Top 10 Oldest Languages in IndiaPeople from all over the world live in the large nation of India. As a result, Hindi and English are among the many languages that are widely spoken throughout the nation. Indian communities speak a much greater number of languages than those in other areas of the world, nonetheless. India, one of the largest countries in the world with a population of over a billion, is home to many different language groups. In India, numerous different languages are all combined and counted. The languages of India are highly diverse from one. Each Indian language has its unique traits, cultures, and history. Some of them are even regarded as classical languages, which denotes that persons who speak them are regarded as classics because they have a distinct and autonomous body of written literature that predates those of other languages. Some individuals believe that Hindi is India's oldest language. Some experts assert that there is a language that predates Hindi. So let's investigate this and determine what language it is. This post will discuss the eight oldest languages in India and other fascinating information. 
Before the founding of civilizations, the establishment of kingdoms, and the development of social norms, humans used hand signals and crude oral noises to communicate. About 10,000 years ago, languages started to develop, which shaped the course of human history. The development of the human race and our current state are both the results of the use of languages. Although there is fierce debate about the world's first language's genesis, some ancient documents and cave paintings reveal some of the oldest tongues. India is one of the world's nations with a diverse language population. Due to the diversity of cultures and ethnic groups present in India, each region's residents speak their unique languages, which have been assimilated by the vast majority of people who have interacted with them over time. The following list includes some of India's earliest languages. The Indo-Aryan and Dravidian languages are the most widespread of the various language families into which the languages of India are divided. Other language families, like Austroasiatic and Sino-Tibetan, are spoken by smaller communities. These languages span a variety of ages, some of which are quite recent. With the introduction of the Brhm script, linguistic records were first kept in the third century BCE. 19 500 languages are used in India. Twenty-two languages have been designated as official. Some of India's most ancient languages are listed here. 1. Sanskrit (7000 years)
Several Indian languages use the ancient Indian language Sanskrit as their common language. Also, Sri Lanka, Nepal, and India have it as their official language. With records reaching back to 1500 BCE, Sanskrit is one of the oldest languages in the world. Until around 500 CE, when the Devanagari script was created, Sanskrit was written in its earliest form known to man in the Brahmi script. The earliest Sanskrit text manuscript dates to around 1000 CE and is thought to be from the Gupta era (4th-6th century C.E.). 2. Tamil (5000 years)
Tamil is a language with native speakers in Malaysia, Sri Lanka, and India. It is the national tongue of India, Tamil Nadu, and Sri Lanka. Tamil is a classical language. Hence it has a vast amount of literature. Tamil literature and writing are both diverse. Tamil, which continues to be used to publish hundreds of daily newspapers, is the oldest language still in use today. Many people think that Tamil first appeared around 2500 BC. The majority of words from classical Tamil are still used in contemporary Tamil. The modern Tamil language does, however, frequently use several loanwords from Sanskrit and Prakrit. This has led to most Tamil native speakers today being able to understand classical Tamil to varied degrees, along with the value put on understanding ancient works like Tirukkural. 3. Kannada (2000 years)
The Dravidian language family includes Kannada, which is a member of the southern branch. Kannada was first employed in writing on the Badami Rock Edicts, which Ashoka is thought to have penned about 1000 B.C. This is the earliest known use of Kannada. It is one of the classical languages of ancient India, along with Sanskrit and Pali, which were used as court languages by kings in antiquity and later became popular among poets and artists. It eventually became a literary language that could stand alone and was crucial to Hinduism. It has been spoken in Kannada for 2500 years. Many of its terms seem to have been transformed by switching the letter "pa" for the letter "ha" after being borrowed from Tamil or Sanskrit. 4. Telugu (1500 - 2000 years)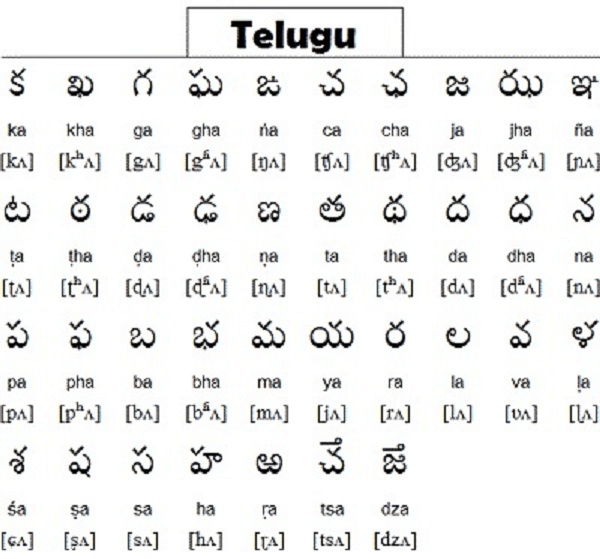
India's state of Andhra Pradesh has Telugu as its official language. It is also the official language of Telangana. The progenitor that is most frequently referenced in the lengthy history is Sanskrit. Three writing systems, including the Kannada, Tamil, and Devanagari scripts, have been used to write Telugu in contemporary times. Telugu ranked third among Indian languages in terms of the number of native speakers in 2016. Telugu had a significant influence on Sanskrit, and as a result, certain of its expressions over time came to be thought of as Telugu words. While some words from Tamil and Kannada also made it into Telugu, their adoption could have been more successful. 5. Malayalam (2000 years)
In the Indian state of Kerala, Malayalam is a language used. It is the mother tongue of many Malayali people. A sizable portion speaks of the population in other regions of India and several locations in the Middle East. In the Vazhappally inscription, written around 830 AD, Malayalam is first found in writing. The Malayalam script originated from the vattezhuthu (round writing), a Brahmi script progenitor used in the early thirteenth century. The Malayalam language as it is today is commonly acknowledged to have its roots in Ezhuthachan. In the organized growth of the current Malayalam language, the Tigalari script was extremely important. 6. Marathi (1500 - 2000 years)
The Marathi language is a member of the southern branch of the Indo-Aryan language family. Most people who live in that part of western India speak it as it has been the state of Maharashtra's official language since 1966. Maharashtra, Marhatti, Mahratti, etc., were earlier dialects of Marathi. One of India's 22 official languages, Marathi, joins Hindi, Bengali, Telugu, Tamil, and others. According to the state government of Maharashtra, Marathi is one of the most important languages. 7. Odia (2000 years)
India's official state language in India. It is a member of the Eastern, or Dravidian, family of languages and is of the Austroasiatic branch. It is used in Odisha, an Indian state that borders Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra. The writing system was developed by King Bhoja in the fourteenth century A.D. and has since been in use. Its alphabet has 36 letters, comprising 17 vowels and 21 consonants. However, several consonants are blended to create various syllables. 8. Bengali (1500 years)
One of India's six official languages is Bengali, sometimes known as Bangla, which is also the national language of Bangladesh. The closest relatives of Bengali are Assamese and Sinhalese. Bengali has a long literary history. However, works that date back to before the 12th century have yet to survive. Hindi and Marathi have characteristics in common with Bengali. The Bengal Sultanate was established as a result of Muslim invasions that took place in the fourteenth century. 9. Gujarati (1000 years)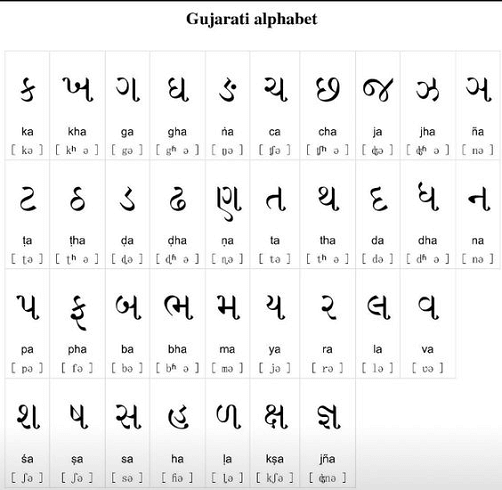
The Gujarati people's native tongue is Gujarat, the oldest Indian Arian. The Indo-European linguistic family includes it. It is also spoken in Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Nagar Haveli, Dadra, Daman, and Gujarat. 10. Hindi (1000 years)
India's national language, Hindi, is used in several states, including Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Bihar, etc. This language is quite popular because 422 million people in India speak it widely. The North Indian languages, like Punjabi, Gujarati, Marathi, etc., are based on this ancient language in India. The ConclusionI hope you've learned some of the oldest Indian languages. All of this general knowledge information is available on our website.
Next TopicTop 10 Private Companies in India
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









