Present Indefinite TensePresent Indefinite Tense is a type of tense; before understanding it, let us learn 
What Tenses Are?There are three primary sorts of verb tenses in English grammar: past, present, and future. The past tense relates to something that has already occurred, the present tense depicts what is currently happening, and the future tense pertains to what is yet to occur. While these three tenses may appear to be simple concepts, knowing the complexities of the numerous forms of each tense is a difficult task. Because tenses are vital in contributing to your writing skills and are frequently included in language proficiency tests such as IELTS, TOEFL, PTE, and others, it is critical to developing your verb tenses fundamentals. Simple Present Tense or Present Indefinite Tense What is Present Indefinite Tense?Tense represents the time period in which the activity occurs and is conveyed using the verb. Present Indefinite Tense or Present Tense can be described as an act that is completed in the present but has no definite time period for completion. This tense can also be used to describe genuine events, the near future, habits, nature, and so on. Example: Shalu enjoys cheesecake. Noah consumes an apple every day. The other is to discuss habitual acts or events such as: Each day, I go to work. Daily, Dad wakes up early. Please keep in mind that we normally employ the present continuous to denote a transitory action that is now taking place: Serena is unable to answer the phone at this time as she is sleeping. The simple present is a verb tense that has two main applications. When an activity is taking place at the moment or regularly (or continually, it is due to this that it is most often referred as present indefinite), we use the simple present tense. This tense is formed differently relying on the individual by employing the root type or by fixing s or es to the end. I'm in a terrific mood! Christine enjoys pie. I'm sad to hear you are ill. The other choice/option is to describe habitual activities or events. Each day, Pauline practices the piano. During the summer, Ms. Jackson travels. Hamsters keep running all night. When we wish to express a present momentary action, we usually use the present continuous: Jessica can't answer calls right now as she is combing her hair. 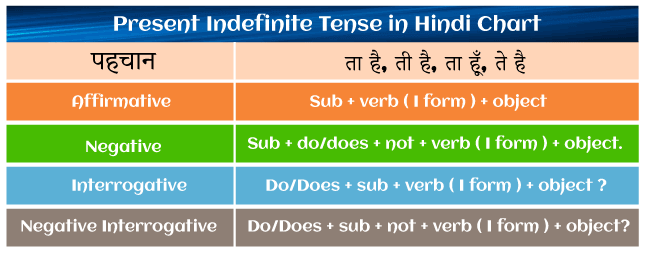
How to Form Present Indefinite TenseWith exception for the third-person singular, most common verbs use the root type in the simple present (which ends in -s). Singular first person: I compose. Singular second person: You compose He/she/it writes in the third person singular (notice the s). Plural of the first person: We compose Second-person singular: You compose Third-person singular: They compose The third-person singular of some verbs ends in -es rather than -s. These are mainly verbs that root type concludes in o, ch, sh, th, ss, gh, or z. Singular first person: I go Singular second person: you go He/she/it goes (notice the es) in the third person singular. Plural of first-person: We go Second-person singular: You go Third-person Plural- They go Most ordinary verbs are followed by the negative of the verb, e.g., "She won't go" or "I don't feel any of it." The irregular verb to be is: Singular first person: I am Singular second person: You are You are It's he/she/it is Plural of first-person: We are We are You are Third-person plural: They are Applications of the Present Indefinite TenseLet's look at the various kinds of actions that the Present Indefinite Tense can be used for: 
To describe or illustrate the universal truth. The earth rotates around the sun; human is mortal, and the sun rises in the east. In the case of a current action: Boys are playing football; I am reading a book, and she is singing a song. For routine activities and those including adjectives such as always, never, infrequently, and rarely. For example, I never lie; she always tells the truth, and my office opens at 11 a.m. There will be the following events in the nearish future: My school starts next week, and the third semester starts in a month. How to Negate or to make the Simple Present sentences negative?Do/does + not + [root form of verb] is the rule for formulating a negative sentence. Rather than do not or does not, one can utilize the contraction don't or doesn't. Sandra does not wish to share the dessert, and he does not think there is sufficient to have. Her pals do not commit. In any case, I don't want cheesecake. The rule for making the verb negative is [to be] + not. I am not a huge fan of pies, but Pauline is. You are not ready for such delectable pastry. Now it is time to move on and let take a dip into a few more aspects of Present Indefinite Tense. What Is the most ideal way to Ask a Question? Do/does + [subject] + [root form of verb] is the strategy for asking a question in the simple present. Do you know how to make a pie from scratch? How much pie does Sophie adore? How to make Present Tense Positive or Affirmative?For Affirmative Sentences: There isn't an auxiliary verb in this. The primary verb is conjugated by adding s to the third person singular. For Negative And Question Phrases, Use The Following: In the Present Simple, the auxiliary verb (do) is covalently linked as follows: do, does The primary verb is always in the root word: base. We add not between the auxiliary verb and the primary verb in negative phrases. We swap the subject and auxiliary verb in question phrases. A small tip for the same is; Normally, we do not use the auxiliary verb do in positive sentences, and however, we can use it to emphasize (stress) something. Rather than saying "I like your gown," we could say "I do like your costume" to emphasize how much we like it. Here are some additional examples: I really wish you'd stop. I sincerely apologize. 
Present Simple with the main verb beEven for questions and negatives, there is also no auxiliary verb. The primary verb (be) is covalently linked in the Present Simple: am, are, and aren't. We use not after the main verb in negative sentences. We swap the subject and primary verb in question sentences. How should the Present Simple tense be used?We can use Present Simple to discuss: time in general (action verbs) situations right now (stative verbs) now is the general time and situation (verb be) For a general time, use Present Simple. When we use the Present Simple tense, we mean: The action is broad. The action occurs all the time, or on a regular basis, in the past, present, and future. The action is not limited to the present. The assertion is always correct. For the time being, present Simple. To discuss now, we can utilize the Present Simple with stative verbs. Stative verbs are not used to describe an action, and they define a state and include verbs such as "like," "sound," "belong to," "need," and "seem." We could use these verbs with the Present Simple tense to communicate about a specific activity in the present rather than a general topic. I want a cup of tea That sounds fascinating. Do you require assistance? For general time and now, use Present Simple. The verb be is always unique. It is a stative verb, and we utilise it in the Present Simple tense to discuss both current and general events. Consider the following instances of the verb be in the Present Simple tense - some normal/ typical, some specific: I am not overweight. Why are you so stunning? Ram is quite tall. Am I correct? Tara is not present. We are starving. Thus conclusively, The "indefinite tense" is a type of verb tense, and it teaches the simple past tense, simple present tense, and simple future tense. In contrast to the other tenses, the indefinite tenses focus on actions without specifying whether they are finished or continuous. When an activity is currently happening or occurring presently or on a regular basis (or unceasingly, that's why it's occasionally called present indefinite), we just use the simple present tense. The simple present tense is formulated differently ; this further depends on the person using the root type or attaching s or es to the end. I'm in a great mood! The present indefinite tense, also known as the simple present tense, refers to a static, habitual, or eternally true action. Now, in the end, let us have a look at some of the examples of Present Indefinite Tense that can help us have a better understanding of the concept; Examples of the same are;
Next TopicPresent Perfect Tense
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









