Types of PronounNouns play an important role in our statements. They play the vital roles of subject and object. However, there are situations when a noun requires a break, or there isn't a noun that precisely fits a sentence. Who will nouns turn to for assistance when they are in necessity? They use pronouns, not ghostbusters (which is still a noun). 
Pronouns are an important aspect of speech, and utilizing them effectively will vastly enhance your speaking and writing. Pronouns can perform all of the functions of noun, although several of them are short and more adaptable. Pronoun allow us to state phrases like "I am confident of myself" or "It is time to request for aid." What is a pronoun? A pronoun is a term that can substitute the nouns in a statement. An antecedent is the nouns that is substituted by a pronoun. In the statement, I miss my cat because he is sweet and obedient; for instance, the term he is a pronoun that replaced the noun cat. Pronouns, in general, assist us in abbreviating our phrases and making them appear less repetitious. As an instance, Laborers are building the office building. The employees on the construction site are making great strides. The construction personnel will be able to deliver the project quickly. Construction laborers are building the workplace. They're making great strides. They will be able to deliver the project quickly. Tip- Pronouns are similar to nouns in that they could be used as subjects and objects, relate to people, locations, and objects, can be singular or plural, and can be changed by an adjective. The "noun" in pronoun may assist you to recall that pronouns act similarly to nouns. Types of PronounPersonal pronounThis is one of the most common types of pronoun. They perform as the substitution for an individual's name. Subject pronouns switch the name of the statement's subject, while object pronouns substitute the name of the statement's object. 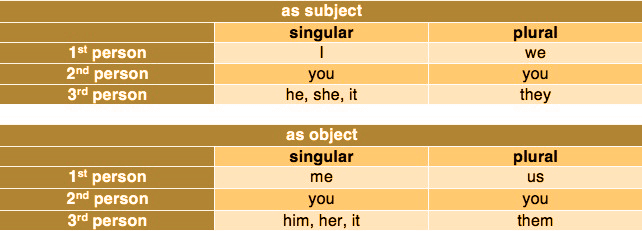
The following are the most common personal pronouns: Subject Pronouns include - I, you, he, she, it, we, they Examples for the same are; I don't feel like visiting the museum. You are a talented girl They are elite people Object Pronouns- me, you, her, him, it, us, them. Examples for the same are; Go and meet her Did you get to meet him? This movie is liked by us. Many factors influence the personal pronouns you choose, such as the sentence structure and a person's chosen pronouns. Many style guidelines now include advice on using they/them as single pronouns. Possessive PronounNext in the list of types of pronouns is the Possessive Pronoun. Possessive pronouns indicate possession or ownership of the nouns. They take the place of a noun that would normally be followed by an apostrophe and an "s," like "Bethany's." Possessive determiners that could also operate as pronouns and individual possessive pronouns that relate to an originally stated noun are the 2 types of possessive pronouns. It's worth noting that possessive determiners are always used before a noun, whereas independent possessive pronouns might exist alone. His and its are the two possessive pronouns that seem to be the same in both contexts - the words are spelled the same regardless of how they are used as a pronoun (without any apostrophe in its). Possessive Determiners include- my, our, your, its theirs, his, her. Examples of the same include Is that my pencil? Your cat is adorable His job is tedious Whereas the Independent Possessive Pronoun includes- mine, his, its, theirs, ours, yours, hers, etc. Examples of the same include; This jacket is mine Ours is the most beautiful The final choice is theirs. Demonstrative PronounNext in the list of types of Pronoun is the Demonstrative Pronoun Demonstrative pronouns play the role of a previously specified noun. Singular or plural demonstrative pronouns can be used. They are five in number and can also be used as a demonstrative adjective. Demonstrative pronoun can be used as demonstrative adjective as well. If you insert a noun into the phrase, such as "Neither outfit looks good on me," neither becomes an adjective describing the outfit. For instance, in the sentence "Neither outfit looks good on me," neither is acting as a pronoun. Singular Demonstrative Pronoun includes- this, that, none, neither, such. Examples of the same are; This my blanket That doesn't make a difference Neither outfit suits me Plural Demonstrative Pronoun include- these, those Examples of the same are These dishes are outstanding in taste and smell. Those are one of the most reasonable shoes. 
Reflexive PronounNext pronoun in the list of types of pronoun is the reflexive pronouns. This is a type of pronoun when a statement alludes to the same individual or object in the subject; reflexive pronoun replaces the object. These pronouns finish in -self (single reflexive pronouns) or -selves (plural reflexive pronouns) (plural reflexive pronouns). They normally come after the verb in the phrase, although they can also come after a preposition. Although they are more strange, these pronouns are still acceptable if you substitute them with the nouns in the statement. The phrase "Nina taught Nina French" is more difficult to understand than "Nina taught herself French." Interrogative PronounAnother pronoun in the list of types of pronouns is the interrogative pronoun. Interrogative pronouns are similar to relative pronouns in structure, but instead, they pose a question. Interrogative pronouns are pronouns that have been used to inquire about unknown individuals or objects. Some individuals get interrogative pronouns mixed up with interrogative determiners, which occur before a noun. Like all other pronouns, interrogative pronouns must be followed by a noun. There may be terms not present in the listing provided, such as where and why. They are not interrogative pronoun; rather, they are the adverb that specify more about the verb. Some of the interrogative pronouns include- whose, what, whom, which, who Examples of the same include Who is standing there? Which one is expensive? Whose box is this? However, there are other interrogative pronouns as well, including - whoever, whomever, whatever, whichever, etc. Whichever did you choose? Whatever does this imply? Whomever should they call? 
Indefinite PronounAnother pronoun in the list of types of pronouns is the indefinite pronoun. Indefinite pronoun in any case not imply to the certain or specified nouns. When an item does not need to be properly recognized, we utilize them. There are singular indefinite pronoun that serve as singular noun and plural indefinite object that serve as plural noun. Several indefinite pronouns can be used in both directions. Many indefinite pronouns exist whether the noun appears before or after the pronoun. However, explaining the term in the prior sentence may help clarify any confusion. Singular indefinite pronouns include- everyone, somebody, little, no one, nothing, everybody, anybody, anybody, anything, anything, etc. Examples of the same include Everybody liked the chocolate dessert Nothing is impossible to achieve One must not lose hope and faith. Plural indefinite pronouns include both, many, few, etc. Both are good for the function Few people have been invited Many people offer help here. Singular and Plural indefinite pronouns include- all, most, none, some, any, etc. All individuals are thankful More people can sit on the sofa Can you have some sweets? Reciprocal PronounAnother pronoun in the list of types of pronoun is the reciprocal pronoun. Reciprocal pronouns indicate that two or more nouns are undertaking an activity together. There are just two reciprocal pronouns in English, yet they play an important role. They are also not utilized in the same manner. Some people struggle with punctuating reciprocal pronouns. When employing each other or one another as the possessive pronouns (like in "We unwrapped each other's gifts"), consider it as a singular noun and incorporate an apostrophe and "s," not an "s" and an apostrophe as with the plural possessive nouns. Reciprocal pronouns for two nouns include- each other. Examples of the same are; My grandparents adore each other like newlyweds. Reciprocal pronoun for more than 3 or more noun - one another The dogs are fighting with one another for the milk. It is essential to respect one another in society. Emphatic PronounAnother pronoun in the list of types of pronoun is the emphatic pronoun Emphatic pronouns are utilized to stress or emphasize the subjects. They emphasize the subject by eventually returning to it in order to demonstrate that the subject takes action. The subjects can be the nouns or the pronouns, as is customary. As a result, they're also called as Intensive Pronouns. Emphatics pronouns are simply reflexive pronouns with a different role. These can also be produced by appending -self (single) or -selves (plural) to specific personal pronouns. The noun's number and gender determine them. Emphatic pronouns are usually known as the compound personal pronouns for emphasis or stress, like 'himself, "myself," and "yourself." For example I will construct the residence myself. We'll follow the series ourselves. You can inform us about the problem yourself. We were able to see the King himself. Distributive PronounAnother pronoun in the list of types of pronoun is the distributive pronouns. Individuals, animals, and things are referred to as people within bigger groupings via distributive pronouns. They allow you to identify people while still recognizing that they are part of a broader community. The following are examples of distributive pronouns: Either ;Each ;Neither ;Any ; None Here are some statements with distributive pronouns: My buddies all joined the Halloween party, but none of them won. Snack options include biscuits and cakes. Neither appeals to me. 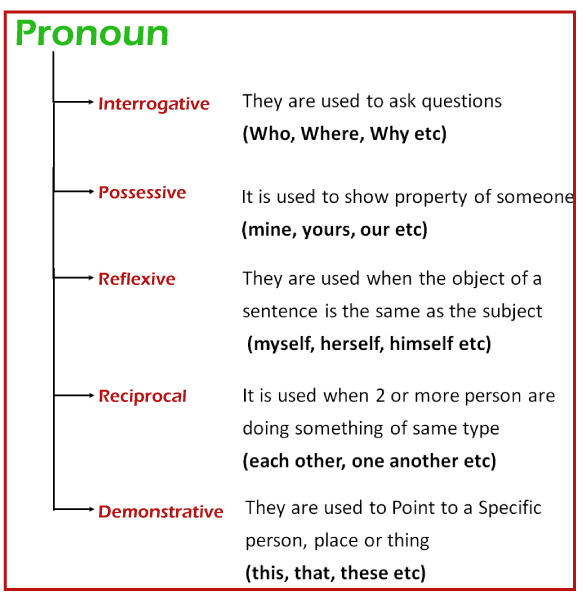
Object PronounAnother pronoun in the list of types of pronoun is the object pronouns. Object pronouns replace the antecedent object as the object or indirect object in a statement. After prepositions, this variant of the pronoun is often used. Example: They will give you a gift on your anniversary. I have a fantastic suggestion for you. (After the preposition) Inform her that you will accept the position. I've got a present for your employer. Please give it to your employer. ('It' serves as an object here.) The pronouns that receive the actions in a phrase are known as object pronouns. They are me, you, him, her, us, them, and whom. And if they are indirect object pronouns or direct object pronouns, these pronouns invariably accept the objective case. Robert drove her to the office the next morning. Could you please inform them to come in? He was dishonest to you about where he was on Friday. Our grandmother gave us treats, and our gums are just alright. Now that you all understand and know about the types of pronouns, the key to getting them right is by practicing them every day.
Next TopicDemonstrative Pronouns
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










