indirect object in this sort of phrase. A statement's predicate could be a verb phrase. For instance, the boat traveled across the sea. An adjective phrase: This refers to the type of phrase that characterizes a noun. For instance- Ashwin took his smart, energetic dog Rocky for an outing. Prepositional Phrase: These phrases are used in sentences and are accompanied by a preposition. For example, Mary owns the textbook on the shelf. Participial Phrase: The participle phrases often begin with a past or present participle, accompanied by the subject or object. This phrase could also be utilized as an adjective at times. For instance, Noticing the circumstance, the authorities decided to fire teargas. Conjunctional Phrase: This is a type of phrase that is used to join two sentences together. For instance, Every pupil has to work extremely hard so that they can pass with flying colors. Gerund Phrase: A gerund phrase resembles a participle phrase, except it functions as a noun in a statement rather than an adjective. For instance, Consuming cold drinks in cold weather can be an unhealthy experience. Infinitive Phrase: These types of phrases are ones that have an infinitive character linked with them. For example: Allow me to teach you the quickest technique to shatter the door swiftly. You will understand what idioms and phrases are and what they mean by looking at the examples above. It is recommended that after learning about this topic, you practice creating sentences with idioms and phrases. How Do You Distinguish Between Idioms and Phrases?Idioms are easily distinguished because they deviate significantly from their actual meaning. "You have a chip on your shoulder," for instance. The literal meaning of this idiom is to hold on to the grudges. An idiom can be identified when the actual term does not sound right in a sentence. In contrast, phrases carry literal meaning. Examples of the Difference Between Idioms and Phrases Instances of Phrases and Idioms will help you understand the distinction. Phrase: Thursday turned into a cold, rainy night. Idiom: It's raining cats and dogs. Hopefully, you found the article on the distinction between phrases and idioms useful ; you can also read the articles listed below. 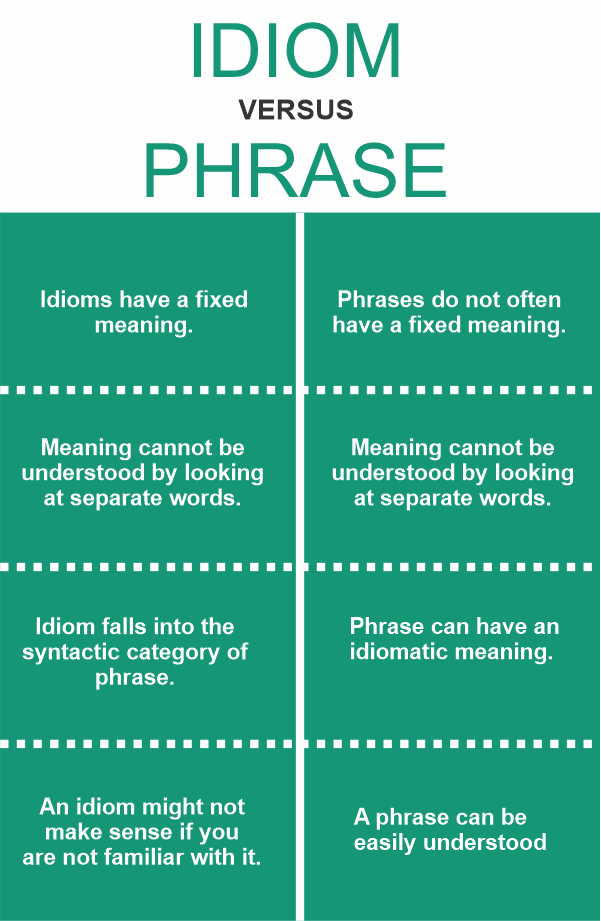
What Is the Difference Between Idioms and Phrasal Verbs?As previously stated, an idiom is a regularly used set of words that have no relation to the meaning of the specific words employed in it. However, phrasal verbs are distinct. Phrasal Verbs are formed when prepositions or adverbs accompany verbs to gain an idiomatic meaning. The Primary Distinctions Between Idioms and PhrasesHere are some of the main differences between idioms and phrases
ConclusionBoth phrases and idioms are employed to make the information more appealing and meaningful. They both add to the unique and fascinating nature of the literature. However, a problem can develop if a person is unfamiliar with the meaning and essence of a phrase or an idiom. This might lead to misunderstanding and misinterpretation. Furthermore, the author or poet must understand where and when to utilize any of them to improve the quality of the content; use in the wrong place, or extensive use can have a poor and bad effect on the literature/content.
Next TopicDifference Between Phrase and Clause
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









