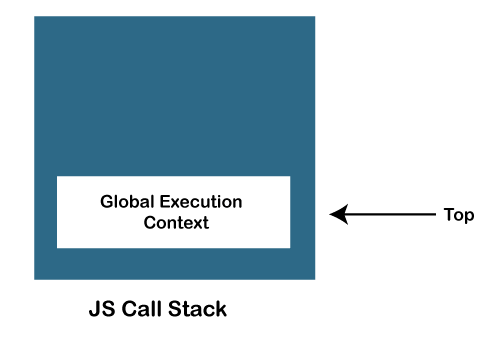
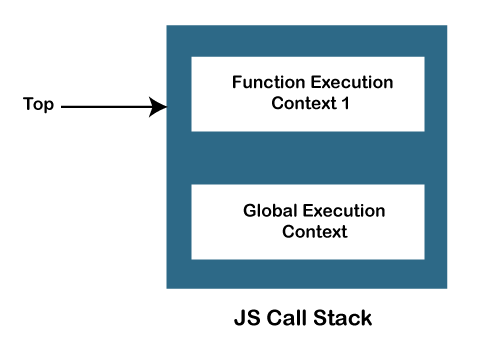
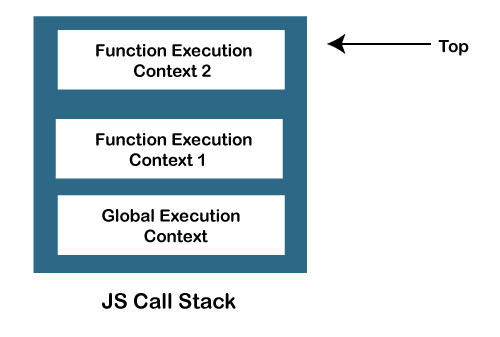
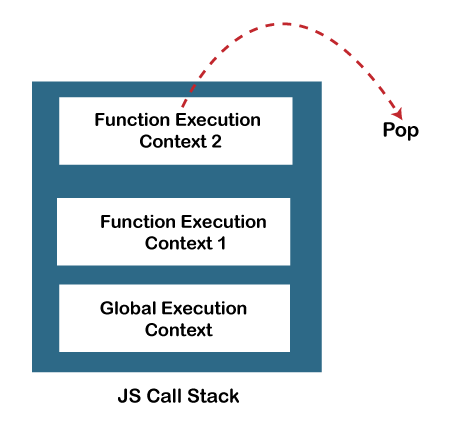
JavaScript Call StackIn order to manage the execution contexts, the JavaScript engine uses a call stack. The working of the JS call stack is performed internally, but we will understand it's working here. In this section, we will discuss the JavaScript call stack, it's working. We will also discuss an example that will make us to better understand the concept. What is JS Call StackThe JavaScript execution contexts (Global execution context and function execution context) are executed via the JavaScript engine. In order to manage these execution contexts, the JS engine uses the call stack. So, the JS call stack is a data structure that keeps track information of the functions being called and executed. Thus, if the user invokes a function for execution, the specified function gets pushed/added in the call stack, and when the user returns from a function, it means the function is popped out from the call stack. Thus, call stack is a normal stack data structure that follows the stack order principal, i.e., LIFO (Last In First Out). Role of JavaScript Call StackThere are the following points where the call stack is being used by the JS engine:
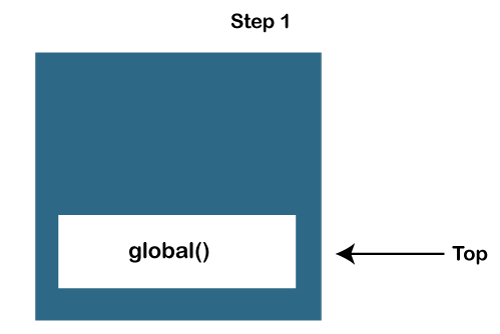
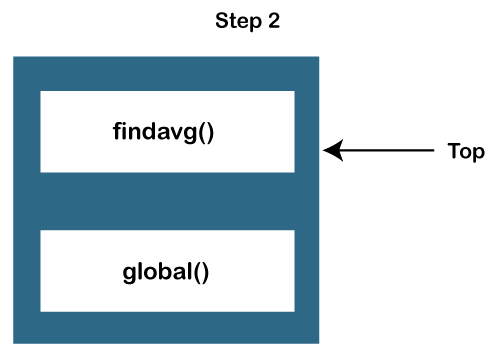
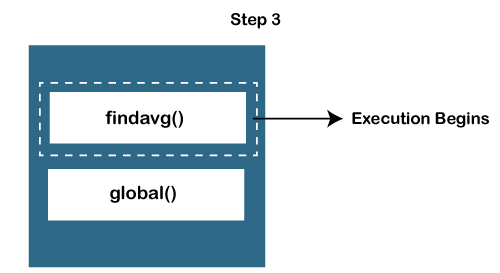
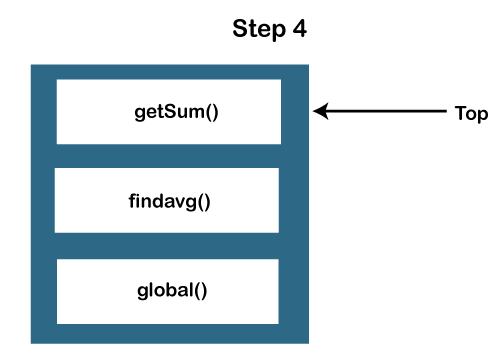
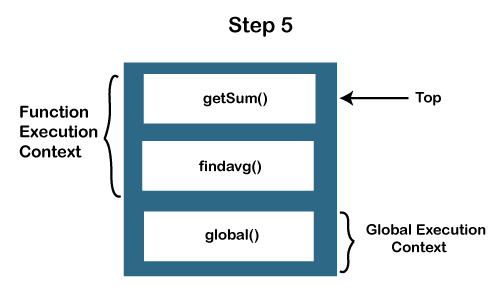
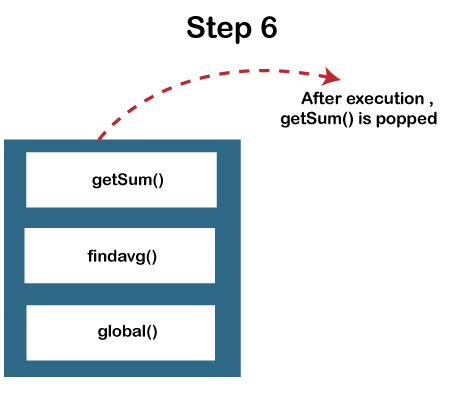
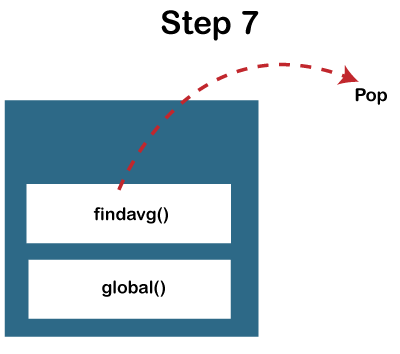
JavaScript Call Stack ExampleLet's see an example to understand the use of the JavaScript Call Stack function: How the code worksIn the above code, we have created two functions, getSum () and findavg (), and the execution of the script begins in the following described steps:
When does call stack overflow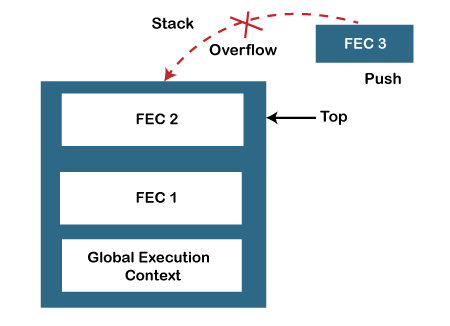
The overflow condition occurs when there is no more space left in the call stack, or the condition may occur when there is a recursive function that has no exit point. The JavaScript call stack is defined with a fixed size that depends on the implementation of the host environment (which is either the Node.js or web browser). So, when the limit of the defined size of the stack is exceeded, then stack overflow occurs. Thus, it throws a stack overflow error. Example: The below example describes the stack overflow condition: So, in the above code, we can see that we have invoked the test () function recursively, which means this function will execute until the host environment maximum call size exceeded, and thus the stack throws the stack overflow error. Point to be noted: JavaScript is a synchronous and single-threaded programming language. It means that when any script gets executed, then the JS engine executes the code line by line, starting from top to bottom. So, the JavaScript engine has only one call stack, and it can do only one thing at a time.
Next TopicFibonacci series in JavaScript
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share