Personal PronounsA personal pronoun is a brief word that we employ as a simple alternative for an individual's proper name. Each English personal pronoun indicates the noun's grammatical individual, gender, number, and situation. Personal pronoun encompass of- I, you, he, she, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, and them. 
Personal pronouns are grammar's real actors; they step in for the individuals (and maybe animals) that appear in our statements. They help us to speak and write more efficiently since they prevent us from repeating difficult proper nouns the whole day. What Are Personal Pronouns? - Definition and OverviewPersonal pronouns refer to those that are mainly linked with a specific grammatical individual - first person (as in I), second person (as in you), or third person (as he, she, it, they). The personal pronoun can also take several types based on their numbers (typically solitary or multiple), grammatical or natural genders, cases, and formalities. The word "personal" is used here solely to denote the coherent sense; personal pronouns can relate to animals and things in addition to people (as the English personal pronoun it usually does). The T-V difference refers to using one personal pronoun in certain dialects to denote a second personal pronoun with formalities or social distances - often a second person plural to indicate a second person singular formal - as from Latin pronouns tu and vos. The magnificent plural in English, including the use of "vous" instead of "tu" in French, are two instances. This text becomes much simpler and less bothersome to read when personal pronouns are used. Archbishop Desmond Tutu was born in South Africa in 1931, and he grew to international prominence as an adversary of apartheid in the 1980s. In 1984, he was the one who won the Nobel Peace Prize. He is the author of seven books and has co-authored or contributed to many more. Personal pronouns, just like all the other pronouns, only substitute nouns but no other parts of speech such as verbs or adjectives. In reference to the grammar , they function identically like nouns and can serve as the subjects or objects of a clause, phrase, or statement. 
Although personal pronouns are normally used to address people, they can also be used to allude to animals. As an instance, I purchased a small toy for my kitty, and he adores it. Some personal pronouns can also apply to inanimate items or concepts, such as: Our residence looked stunning after we decorated it. Follow the cake recipe accurately because they must be completed in a precise sequence. 23363733 Personal pronouns listWe can refer to a single individual or an object using personal pronouns or can even refer to numerous individuals/ items. Personal pronouns- singularIt is singular if a personal pronoun pertains to only one specific individual/item. The following are the most regularly used singular personal pronouns: I, me, in the first person. You is used in the second person. Third-person pronouns include - she, her, he, him, it. Personal pronouns - pluralIf a personal pronoun pertains to more than one individual or object, it is plural. The following are the most regularly used plural personal pronouns: First-person singular: we, us You in the second person. They, them in case of the third person. Pronouns in the First, Second, and Third PersonA personal pronoun can allude to one of three "people." The first-person pronoun is used to indicate to the speaking person, whereas the second-person pronoun is used to allude to the individual being spoken to, and last but not the least third-person pronoun is used to relate to the individual being spoken about. There is plural for each one of these three grammatical entities. Pronouns for the Subject and ObjectIn a statement, personal pronouns could be either subject or object. Subject pronouns are usually in the nominative case, while object pronouns are in the objective case. The first form of the singular includes - I/me The second form of the singular includes - you The third form of the singular includes - he, she, it/him, her, it The first form of the plural includes - we/us The second form of the plural includes - you/you The third form of the plural includes - they/them All three people have almost the same interrogative pronouns: who (nominative) and whom (objective). Many individuals are perplexed about whether to employ the interrogative objective pronoun whom, although it is a simple skill to master. Mrs. Malik requested that the box be handed to her at work. (her = third-person singular objective) To whom should I handover the letter ?(whom = objective (interrogative); I = first-person singular nominative) We want to ask Jessica to have dinner with us. (We = first-person plural nominative; we = first-person plural objective.) Singular Pronouns- They vs. Them overviewWhile the terms they and them are normally used in the plural, they can also be used in the solitary. They and them, as singular pronouns, are commonly employed in reference to an individual without distinguishing their gender. As an instance, An individual is allowed to do whatever they want. The physician tried to help everyone who visited them. Even when used singularly, the term they employs a plural verb: I believe you should always pay attention to your closest friends. They are aware of what is correct for you. They and them are at certain times utilized as single pronouns by nonbinary people: I'm going to meet Harper at the shopping center. They would like to go shopping for groceries with me. 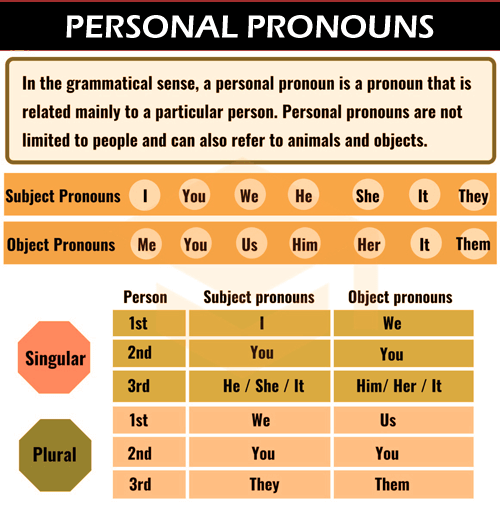
What Is A Gender-Neutral Or Nonbinary Pronoun?The terms she, her, he, and him are distinctive in the list mentioned above of singular personal pronouns such as they have been used to define a person's (or animal's) gender. While these are the most prevalent, there are a plethora of many other personal pronouns present that are not associated with a certain gender. It is critical not to misidentify somebody, even inadvertently, by using gendered terminology when it is not required. Fortunately, there is a simple strategy to ensure that your speech and writing are inclusive of all gender expressions: adopt gender-neutral vocabulary. If you are unsure of which personal pronoun you should use, or not or if you choose not to employ a gendered pronoun, the term they is appropriate. They can (and is increasingly being used) as a singular gender-neutral or nonbinary alternative for the gender-specific pronouns like he and she. (Other words are being used in this manner as well, but they term is the most popular.) You can employ or utilise it when you don't desire and need to define someone's gender. It can also be employed to describe someone who qualifies or becomes a nonbinary. In this instance, it's always vital using the person's preferred pronouns. Personal pronoun examplesSingular personal pronouns
Examples of Personal pronouns (plural)
Personal pronouns: How to Use ThemEvery personal pronoun has a distinct meaning. It is critical to understand all of them so that you can utilize them correctly in phrases. The words "I" and "me" are often employed to allude to the person speaking or the writer of a piece of writing. Both of these nouns are singular. I am used as both a subject and an object. You refers to an individual or people who are not speakers or authors. The term "You" can be used as a subject or an object, but you can also be employed as singular or plural. He, him, she, and her are all pronouns related to another individual or animal. These terms are gendered pronouns: he and him are usually used to pertain to male people/animals, whereas she and her refer to female people/animals. These are all singular terms. He and she serve as subjects, while he and she serve as objects. It is utilized to describe non-living objects, abstract notions, or animals with uncertain sex. "It" is a single word that can be utilized as both the subject and the object. We and us are utilized to allude to a speaker or the author as well as other persons. Both nouns are in the plural. We are employed as both a subject and an object. They and them are words employed to refer to other individuals or things. They word is utilized as both a subject and an object. While they and them are frequently utilized as plural phrases, they and them can also be used as solitary words to allude to an individual of indeterminate gender or a nonbinary person. It is a great idea to utilise a personal pronoun following the noun that it is substituting. This will ensure clarity. As an example: Less clear: He went shopping and purchased a new cap. More clear: Tim went to the store, and he purchased a new cap. You do not have to do this with the pronouns I, me, and you in particular. These pronouns can solely relate to the speaker/writer or to all others. Personal pronouns adhere to the same main rule as all other pronouns. They exclusively substitute nouns and obey the same grammar rules as nouns. This states that personal pronouns can be used as subjects or objects: Subject: We went to the beach and searched for shells. Object: Rita said that she handed you the package. Personal pronouns must be used in accordance with subject-verb agreement. This indicates that a singular personal pronoun employs a singular verb, whereas a multiple personal pronouns employs a plural verb. As an example, He is my best friend in the singular. (He is both a singular pronoun and a singular verb.) Whereas in the case of a plural example, I purchased the sneakers because they were on discount. (They and were are both plural.)
Next TopicPossessive Pronouns
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









