FungiAncient historyIn ancient history, the earth was graced with different organisms like bacteria and archaea (floating, thriving, and swimming) in the ancient ocean that covered almost all the earth. With time, this organism got larger and more complex. Once a time, dinosaurs ruled on the earth, followed by mammals. Nowadays, humans are the dominant species on earth who are ruling all over, but in history, we had hardly heard about the: age of the fungus! Around 250 million years ago, 90% of life on the earth vanished (animals and plants were decimated). Massive fields of dead wood and dead animals started degrading, and an organism thrived on them. Yes, an organism named fungi that ate dead plants and animals resulted in the domination of the landscape. From there "golden age of fungi" had begun. This organism is singularly called "fungus" and plural called "fungi". The study of fungi is called mycology. 
FungiFungi are multicellular eukaryotic organism that includes yeast, mushroom, and molds like microorganisms. These organisms are classified as heterotrophs (cannot make their food), and in the fungi kingdom, these organisms contain a cell wall and are omnipresent. Still, slime molds and oomycetes are exceptions that don't belong to the fungi kingdom but are fungi. These fungus organism are evenly distributed all over the earth and have great medical and environmental use. Various fungi-like organisms are included in the chromista kingdom. Fungi are distinguished in the plant kingdom and by animals due to their unique and physiological features (cell wall and cell membrane). Fungi can also be defined by their principal growth mode and nutrient intake. 
Fungi are found in humans and other animals as skin infections or fungal diseases. Common examples of fungi are found in life - if we keep bread outside for some days, black or green spots appear on them. Mushroom and yeast are also common examples used to produce beer and bread. One common characteristic of these examples is that they survive and grow in moist and warm conditions. 
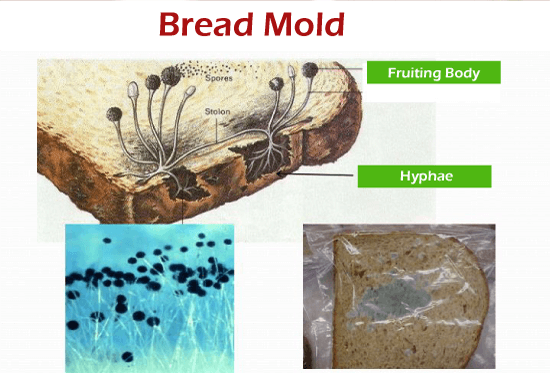
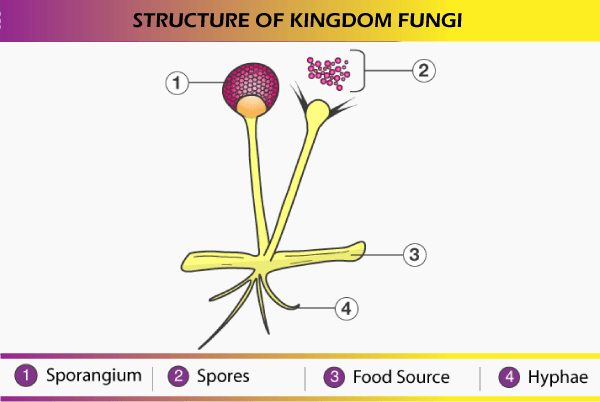
Formation of fungi
Fungi CharacteristicsVarious characteristics of fungi are as follows:-
Fungi classificationFungi are studied under mycology as they can only be observed under the microscope. Fungi play an important role in shaping aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems as they can engage in organic matter degradation, formation of symbiotic relationships, and phosphate fixation. Based on research, fungi have been classified on the bases:- 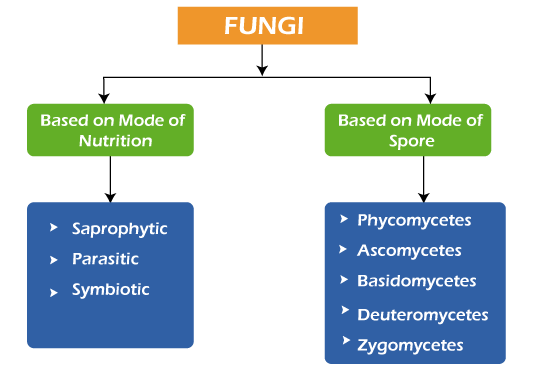
This mode of division is further divided into many parts. a) Based on mode of nutritionThis model has various types:- 1. Saprophytic Examples of saprophytic fungi are- Penicillium, Rhizopus, and Aspergillus. Saprophytes cannot make their food. They feed on dead organic substances for nutrition. These are of two types:
2. Parasitic Examples of parasitic are- Taphrina and Puccinia. They survive on other living organisms(host) for their nutrition. Firstly they attack the living or dead organisms and harm them by causing disease. The host and parasite relationship is called parasitism. Based on the location, these are of two types:-
3. Symbiotic Examples of symbiotics are lichens and mycorrhiza. They get nutrition and grow on other living organisms and mutually beneficial for both of them. Lichens are a great example as they show an association between algae and fungi. Algae provide food to the fungi, and in reverse, fungi provide shelter to them. 
b) Based on the mode of spore formationFungi are differentiated on these points:- 1. Phycomycetes In these types of fungi, mycelium is coenocytic and separate. Found in moist and marine places (decaying wood and aquatic habitats). For example, Mucor, Rhizopus, and Albugo. 2. Ascomycetes Ascomycetes are widely known as sac fungi and are decomposers, coprophilous, parasitic, and saprophytic. Most of the Ascomycetes are multicellular, and rare are unicellular. Examples are Aspergillus, Claviceps, and Neurospora. Sexual reproduction - Ascospores Asexual reproduction - conidiospores Mycelium - branch and separate form in Ascomycetes. 3. Basidiomycetes Sex organs are absent, and mycelium is in separate and branched form. A common example of Basidiomycetes are mushrooms that grow in soil, tree trumps, and event logs. Other examples are:- Aspergillus, Neurospora, Agaricus, and Claviceps. Sexual reproduction happens due to basidiospores. Asexual reproduction happens with conidia, budding, or fragmentation. 4. Deuteromycetes This type of fungi is imperfect fungi as they do not follow a regular reproduction cycle (only asexual reproduction). Asexual reproduction happens by conidia (asexual spores) We can see the vegetative phase of fungi in which mycelium is in a branched and separate form. Various examples are Alternaria, Colletotrichum, and Trichoderma. 5. Zygomycetes The fusion of two different cells forms zygomycetes. Fusion can be sexual or asexual, in which hyphae are without septa. Asexual fusion is called sporangiospores. Sexual fusion is known as zygospores. Reproduction: Yeast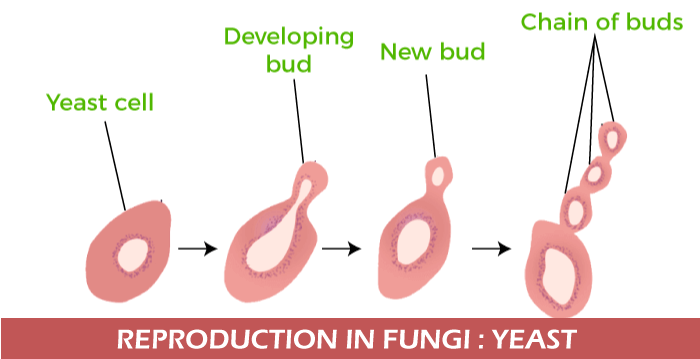
Yeast cells are small that multiply themselves by budding process ( a daughter cell off from the parent cell). Yeast cells are the same size as red blood cells, but they are lemon-shaped single cells. A scar is left on the parent bud when a child bud breaks off. Bread and cheese formation is impossible without yeast (Saccharomyces). Yeast is used for the medical research of diseases like cancer and genetic research. Yeast in humans can cause infection due to a low immune system (candida). Mushrooms Every person knows about mushrooms as fungi as they are eatable or non- eatable. Mushroom has a large cap on the stalk that produces the spores released by mushrooms to produce and colonize new environments. Some mushrooms are poisonous (wild mushrooms mainly). They are found springing up on dead wood after cool, wet weather. 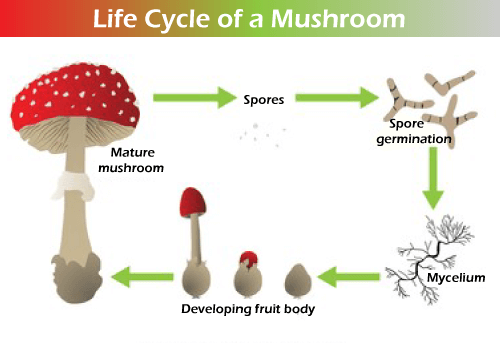
Reproduction in fungi can be vegetative, sexual, or asexual.
Uses of fungiFungi play an important role in the biosphere and have great economic importance. It has lots of benefits and harmful effects too. There are several uses of fungi such as:-
Examples of fungiExamples are - Yeast, moulds, mushrooms, and truffles.
Next TopicTypes of Biodiversity
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share