What Are Tenses?Explaining tenses, tense is a verb-based means of indicating the timing, and occasionally the continuance or completion, of an action or condition in connection to the period of speaking. 
ORIGINAL LANGUAGE Latin tempus "time." Tenses are verb types that convey the timing, continuation, or accomplishment of an action or condition in relation to the time at which comment about it is made. There are three major tenses: present, past, and future. 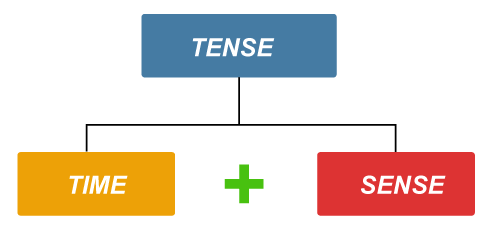
The present tense refers to something which is happening or occurring right now. The present tense is sometimes known as the simple present or the present simple. The past tense refers to that which occurred or existed in the past. The past tense is also known as the simple past or past simple. The future tense relates to anything that has not yet happened already. The terms will and shall be used in the future tense. 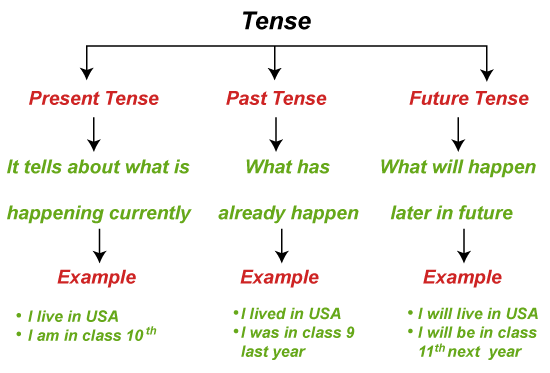
In English, the idea of tense refers to how we refer to time - past, present, and future. Several languages employ tense to express time. Many languages have no idea of tense at all, yet they can nevertheless communicate about time, although in various ways. So, in English, we speak about time using the present tense. But, and this is a huge but: we may speak about time without the use of tense (for example, going to is a specific construct to communicate about the future, it is not a tense), and one tense does not necessarily talk about one time (For instance, one could use present or past tense to speak about just the future ) Tense is a grammatical term in English. It depicts the verb's form in comprehending the circumstance alluded to in time. In the phrase, Yash walked for 2 hours and then went to sleep, the past tense verb type, walk(+ed), indicates the duration of the walk in the past. Tense is used to provide a temporal element to a statement. Tenses, like time, are broken down into three parts: I swam in the past tense. I swim in the present tense. I will swim in the future. 
Before we begin with the more sophisticated subdivisions, there are three points to remember: Just indicative verb types are tensed. Every sentence has progressive and non-progressive versions; for example, I study here/I am studying here are both Present tense. Whenever a verb form is complicated and incorporates more than one auxiliary, the first auxiliary, not the primary verb, is indicated for tense. We can't talk about tenses without mentioning two important aspects of many English tenses: time and aspect. To put it simply... 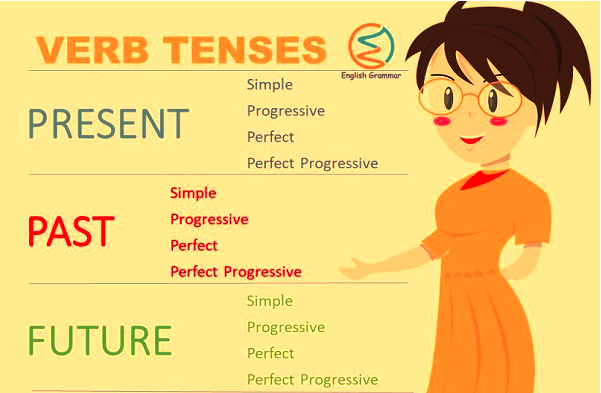
Time demonstrates: before now - in the past present - right now, or any period that encompasses right now future - after right now Aspect can indeed be: progressive - unfinished action perfective - a finished activity or state. Several people claim that simple tenses have "simple aspect," but in reality, simple tenses are merely unlabelled for aspect.) The progressive aspect gives rise to progressive or "continuous" tenses such as past continuous, present continuous, and future continuous. Perfective tenses are produced by the perfective aspect: past perfect, present perfect, and future perfect. Furthermore, the two features can be merged to form perfect continuous tenses: past perfect continuous, present perfect continuous, and future perfect continuous. The preceding is a synopsis of the English notion of tense. Other characteristics, such as voice and emotion, enable us to construct more than the 12 tenses. For the most important aspects There are four elements to each tense: simple, continuous or progressive, perfect and perfect continuous or perfect progressive. 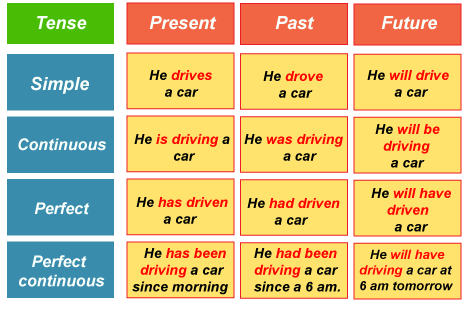
The current aspect informs us that the activity occurs in the present and conveys broad facts and habits. The continuous aspect denotes an uncompleted activity or state of being at the time of reference. It is constructed by combining the main verb's present participle with the auxiliary verb's applicable tense to be. A finished activity in the present, past, or future is referred to as the perfect aspect. It is constructed by combining the applicable tense of the auxiliary verb have and the primary verb's past participle. 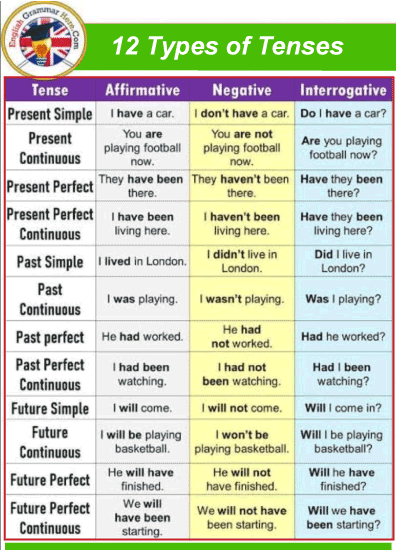
The perfect continuous component includes the continuous and perfect characteristics. It refers to an activity that has lasted up to the present, a point in the past, or a point in the future. The twelve tense and aspect combinations are made feasible by the three verb tenses and four verb aspects.
Next TopicRules Of Tenses
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









