Difference Between Adjective and AdverbThe boy took up a pen and paper and began to write. This sentence is totally fine because it tells us what the man did. However, it appears to be a little plain. How about we spice up this sentence a little? The stylish, jovial boy sat down to write. Things suddenly become a lot more exciting. Let's give it another shot: The boy wrote a poem while hanging from a rope. Another intriguing sentence! 
We employed two key parts of speech in these sentences: adjectives and adverbs. While both of these are employed to spice up phrases by changing words, they are not interchangeable. We utilized modifying words in both of our new phrases to provide extra information about the boy who was doing something or about what the boy did. There are eight different parts of speech. Adjectives and adverbs, in particular, are frequently juxtaposed because they provide extra information about another component of speech. Let us quickly have a look at the difference between adjective and adverb, adjectives are usually employed to convey more information about a noun or a pronoun, such as persons, locations, animals, or objects. Whereas in contrast, adverbs are employed to provide more information about the verbs, adjectives, or adverbs. Let's look at an example to comprehend the difference between adjective and adverb better: An adjective is the term that alters the meaning of the nouns or pronouns. In practice, an adjective aims to characterize a noun or pronoun by describing its properties or offering further information about it. In the statement, Helen has a big cat. For example, the adjective big indicates that the cat (a noun) is big in size and weight. An adjective is a term that we employ in a sentence to elaborate on the meanings of nouns or pronouns, i.e., it functions as a modifier of a noun to convey the qualities of the thing stated, express its number, extent, or emphasize something that is uncommon in nature. Simply expressed, the adjectives limit the meanings of the nouns or the pronouns. 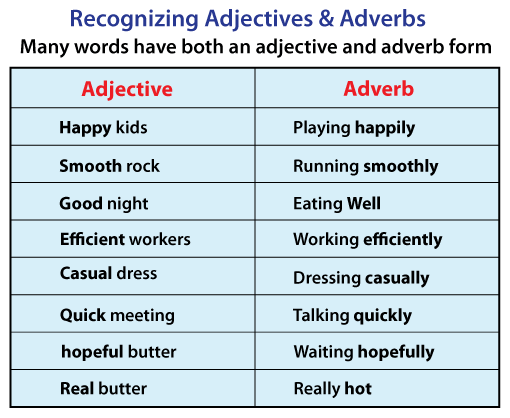
An adjective comes preceding the nouns or pronouns it describes in most cases. It may, however, appear after the phrases that identify or describe them. Here are some examples of adjectives. The adjectives have been highlighted for ease of recognition, this will help you better understand the difference between adjective and adverb.
Moving on to the difference between adjective and adverb, Adjectives can be used immediately next to the nouns/pronouns they alter or as a subject complement after a connecting verb: The hungry rhinos devoured the delectable berries. (The adjectives hungry and delectable are next to the nouns rhinos and berries.) I'm exhausted. (exhausted is a subject complement that comes after the linking verb am.) Adjectives ListThere are numerous adjectives, each with a unique function. This list contains only a few instances of several different kinds of adjectives that individuals use: angry, busy, cautious, dizzy, eager, afraid, glad, warm, icy, twitchy, klutzy, lazy, lonely, nice, opened, calm, quiet, prepared, soft, clear, unlucky, successful, wobbling, yellow, spicy Adjective examples in sentences. The adjectives have been highlighted for ease of recognition.
A compound adjective is the type of adjective that is made by merging terms with a hyphen, for instance a tech-based association, for example. Moreover there are three types of adjectives, that are referred to as degrees of the adjective. When an adjective appears in its normal form, it is referred to as a positive degree. The other two degrees are utilized for comparison, namely the comparative and superlative degrees. 
There are four demonstrative adjectives: this, that, these, and those. Similarly, Which, What, and Whose are interrogative adjective. These adjectives are often used to start a query. The below mentioned are the main seven kinds of adjectives. Possessive Adjectives: As the title suggests, these adjective are employed to denote ownership. These can also be utilized as possessive pronouns. Here are a few examples: My, You, His, Her, Its Our, Their Demonstrative Adjectives: These are words that are used to identify or demonstrate certain persons, animals, or objects. This, those, these, and that are instances of demonstrative adjectives. Coordinate Adjectives are separated by commas or words and occur one after another. Number Adjectives- A number is an adjective if it addresses the inquiry "How Many?" Interrogative Adjectives: The three interrogative adjectives are Which, What, and Whose. They are often used to alter nouns and to pose queries. Which choice interests to them the most? What time the college starts? Whose shoes are those? Indefinite Adjective: They are often used to discuss things that are not specified, such as the articles a and an. Any, many, no, several, and few are the most common indeterminate objectives. Attributive Adjectives are used to talk about qualities. They discuss distinguishing characteristics, qualities, or features. As an example- The size and form feature refers to physical activity. A specific age is denoted by an age adjective. The material adjectival denotes the material of which something is made. Color Adjectives- As the title implies, these adjective describe color. What is an Adverb? What is the difference between adjective and adverb?An adverb is the most important part of eight parts of speech that describes or provides the details about a verbs, adjectives, phrases, or adverbs. It functions as an intensifier, emphasizing the verb, adjective, sentence, phrase, or adverb. In essence, it implies to the time, place, degree, frequency, and manner of everything. You may quickly recognize an adverb in a statement by looking at the suffix; for example, an adverb ends in -ly. Some adverbs, though, do not finish in -ly, such as rapid, hard, early, late, and so on. These are used either before or after a verb. 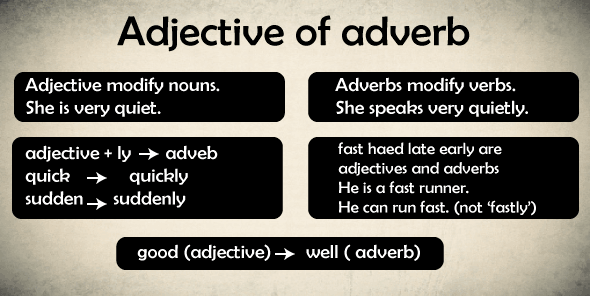
Let's look at some adverbial examples, this will help us understand the difference between adjective and adverb better; An adverb is a term that alters another term, such as the verbs, the adjectives, the phrase, or another adverbs. Adverbs, on average, offer far more detail that answers queries like When?, Where?, How?, and Why? In the statement Mary walked slowly, for instance, the adverb gradually tells us how Mary walked: she took her time and didn't rush. Adverbs can appear before or after the term they alter when altering verbs: John checked quietly. John quietly reviewed. An adverb can even be distinguished from the verb it alters by an object: Helen finished her housework quickly. Adverbs that change adjectives or other adverbs are frequently put immediately just before terms they change: They were completely tired. Antonia sang beautifully. Adverbs, like adjectives, come in a variety of forms that we employ in our statements. Here are a few examples: suitably, boldly, carefully, dangerously, effortlessly, blankly, gallantly, hastily, sarcastically, happily, kindly, longingly, skillfully, needlessly, openly, wonderfully, swiftly, rashly, silently, tragically, naively, publicly, wastefully, yesterday Adverbial Examples in Sentences
Adverbs, in addition to verbs, can change adjectives. They are a type of modifier that can be used to alter verbs or adjectives. You can tell whether a term is an adverb based on its purpose in the statement. 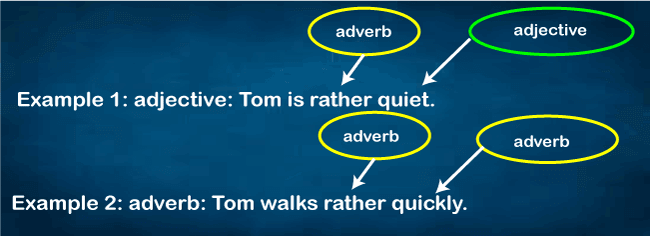
Because the +ly form is so popular, here are a few examples.
Because they describe verbs and end in ly, you can guess that the terms mentioned above are adverbs. Numerous high-frequency terms, however, are also adverbs, such as very, much, more, and many.
Adverbs of Time- It gives further details about when a verb occurs. They are frequently used at the start or finish of a statement. Never, recently, just, always, during, and yet are some examples. Adverbs of Place- This type of adverbs describe the location of the verb. It comes following the main verb or object. Here, there, nowhere, and everywhere are some examples of such adverbs. Adverbs of Manner these are the prevalent type of adverb. These adverbs describe how a verb is carried out. For example, neatly, quickly, slowly, and regretfully. Degree Adverbs- It expresses the level of the verbs, adjectives, or another adverbs. For instance, virtually, quite, nearly, and so on. Adverbs of Frequency- This type of adverb describes how frequently the verb comes. They are put prior to the sentence's primary verb. Adverbs of Frequency Examples: never, always, sometimes, generally, again. 
The Essential Differences Between Adjective and AdverbThe difference between adjective and adverb can be clearly defined on the following grounds: The adjective is one of the eight parts of speech in grammar that identify and define the nouns or pronouns, i.e., a person, place, animal, or thing. In contrast, an adverb is a part of speech that provides more details about the verbs, adjectives, or any other adverbs. Another difference between adjective and adverb is that an adjective qualifies the nouns or pronouns, whereas an adverb modifies the verbs, clauses, phrases, adjectives, prepositions, or conjunctions. Another, difference between adjective and adverb is that Adjectives answer queries like which, how many, what kind, and so on. Adverbs, on the other hand, always respond to the queries that include- like how, when, where, how much, how often, to what extent, and so on. 
How To Remember The Difference Between Adjective And AdverbAdverbs and adjectives both expand on another part of speech. Adverbs are made by adding -ly to the end of adjectives such as emotionally, hopefully, cautiously, terribly, principally, and so on, which also serves as their identity. However, some adverbs appear to be adverbs but are actually adjectives, such as hourly, daily, monthly, and yearly. 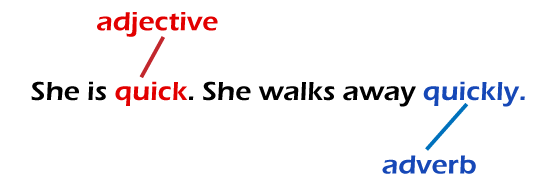
This will not only aid you in recognizing or understanding the difference between adjective and adverb in a sentence. Moreover, it will help you sharpening your writing skills and eliminate grammatical problems. Take note of whether the word verb or subject is used in the phrase. If the word changes the subject, an adjective should be used. Similarly, if it alters the verb, an adverb should be used. ConclusionThe usage of an Adjective and an Adverb in a statement provides emphasis and significance to it. It also indicates the significance of the conveyed action or statement. Knowing the difference between Adjective and Adverb not only allows you to write or talk properly but also allows you to express the phrases correctly. It also recommends you to select a better term so that your writing is stronger and the necessary information is conveyed without a problem.
Next TopicAdjectives
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









