Present Perfect TenseWhat is Present Perfect Tense?The present perfect tense implies or refers to actions or situations that happened at an undetermined time in the past (e.g., we have previously discussed) or that started in the past and proceeded to the present time (e.g., he has grown anxious over the last thirty minutes). The conjunction produces this tense have/has + the past participle. 
How is Present Perfect Tense formed?The formulation of this verb tense is simple. The first part is either have or has, based on the subject with which the verb is conjugated. Another important element is the verb's past participle, that is normally created by putting -ed or -d to the verb's base (e.g., marched, scrubbed, texted, bounced, giggled, cooked). 
However, there are some/few irregular verbs in the English Language, like past participles (e.g., done, said, gone, known, won, thought, felt, eaten). These cases indicate how the present perfect can express anything that happened or the state of things at an undetermined point in the past. I have marched on this road before. We have eaten the pasta here. Remember that you cannot utilize the present perfect tense if you're detailed about when the event occurs. Correct Usage: I have finished all of the housework. Incorrect Usage: I have finished all the household chores at 10:00 this morning. You can use the present perfect for discussing the timeframe of an activity of event that started in the past and is still happening in the present. He has had the flu since Wednesday. Origin and History of Present Perfect TenseThe Present Perfect tense is essential in English, but it can be problematic for speakers of other languages. This is due to the fact that it employs notions or concepts that do not belong in those languages. In truth, the Present Perfect has a relatively simple construction, and the difficulties arise from the utilization of the tense. The present perfect is a grammatical blend of the present tense and the perfect aspect, which is utilized to represent a past event with present ramifications. The word is most frequently used by English grammar references to relate to forms such as "I have accomplished." The variants are present since they utilize the present tense of the auxiliary verb have, and perfect since they employ that auxiliary verb in conjunction with the primary verb's past participle (There are other perfect forms, such as the past perfect: "I had consumed.") Analogous types can be observed in multiple languages. They can also be defined as present perfect; they are sometimes known by other titles, such as German Perfekt, French passé composé, and Italian passato prossimo. They may also have various ranges of utilization: the expressions in question serve as a broad past tense in all three of the languages previously listed, at least for finished activities. In many cases, accomplished activities in English are attributed to the simple past verb form instead of the present perfect. In the Present Simple, the auxiliary verb (have) is constructed as follows: have, possess The primary verb is always in the past participle type: -editor (or irregular) We add " not" between the auxiliary verb and the primary verb in negative sentences. We swap the subject and auxiliary verb in question sentences. Present Perfect ContractionWhile we utilize the Present Perfect in conversation, we frequently condense the subject and auxiliary verb, and this is something we do in casual writing as well. Consider the below mentioned statements in the Present Perfect tense: I have--I've You have--You've He has- He's She has--She's It has--It's John has----John's The car has---The car's We have--We've They have--They've You've said that already. Johnny has seen Harry Potter. In negative sentences, we can combine the auxiliary verb with the word "not": You did not win the competition. She has not heard from him in a long time. Pro-Tip in English: Is it his, or he's? Take care! For the auxiliary verbs have and be, the's contraction is employed. "It's eaten," for instance, can mean: It has eaten. (Present Perfect tense, active voice) It is eaten. (Present Simple tense, passive voice) It is evident from the meaning and explanation. 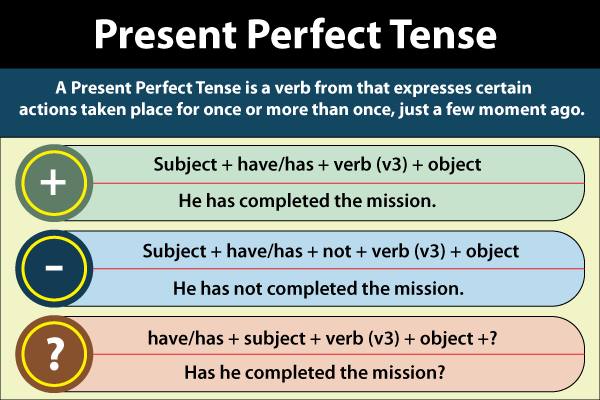
How should the Present Perfect tense be used?This is known as the Present Perfect tense. There is always a link between the past and the present. We can use the Present Perfect to discuss: Experiences Changes Continuous Situations Let us understand in detail how Present Perfect Tense can be utilized. Experience We frequently use the Present Perfect to discuss prior experiences. We're not concerned about when you did things, and all we want to know is if you accomplished it: I have seen an extra-terrestrial. He has lived in Canada Have you been there? They have never taken alcohol. The action or state took place in the past, but the memory is there in the present. Link to the past: the event occurred in the past. Linkage to the present: I now have a memory of the incident in my thoughts; I know a little about the occurrence, and I have personal experience with it. We just use present perfect for discussing events that have not occurred in our lives without referring to a specific period. We frequently use 'ever' in inquiries and 'never' in negative phrases with this usage. As an example, Have you ever visited Montreal? No, I have never visited there. She has been to Sydney five times! We have never missed a flight, luckily. Has this group ever won a title? Following a description of the primary life experience in the present perfect, it is customary to provide details in the simple past tense. As an instance, She has received two vital increments in her professional life. (present perfect) The final one was for the deputation as the Chief Manager. (past tense) 2) Recent eventsWe can utilize present perfect for expressing a recent event or activity or inquiring whether something has occurred recently. It's frequently used in conjunction with terms like just, already, yet, and still. Whenever an event or action has an influence on the present, we frequently employ the present perfect. As an instance, I have misplaced my travel documents so I cannot get on the flight! (Recently completed action - immediate result.) Here are a few more examples: Have you completed the research yet? I have not noticed Aaron today. Sally has just left the house. They have already eaten. They still have not accomplished that goal. 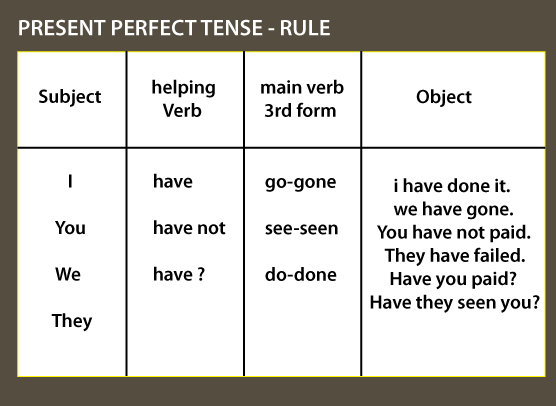
3) Uncompleted tasksWe can also utilize this tense to describe activities or events that began in the past and are still happening in the present. We use 'since' to indicate the time the activity began and 'for' to indicate a period of time. As an example, We have been here for ten years. They have been together for over a quarter-century. How long have you been researching for this organization There has not been any rain for weeks. You have had that automobile for a long time. For a change or something that has happened was not in the past. The Present Perfect is also used to describe a change or new information: I have purchased a television. I did not have a TV until last week, but now I have a TV John has a leg injury. John had a good leg, but now he has an injury Has the value risen? Was the cost $1.50 yesterday? Is the current price $1.70? The cops have arrested the assassinator. Yesterday criminal was free bit now he is behind the bars Relationship with the past: the past is the total opposite of the present. Relationship with the present: the present is the total opposite of the past. Present Perfect Tense for an ongoing situation When discussing an ongoing situation, we frequently utilize the Present Perfect. This is a condition that began in the past and persists in the present (and will mostly continue into the future). This is a scenario (not an action). With this form, we normally use for or since. I have been here since June. He's been sick for 48 hours. How long have you been friends with Tara? (For) The problem began in the past, and it is still going on and is likely to continue in the future. Relationship with the past: the predicament began in the past. Connection to the present: the problem is still ongoing in the present. With the Present Perfect tense, for and since Alongside perfect tenses, we frequently use for and since: We use "For" to refer to a specific time period: 5 minutes, 2 weeks, and 6 years. We use "since" to refer to a point in the past: Monday, January 1st, 9 a.m. Consider the following examples of for and since statements in the Present Perfect tense: I have been here for about 20 seconds. I have been here since 8:00 a.m. Thomas has not visited for 6 weeks Ben has not talked since April. He has studied in New Jersey for a long time. He has been working in New York since he graduated from high school. Here is a pro tip that can make this easier for you; The word for could be used in all tenses. Since it is only used with perfect tenses. 
When should you use the present perfect or the past simple?When deciding whether to use the present perfect or the past simple, consider the following: Is the action over? NO, Make use of the present perfect. YES Next, ask the following question to yourself; Is there a complete-time representation? YES, Make use of the simple past. NO, use the present perfect tense. It is important to understand that once you grasp and retain these crucial characteristics about the present perfect, it's much simpler to use it than you might have imagined. Of course, practice is vital, especially practice through speech.
Next TopicPast Continuous Tense
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










