Homonyms and HomophonesThe terms ate, and eight are homophones. Are they also homonyms? Perhaps they are neither - or perhaps they are both! Homonyms are words that are pronounced the same but have different meanings or are spelled the same but have different pronunciations. For example, "buy" and "by." Homophones, on the other hand, are words that have the same sound but different spellings and meanings. It can be examined thoroughly using homophone instances. 
Homophones must be understood in order to improve one's mastery of the English language. It aids in the growth of a person's lexical knowledge. When speaking, thousands of homophones are utilized, which causes difficulties for both native speakers and learners. Learn the distinction between homonyms and homophones, as well as if they are synonymous with homographs. Differentiating Homonyms and HomophonesThe terms homonym and homophone are frequently used interchangeably. Both words contain the Greek prefix homo-, which means "the same," and both indicate a connection between two or more words. Their definitions, however, differ slightly.
The words eight and ate, for instance, are homophones since they sound the same. Since they share the same spelling and pronunciation, the terms bar (a metal stick) and bar (a place that offers beverages) are homonyms. Another Meaning of HomonymAccording to some sources, a homonym is an umbrella term for homophones and homographs (a term that shares the spelling but have distinctive sounds). To be a homonym, a word pair must share either spelling or pronunciation, as per this definition. On the other hand, the stricter definition considers a homonym to be a homophone (share the same sound) and a homograph (share the spelling). 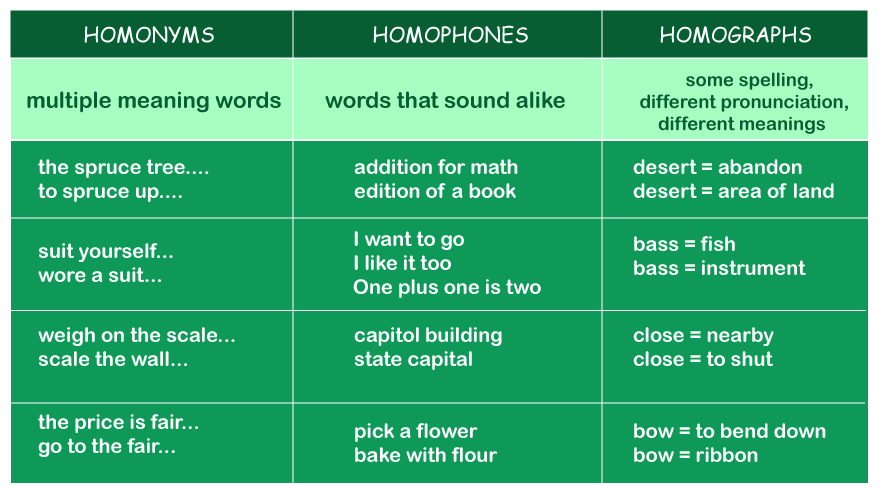
What Is a Homonym: The Same Sound, Different Spelling?A homonym is Greek for "same name," and it means that two words are spelled and spoken similarly. In other terms, homonyms are words with numerous meanings. Each homonym has a unique definition. Homonyms ExamplesInstances of homonyms include the following words :
Homophone Definition: Identical Sound, Distinct SpellingHomophones are any two words that share the same sound irrespective of spelling. Right and write, for instance, are homophones since they sound identical but are spelled differently. Homophone ExamplesHere are some examples of homophones :
How Do Homographs Work?Homographs are antonyms for homophones. These terms have the same spelling but may sound distinct. Here are a few instances of homographs :
How to Distinguish Between Homonyms and HomophonesThe difference between homonyms and homophones can be found in their Greek roots. Homonym implies "identical name" and refers to words that have the same sound and spelling. Homophone implies "same sound"; homophones are terms that sound the same. Homophones are words or sets of words that share the same sound but vary in meaning. Homonyms share the same spelling or pronunciation but distinctive meanings, as demonstrated by examples of homophones. Consider the cell phone. Consider your best friend's phone. They would sound identical if they rang at the same moment. How were you supposed to tell them apart? They appear to be distinct - exactly like homophones. Understanding Your Word ConnectionsThe context of the statement - and the definition in your dictionary - determine whether a word is a homonym or a homophone. Whatever the name of the term relationship is, picking the proper word will assist you in explaining your message. Homonyms Homophones and HomographsWords that sound similar and may be spelled similarly yet have different meanings. Homonyms are regarded as synonyms for homographs and homophones. A homograph is a word that has the same spelling but alternate meanings, whether they are pronounced alike or not. For instance, Bass (instrument) and Bass (instrument) ( a fish). Simultaneously, homophones have the same sound and may have the same or distinct spelling, but they vary in meaning. There are homophones such as they're, their, and there. As a result, homophones and homographs are classified as homonymy. Homonyms are frequently utilized, which confuses both novices and native speakers. They aren't particularly vital, but understanding how to utilize them correctly is essential for creating excellent, understandable sentences. 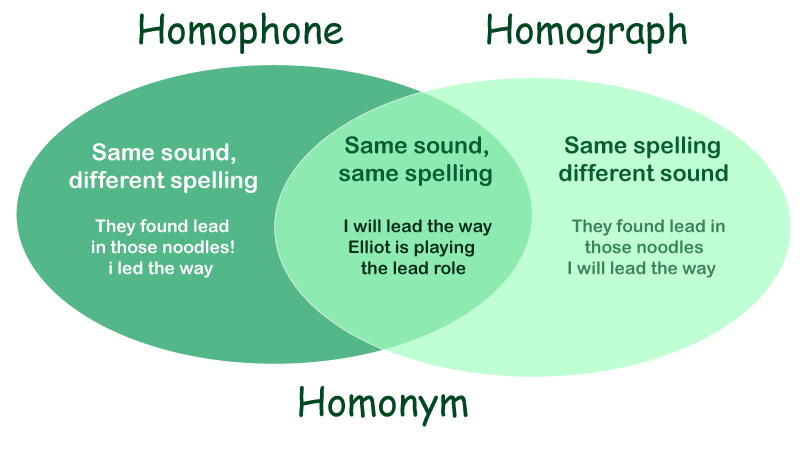
The distinctions between the three will aid in comprehending the message. At the same time, the word itself aids in identifying the distinction between these three. Homophones, homographs, and homonyms all start with the word "homo," which indicates identical or similar. The homophone "phones" refers to the sound. And "graph" refers to the writing in the homograph. Simultaneously, "nyms" derived from homonyms determine the name. As a result, homonyms are both homographs and homophones. It's also utilized as a synonym for both of these terms. Homonyms are more commonly used than homographs and homophones among these three. Your, you're, to, and two categories of words generate uncertainty in comprehending their meaning since everyone pronounces them the same way in everyday life. These are examples of homophones that are commonly used when speaking English. Commonly confused homophones include:
While natural speakers have no difficulty communicating because they can easily recognize homophones, novices and pupils, have difficulty understanding them. As a result, several activities have been added to the topic assigned to pupils by professors. Here are some examples of homophones. Both have the same pronunciation but alternate meanings.
ConclusionHomonyms are essential for comprehending the English language. Instead of comprehending the examples, comprehend their application and meanings, which will be beneficial to the general situation of homonyms. Homonyms are classified into two categories. Homophones and homographs vary in spelling and pronunciation, while homophones and homographs vary in sound. In comparison, both are significant in the language itself. As noted in the article, several examples of homophones are regularly used. All of the homonym details and brief annotations are part of language comprehension for speaking and writing. To avoid the misunderstanding caused by homonyms, it is essential to comprehend them. Homophones, homographs, and homonyms are among the most perplexing features of English, with which most people struggle. However, understanding the concept and practicing daily can help in mastering the concepts.
Next TopicHomophones Sentences
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









