10 Functions of Brain
The brain is an extremely potent organ in humans. All the body's organs are under its control. Additionally, it regulates the person's emotions and thinking. The human brain is responsible for a variety of processes, including controlling body temperature, regulating behaviour, breathing, blood flow, sight, hearing, and speech. It is the most intricate component of the body and weighs roughly 1.5 kg. The skull protects it. As a result, distinct regions of the brain regulate various bodily functions. Several crucial areas of the brain include:
- Forebrain
- Midbrain
- Hindbrain
Functions of Brain
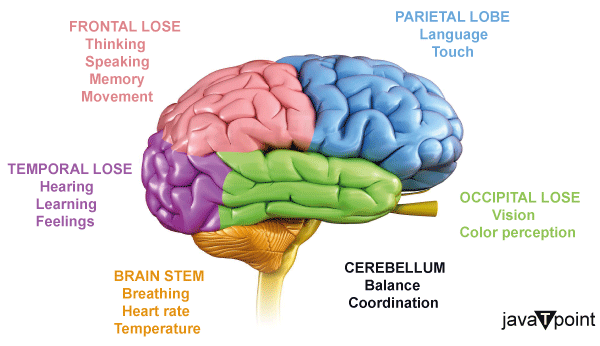
Your five senses-Sight, Smell, Hearing, Touch, and Taste-provide information to the brain. Along with autonomic (involuntary) inputs from your organs, your brain also receives signals from the rest of your body, such as touch, vibration, pain, and temperature. It analyses this information so that you can comprehend and provide meaning to the events taking place around you. The human brain is an amazing and intricate organ. The brain is composed of numerous components, each of which performs a unique and significant role. It regulates how we stand, walk, talk, and eat. It synchronises and controls our breathing, heart rhythm, and blood flow. It is in charge of our capacity for speech, information processing and memory, decision-making, and emotional response.
- Cognition and Thinking: Thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, making decisions, and planning are just a few of the cognitive processes that the brain oversees. To make sense of the world and create appropriate reactions, it processes data from the environment and previous experiences.
- Memory Formation and Recall: Memory development, storage, and retrieval all depend on the brain. It involves a brain structure called the hippocampus, which is essential for transforming short-term memories into long-term memories.
- Motor Control: The brain communicates with the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system to regulate both voluntary and involuntary movements of the body. The motor cortex plays a crucial role in organising and carrying out movements.
- Sensory Processing: The five senses of sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell are received, processed, and translated by the brain. Each sensory modality is processed by a different area of the brain.
- Emotion Regulation: In order to control emotions, the brain is crucial. For instance, the prefrontal cortex aids in controlling emotional reactions, but the amygdala is involved in processing emotions like fear and hostility.
- Language Processing: Brain regions involved in language processing include Wernicke's area for comprehension and Broca's area for voice production. Understanding, expression, and communication in language are made possible through the cooperation of these regions.
- Homeostasis and Autonomic Functions: Through the autonomic nervous system, the brain regulates vital physical processes like heart rate, respiration, digestion, and body temperature. The brainstem and hypothalamus are important components of the homeostatic system.
- Attention and Focus: The brain enables us to focus on tasks, filter out distractions, and switch between different tasks. The anterior cingulate cortex and the prefrontal cortex play roles in attention control.
- Social and Interpersonal Skills: Social cognition, empathy, and understanding social cues are important functions of the brain. Areas like the mirror neuron system contribute to our ability to understand and interact with others.
- Consciousness and Self-awareness: The brain gives rise to consciousness, allowing us to be aware of our thoughts, feelings, and experiences. The exact mechanisms behind consciousness are still debated, but it's closely linked to the overall functioning of the brain.
It's important to note that these functions are interconnected, and the brain doesn't work in isolation. Different regions of the brain often collaborate to perform complex tasks and behaviours. Additionally, our understanding of the brain is continuously evolving, and researchers continue to explore its intricacies to gain deeper insights into its functions.
Interesting Facts about the Human Brain
- The average adult brain weighs 1336 grammes.
- 73% of the human brain is composed of water. If the body is even slightly dehydrated (dehydrated or dehydrated), attention, memory, and other cognitive abilities are compromised.
- There are 86 billion brain cells in the human brain.
- In the first year of life, the human brain triples in size. Up to the age of roughly 18, it keeps growing.
- The brain undergoes one million chemical processes every second.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









