Rules Of TensesEnglish phrases or sentences are formed using tenses rules. There are three forms of tenses: present tense, past tense, and future tense. The past relates to what happened much before, the present tense relates to what is occurring now, and the future tense relates to what will happen after now. They essentially depict temporal elements based on the actual timing. 
Tenses guidelines aid one in understanding how to rightly utilize distinctive types of tenses in a phrase with zero a linguistic error and successfully showing when an occurrence or act has taken place. In English language, tense is a strategy that is utilized to referring to the time - past - that has already happened, present- that is happening, and future - that will happen. Numerous languages utilise the tenses to refer to the time. Different languages have no knowledge of tense by any methods; yet, they can describe time using varied approaches. Rules of Tenses assist in understanding how to appropriately employ the various tenses in a phrase without creating a grammar mistake and readily indicate when a particular event has happened. A tense is a word form used to denote the onset of an event in relation to the time of the speech, and it denotes the end or continuation of an action. Whether you are a school kid or studying for a competitive exam or any other English competency exam, knowing the Tenses will undoubtedly help you score higher. 
Let's look at some samples of different tenses, rules, and usage! As said in the beginning, there are basically three sorts of tenses: Past Tense; The Present Tense; Future tense These three tenses are further categorized depending on action continuation and completion of the activity Simple or Indefinite Tense; continuous tense; the perfect tense and the perfect continuous tense Simple Tense- It is used for continuing or routine activities in the Present Tense, actions that have already occurred in the Past Tense, and activities that will happen in the Future Tense. The action is fragmented, steady, or ongoing in the continual tense. Perfect Tense: The action is completed, accomplished, or outstanding in relation to a specified time period. Perfect Continuous Tense- The action has been ongoing for an extended period of time and is continuously happening. These are mandatory to comprehend the rules of tenses. As the norms and the rules are built around these only. Let us have a look at the rules Past Tense RulesAn event or occurrence that happened in the past, as implied or referred by the past tense. For instance, he participated in football the other week, and the event has already occurred in this phrase. Some of the examples or instances of these include; Reema participated in the wedding festivities. He had already departed when I arrived. Priyanka wrote a letter to her camping pals. All these have already occurred or happened in the past. Simple Past Tense RulesSubject + V2 + Object So the rule for the simple past tense would be Ashok went to the camp Priya ate all the cookies 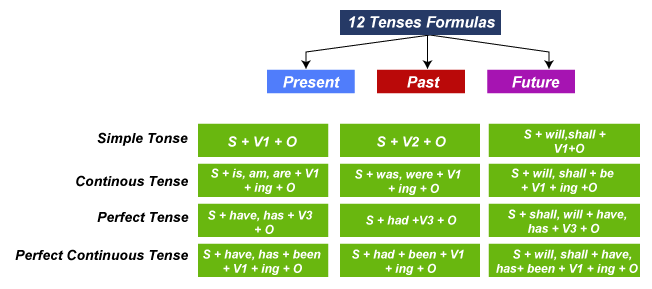
Past Continuous Tense RulesSubject + was + V1 + ing + Object (Singular) Subject + were + V1 + ing + Object (Plural) In English, the past continuous tense is highly essential, and we utilize it to explain what we were doing at a given point in time in the past. Some of the examples of this rule include: Rima was smelling the pudding. Rita was writing a note to the professor. Past Perfect Tense RulesSubject + had + V3 + Object The past perfect tense is simple to grasp and apply in a phrase. This tense refers to a task that happened in the past. If two activities occurred in the past, the past perfect tense is employed to show the older activity. Some of the examples of this rule are: Rima had taken the letter. She had wiped the floor. Past Perfect Continuous Tense RulesSubject + had been + V1 + ing + Object Used to describe a situation that began before a specific point in the past (time) and proceeded till a given point of time in the past. Some of the examples of this type of tense include; Riya was excited. She had been jumping and dancing. Had the child been wandering outside the house? Tom had been waiting in the rain the whole afternoon. Feroz had been munching cookies and wafers for the whole day. Present Tense RulesThe present tense is a term denoting an activity that is now in progress, or that is routinely conducted. It refers to a situation that occurs in common or is actively in progress. The present tense refers to the moment when the occurrences are taking place right now. It may be defined as an articulation for an activity that is now taking place in real life, or that is habitually performed. It is utilized for a typically existing or at present happening expression. Some of the instances of this type of tense are It is a type of verb that states the occurrences/ incidents that are currently going on. I am walking to school. Ram has been part of this association for 3 years now. The movie is spectacular. Simple Present Tense RulesSubject + V1 + s/es + Object (Singular) Subject + V1 + Object (Plural) It is used to depict recurrent acts, universal truths, daily occurrences, and more. Some of the instances of this type of tense are The Sun rises in the East. Seema goes to university. Present Continuous Tense RulesSubject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + object This type of present tense is used to explain, narrate the events or actions happening in the present. Some of the examples of this type of tense are: I am eating the pudding We are going to the part today Riyan was writing the note to the professor 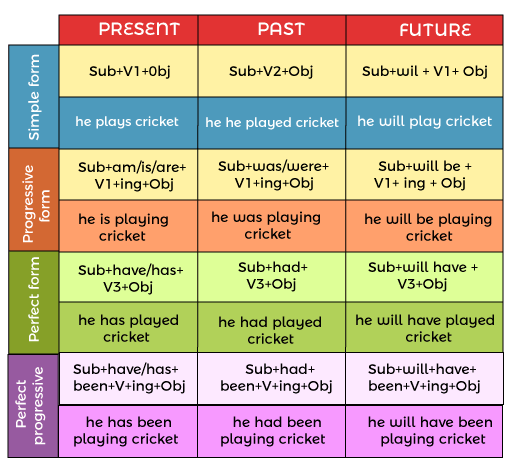
Present Perfect Tense RulesSubject + has + V3 + Object (Singular) Subject + have + V3 + Object (Plural) This is a type of tense that is used to convey the event or the task, which is just/recently accomplished/completed. Some of the examples of this type of tense are: She has just eaten the ice cream. We have just watched the movie. Present Perfect Continuous Tense RulesSubject + has been + V1 + ing + Object (Singular) Subject + have been + V1 + ing + Object (Plural) This tense is used to indicate an act that began in the past and continues in the present. Some of the examples of this type of tense are: I have been mopping the floor regularly since Sunday. He has been using the skin ointment for numerous days. Future Tense RulesThe future tense is mainly used to narrate and explain the future events that have not occurred but possibly will happen in the near future. It is a form or a type of verb that will happen in the future & doesn't exist currently or at present. Some of the instances of this type of tense are; Aamna will be dancing to western music. We will be shifting to the rented house tomorrow morning. The bus will leave in 5 minutes. Simple Future Tense RulesSubject + will/shall + V1 + Object The time that passes after saying a statement is referred to as the future tense. This tense expresses future occurrences and occurring. Some of the examples of this type of tense are: I shall go to college tomorrow. My father will take care of me. 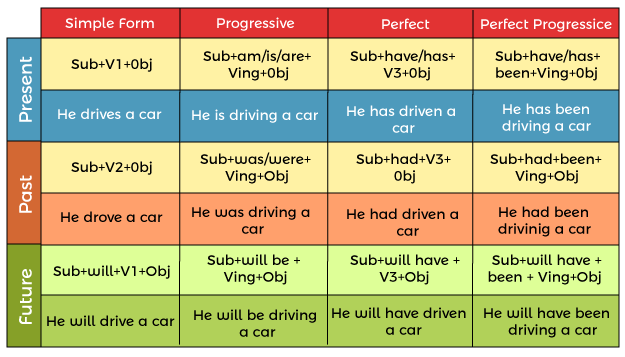
Future Continuous Tense RulesSubject + will be/shall be + ing + V1 + Object It is used to represent an event that will happen or continue in the future. e.g., He will hand out transfer letters at the workplace tomorrow at 12 p.m. In the example, the activity will begin in the future (tomorrow) and will be continued until some point in the future. Some of the examples of this type of tense are: He shall be writing his exam. We all will be going shopping this weekend. Future Perfect Tense RulesSubject + will have/shall have + V3 + Object It is used to represent an activity that will occur in the near future and will be accomplished by a specific period in the future. We can use future perfect to indicate that something will be completed by a specific date in the future. Some of the examples of this type of tense are: I shall have initiated singing by that time. We will have landed at Mumbai by then. Future Perfect Continuous Tense RulesSubject + will have been + V1 + ing + Object It is utilized to describe the events that will begin at a certain moment in the future and continue for an indefinite period of time. The future ideal maintains constant attention on the length of an action that will be in existence prior to another time or occurrence in the future. Some of the examples of this type of tense are: By next month they will be passing the college. They shall be helping the children in the slum area day after tomorrow. Tenses have become an important feature of the English language. It denotes the time activity occurs, whether it occurred previously, is currently occurring, or will occur sooner or later. By modifying the spelling of an action term, tense can be introduced. The rules specified above can be really helpful in having a stronghold and better understanding of the concept of Tenses.
Next TopicTenses Chart
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









