Present Perfect Continuous TenseIntroduction: Present Perfect Continuous TenseThe Present Perfect Continuous employs two auxiliary verbs in addition to a primary verb. The composition and usage of the Present Perfect Continuous tense, along with the use of for and since, are covered in this lesson, along with few examples are given for your understanding. 
It's worth noting that continuous tense is also called as progressive tense. Hence, the Present Perfect Continuous tense is sometimes called as the Present Perfect Progressive tense. The present perfect continuous tense (also called as the present perfect progressive tense) implies that certain activity commenced in the past and is still ongoing in the current or present. The combination has/have been + the present participle (root + -ing) is used to generate the present perfect continuous. I have been reading Wars and Damage for about a week. The usage of the present perfect continuous verb tense in this phrase or the sentence shows that reading Wars and Damage is an action that started in the past and is not yet finished in the current (which is understandable considering the length of Tolstoy's massive tome). Recently and lately are frequently used with verbs in this tense- present perfect continuous tense. Neeraj has been competing in art competitions recently. (And he will continue doing so.) I have not been feeling good lately. (And I am still Unwell at the moment.) Have you seen my paper and pen recently? (This is due to the fact that I am not confident or do not know where they are.) 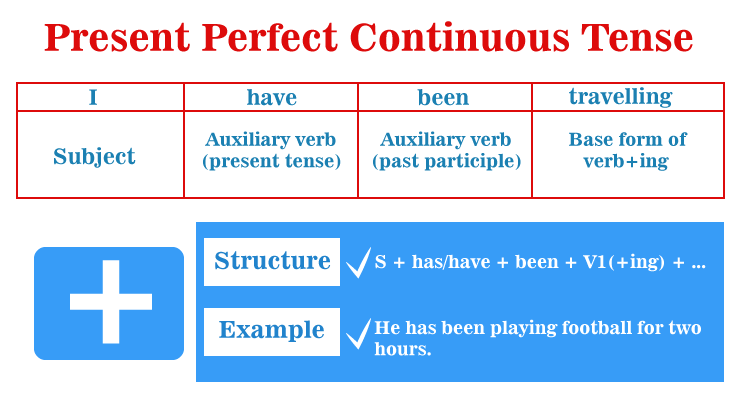
Here is a small tip; As obviously, not all verbs are appropriate for continuous activity. To be, to arrive, and to own are a few instances of such verbs. I have been owning my car since 2005. I have owned my car since 2005. (Present perfect tense) Joy has been being late for an exam recently. Joy has been late for an exam recently. (Present perfect tense) Overview of Present Perfect Continuous TenseThe present perfect continuous (also known as the present perfect progressive) is a verb tense that indicates that activity commenced in the past and has progressed until the present. The present perfect continuous frequently stress time period, or the length of time that an action or event has been ongoing. The present perfect continuous (or present perfect progressive) composition incorporates some of the perfect progressive components into the present tense. It is made up of the present tense of have (have or has), the past participle of be (been), the primary verb's present participle, and the ending -ing. This structure can be used for ongoing action in the past that is still ongoing or has recently concluded: I have been doing/studying on this thesis all night. Why are his eye sockets dark? He's been sobbing. It is often used to express how long or since whenever something has been the case. She has been with us since 1997. How long have you been sitting here? They've been talking about it for 3 weeks. The acts in these lines are still ongoing, but the former portion of them is being considered; therefore, the perfect aspect is utilized. (A sentence with no perfect aspect, such as I've been sitting here for three hours, indicates that the action will be performed for that amount of time.) When stative verbs are not employed in the progressive, or when the situation is regarded everlasting, the present perfect (non-progressive) should be used instead; for instance, see Present perfect above. How do we construct the Present Perfect Continuous tense?The Present Perfect Continuous tense has the below mentioned structure:
We interchange the subject and first/primary auxiliary verb in question phrases or sentences. 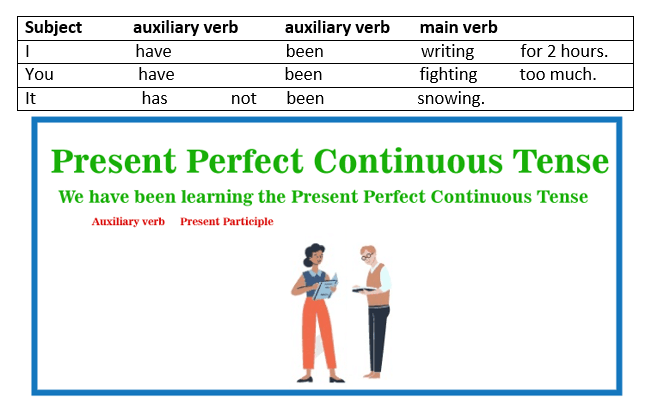
Present Perfect Continuous ContractionWhen we talk in the Present Perfect Continuous tense, we frequently contract the subject and the first auxiliary verb. This is something we do in casual writing as well. I've been studying Jenny has recently been assisting us. In negative sentences, we can combine the first auxiliary verb and the word/term "not." I haven't been playing soccer. It hasn't been raining. Uses of Present Perfect Continuous TenseThis tense is known as the Present Perfect Continuous tense. There is usually a link with the present or now. The Present Perfect Continuous is used to discuss: past action/event that is presently ongoing previous activity that was recently halted USE 1 This Tense is used to show the Duration from the Past till nowThe present perfect continuous is used to demonstrate that the activity that commenced in the past and has remained until today. All of the durations that can be utilized with the present perfect continuous are 5 minutes, 2 weeks, and since Wednesday. Let us have a look at few examples: They have been conversing for the last hour. She has been with the organisation for four years. What have you been readingfor the last 20 minutes? Raju has been instructing at the college since August. They have been standing for over 3 hours. Why has Sheela not been taking her classes for the last two days? Here are a few more examples for a better understanding; I've been writing for two hours now. (I'm still writing right now.) We've been researching since 9:00 am (We're still researching now.) How long have you been learning Mandarin? (You're still learning.) They have not been singing. (And we are not singing now.) Use 2: The Present Perfect Continuous tense is used to express an activity that began in the past and stopped currently. Now, there is generally a result.I'm exhausted (now)because I've been exercising. Why is the grass moist (now)? Has it been snowing? You don't get it [now] because you haven't been paying attention. In this Tense there is the involvement of terms: Recently, Lately One can even put the present perfect continuous to use without a time limit, such as 2 weeks. Without the length, the tense has a broader sense of recently. To highlight this sense, we frequently use the phrases recently or recently. See the examples below Recently, I have been feeling genuinely exhausted. She's been listening to far too much news recently. Have you been working out lately? Sarah has been feeling a little distressed. Lisa has not been concentrating on her Spanish. What have you been doing? Present Perfect Continuous Tense, For and SinceWith perfect tenses, we frequently use for and since: We used to refer to a specific time period: three hours, two months, and ten years We use since to refer to a point in the past: Tuesday, January 1st, 9 am. Consider the following examples of for and since statements in the Present Perfect Continuous tense: I have been dancing for 2 hours. I've been watching television since 8 pm Jessica hasn't been feeling well for one week. Suzanne hasn't been attending classes since January. He has been leanirng guitar for a long time. She has been living in Dubai since she graduated from high school. 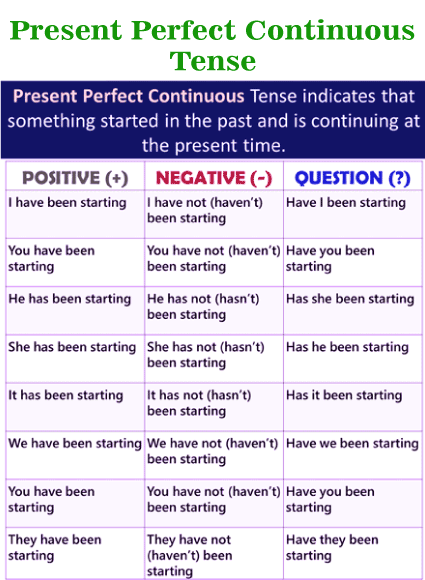
The term for can be used in all tenses. Since it is only used with perfect tenses. Apart from this, there are a few essential points to remember that are required in proper usage of Present Perfect Continuous Tense; Make a note that the present perfect continuous means "lately" or "recently." When you're using the present perfect continuous in an inquiry like "Have you been feeling okay?" it can imply that the person appears unwell or unhealthy. A question like "Have you been drinking alcohol?" may imply that you smell alcohol on the individual. In a question, using this tense implies that you can see, smell, listen or feel the outcome of the activity. It is possible to offend someone if you use this tense wrong. It's critical to note that non-continuous verbs can't be employed in any continuous tenses. Furthermore, some non-continuous interpretations of mixed verbs are not permitted to be employed in continuous tenses. You should use present perfect rather than present perfect continuous with these verbs. Here are the examples for better understanding; Sam has been having his vehicle for one year. This is incorrect. Sam has had his vehicle for the past one year. This is Correct 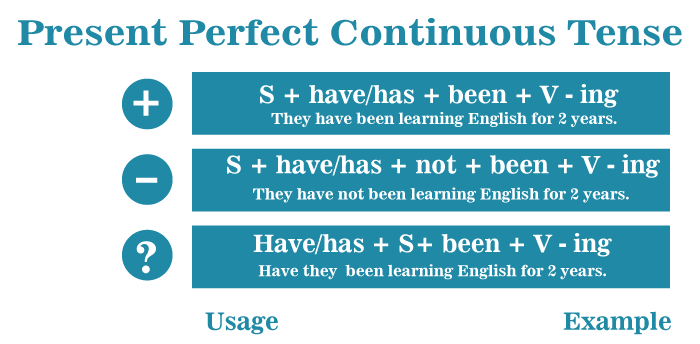
Position or Placement of Adverb in Present Perfect Continuous TenseThe instances below illustrate how to use grammar adverbs like always, only, never, ever, still, just, and so on. Here are a few examples for better understanding; They have only been sitting for 30 minutes Have you only been standing here for 30 minutes? Active or Passive Voice Here are a few examples; Recently, Thomas has been doing the tasks. Active Recently, the project has been being completed by Archana - Passive Voice NOTE: The passive form of present perfect continuous is less usually employed.There are certain verbs that are not used in continuous form. In a place where Verbs that are not used in continuous form, it's better to use the simple present perfect instead of the continuous form for verbs that are not commonly employed in the continuous form (verbs such as know, hate, hear, understand, want). We have wanted to visit Russia for years. He has known Richard since she was a kid. I've hated that tune since the first time I heard it. I've heard a bunch about you recently. They have understood all of it.
Next TopicSimple Present Tense Examples
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









