Parts Of Speech ExamplesParts of speech are groups of words that have common grammatical functions in phrase and sentence constructions. But what are the many parts of speech, and how should you determine which words relate to which grammatical classifications? This section will describe the different parts of speech and how to recognize, change, parts of speech examples and apply them in basic and complex phrases. 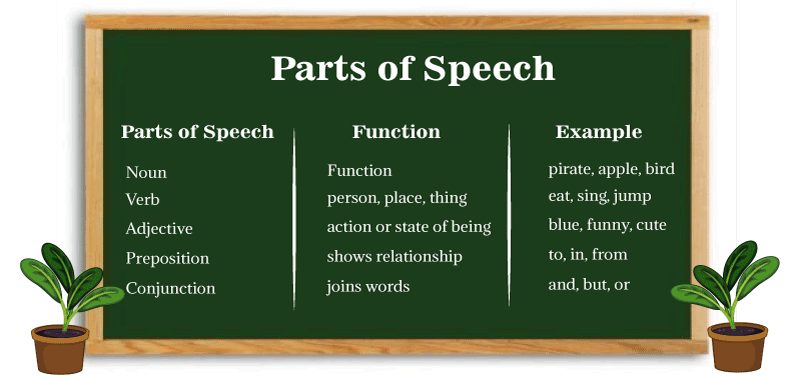
In English, there are many elements of speech that are combined to produce a sentence. The speech would not be able to perform without these parts of speech. What Are the Different Parts of Speech?Parts of speech are word-groups characterized by the grammatical functions they perform in sentence structures. Words are classified according to the grammatical functions and interpretations they generate and communicate. There are 8-9 common parts of speech in English. Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, determiner, and article are parts of speech examples. Though the meaning of these divisions is described in the following sections, you should be aware that these parts of speech play a grammatical role or perform a grammatical purpose in language, comprising sentence interpretation or meaning. Word Class- Open and ClosedClosed word class is a type of parts of speech that remain constant never get new terms. Pronoun, conjunction, determiner, and preposition are examples of these. Open word class is that type of parts of speech that have addition of fresh words with the passage of time. Noun, verb, adjective, interjection, and adverb are examples of them. 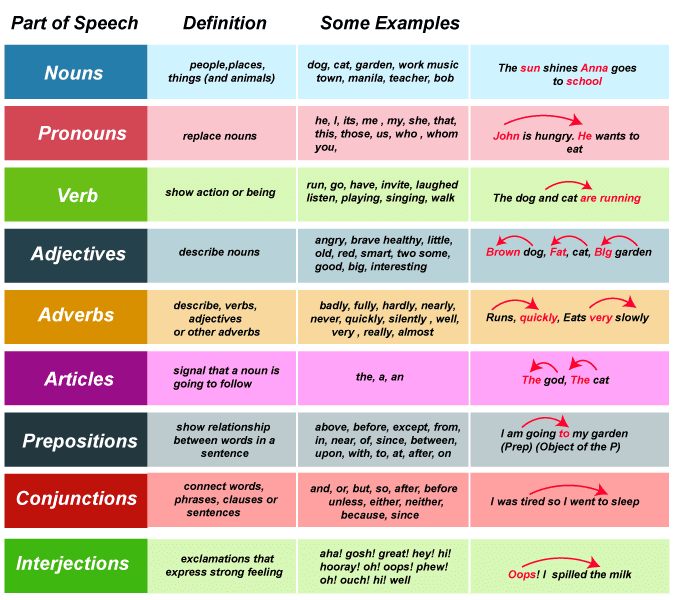
List of Different Parts of Speech ExamplesIn below mentioned portion, we'll have a quick glance at the different parts of speech, like the verbs, nouns, and adjectives, and so on. This will give us a better knowledge of how sentences are generated and how the different parts of speech function. The majority of parts of speech can be subdivided into sub-classes. Prepositions are classified as time prepositions, location prepositions, and so on. Proper nouns, common nouns, concrete nouns, and so on are all types of nouns. It is vital to understand that a word might appear in more than one portion of a speech at times. As an example, consider the term increase. The increase can be used as a verb, for example. Costs increased, and increase can also be used as a noun, as in There was an increase in the number of believers. The Noun (n.)This refers to a term or a word that offers anything a name; in certain situations, they are alluded as 'naming word.' There are several types of nouns, including proper nouns, collective nouns, possessive nouns, and common nouns. Each of these performs a different role; let's take a closer look at this. 
Read on to have a look at these parts of speech examples Daniel, Seoul, pencil, New Year, puppy, kitten, tiger, yard, college, job, song, city, Philippines, professor, farmers, Robert, John, Mike, cop, Paris, espresso, soccer, safety, love... Sentences with nouns: The educator told the kids to pause jabbering in school. Thomas is decent at English but weak at Maths Some more example sentences of Noun: John lives in New Zealand. Lina uses crayons and colored pencils to draw paintings. Send in the candidates. Kerala is pretty this time of the month. His love for cars really depicts. Proper NounThe proper noun is often used to name a certain entity, such as the names of locations or persons or the titles of films or songs. The capital of Germany is Berlin. Jessica is stunning. Eela liked spending time with his friend Paul in Australia. Hyundai and Honda are two vita car manufacturers. We visited Nainital, which is a beautiful hill station in Uttarakhand. Collective NounThis is a type of noun that can be utilized for referring to a group of noun, for example, people or animal group. The swarm of bees was advancing right for our barbecue. On Sundays, the choir sings enthusiastically in prayer. Our team dances spectacularly. The band played mesmerizing melodies. This is an amazing and obedient class. Possessive NounsThis is a type of noun that is often used to demonstrate possession or owner of a thing by using an apostrophe and an s, like in the below mentioned parts of speech examples. This is my cat's toy. That's Anna's pal. The dog's bone was missing. That boy's pen broke. The girl's jacket was lost in the college. Common NounA common noun is the most basic type of a noun that provides an object a name. See the below mentioned parts of speech examples for better understanding. Here is a bowl. Do you want a dessert? Elina loves the holidays in the countryside. They enjoy dancing every evening. The glass fell and broke. PronounA pronoun is a term that takes the position or the place of a noun, and there are many various forms of pronouns in English grammar. Let us just look at some examples of how each one is utilized in different ways. 
Read on to see more about this and have a quick look at these parts of speech examples I, me, we, you, he, she, yours, himself, its, my, that, this, those, us Examples of pronoun words in a sentence: Peter is not at office this month because he's on vacation. Tell her the reality, but don't disclose the whole truth. She put it to the test. You can't make him guilty for everything. The woman who contacted yesterday expressed interest in purchasing the property. The Reflexive PronounThis is a type of Pronoun that is a pronoun that has a reflexive meaning. When referring to oneself, such as myself or myself, a reflexive pronoun is employed. I am keeping this last bite for myself. Andrew is a self-centered individual who almost always places himself foremost. Indefinite PronounYou could see words like anything, few, everyone, or all when this form of the pronoun is often used to allude to a nonspecific or general person or something. Are you able to take all of these? This infection on my arms has to be discussed with someone. Possessive PronounThe Possessive Pronoun is a pronoun that refers to someone who owns something. This is a type of pronoun, that employs terms like as my, his, their, or yours, is used to denote possession or ownership of something. Is this your backpack? I've been taking care of his kid. The Relative PronounAn adjective clause is introduced with a relative pronoun. These are words like who, which, that, and whose that you may be familiar with. This is the lady who will be assisting you. Is this the publication about which everyone is blabbing? The Adjective (adj.)It refers to a word that describes or defines nouns or pronouns. The English language has hundreds of adjectives. 
Let us have a look at these Parts of Speech Examples. Gorgeous, nine, adorable, third, long, purple, furious, courageous, cautious, strong, little, ancient, kind, crimson, clever, three, tiny, majestic, few, excellent, large, helpful, intriguing... A gray dog, a pink van, a tall gentleman, a big rabbit, and a beautiful garden. Examples of Adjectives: Parts of Speech
The Verb (Vb.)A verb is a term that fits an action and is one of the most significant aspects of speech. There are three general forms of verbs, which are illustrated in great detail below; 
Let us have a glance at the parts of speech examples Walk, is, seems, realizes, runs, sees, swims, stands, goes, has, gets, promises, invites, listens, sings, sits, laughs, walks... Sentences with the verb: Do not attempt to run before you have learned to walk. Did you promise anyone? Leave me alone! The Verb of ActionAn action verb accomplishes exactly as it says on time: it expresses a specific activity. A guy strolled the streets. I laughed at his prank. The Linking VerbInstead of showing a physical action, a connecting verb is employed to show a state of being. Sally feels cold. I am very exhausted. The Modal VerbA modal verb is used to 'assist' the primary verb and can reveal the speaker's ideas or attitude toward what they're talking about. Modal verbs include words like might, must, could, and can, and some other verbs. I might stroll to the nature reserve this lunchtime. He can chew the very last slice of chocolate cake. Adverbial phrase (adv.)It refers to a word that alters or clarifies adjectives, verbs, or another adverbs. They can clarify and make life simpler for the listener to comprehend what is being explained in depth by adding additional info to a sentence. Adverbs almost always finish in the letters -ly, but there are a few exceptions, like the phrases very and never. 
Read on to have a look at these parts of speech examples. Every day, tomorrow, extremely, poorly, fully, carefully, hardly, nearly, hungrily, never, swiftly, discreetly, well, really, almost. Example phrases with adverbs: This is an extremely appealing photograph. I have a very large pet animal My vehicle accelerates swiftly. I eat my breakfast rapidly when I am getting late for office. The boy is sobbing uncontrollably. All of his letters were carefully saved by her. The Conjunction (conj.)This refers to a string of words that connects two or more idea or word. The terms for, and, not, but, or, yet, and so are frequently utilised as conjunctions. 
Read on to have a look at these parts of speech examples And, however, still, but, or, so, after, since, before, either, neither, because, unless. My school buddy and I are planning to meet up. I'm going to the store, but not until I've had a bite to eat. This is a gift for a cousin of mine. I was very exhausted, but I still went exercising. The Preposition (prep.)In English, a preposition is often used to demonstrate a connection between two words or phrases. Words like in, before, on, at, to, between, and so on are examples of prepositions. 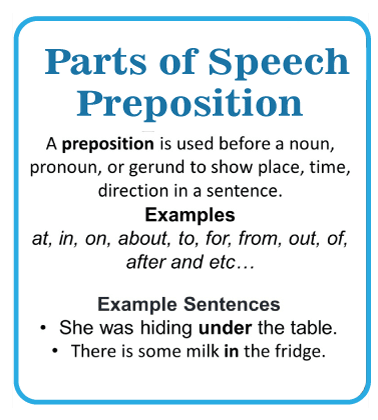
Let us have a look at these parts of speech examples; Between, upon, with, to, after, towards, in, on, at, about, apropos, according to, after, along, above, except, from, near, of, before, since, and so on. Example phrases with prepositions:
Interjections (interj.)An exclamation can also be conceived of as an interjection. They are employed to express passion, reaction, or excitement, and they have no grammatical connection to the rest of the sentence in which they occur. 
Read on to have a look at these parts of speech examples Gosh!, ahem! Aha! Aw! fantastic! Hey!, hi! Hooray! Oh!, yes! Oh no! oops! Eh!, phew! Well! Example phrases with interjections:
Articles and DeterminersDeterminers and articles are components of speech that assist in understanding noun and noun phrases. They are frequently used before noun (or noun phrase) to aid in identification of their identities, quantities, distances (from the speaking individual), or precise number (along other things). DeterminersThese are words that are added to the front of nouns to define their meaning. There are a variety of categories to choose from, including: Articles - a, an, the Numbers - two, eight, ninety-nine Pronouns and possessive determiners - his, her, its, your, my, their, ours Difference determiners - others, the others, another(s) ArticlesArticles refer to a type of adjective that serves as a subclass of determiner. Definitive - shows that the viewer is already aware of the noun's identification. The word the would be a definite article since it denotes a noun that is already familiar to the reader/audience ("I'm going to lie in the backseat.") Indefinite - denotes an unknown noun, or refers to a noun for the first time, or shows that a noun corresponds to a particular class of things. Indefinite articles include words like "I'm going to sit in a backseat," "You're an accountant," and "I was married on a Friday." Demonstrative include the words like these, those, that, this Quantifier include the terms like a little, a few, much, many, some, any, enough, most Distributive include the terms like half, both, every, each, all, neither, either Pre-determiner include the terms like quite, such, rather, what.
Next TopicParts of Speech Exercises
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









