Brain Tumour Causes
A brain tumour is a proliferation of cells in or around the brain. Brain tumours can develop in brain tissue. Brain tumours can also occur near brain tissue. Nerves, the pituitary gland, the pineal gland, and the membranes that cover the surface of the brain are all close by.
Brain tumours can arise in any part of the brain. These are known as primary brain tumours. Cancer can spread from other sections of the body to the brain. These are secondary brain tumours, often known as metastatic brain tumours.
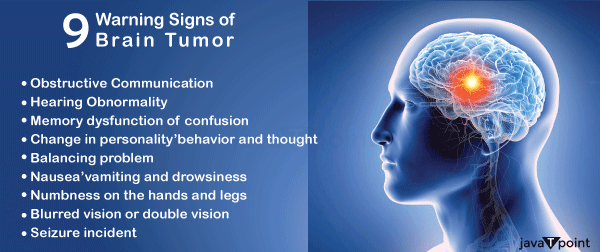
Primary brain tumours come in many diverse types of form, all of them are not dangerous, some of them are harmless also. Noncancerous or benign brain tumours are the most common type. Over time, noncancerous brain tumours can grow and encroach on brain tissue. Other types of brain tumours are brain cancers, often known as malignant brain tumours. Brain tumours can spread very quickly. Cancer cells could penetrate, and damage brain cell and other tissue present in the brain.
Brain tumours range in size from extremely small to quite enormous. Some brain tumours are discovered while they are quite little because they create symptoms that are immediately noticeable. Other brain tumours grow to be quite large before they are discovered. Some brain regions are less active than others part of the body. If a brain tumour begins in a less active section of the brain, it may not show symptoms right away. Before the tumour is diagnosed, the size of the brain tumour can grow huge. The type of brain tumour, its size and location, describe the treatment options. Surgery and radiation therapy are two popular treatments.
Causes of Brain Tumour
- Age- Brain tumours are most common in youngsters and the elderly, but anyone of any age might acquire this.
- Sex- Men are often more prone than women to have a brain tumour. Women are more likely than men to develop some types of brain tumours, such as meningioma.
- Home and work exposures- Exposure to solvents, pesticides, oil products, rubber, or vinyl chloride may increase the risk of developing a brain tumour.
- Family history- Hereditary genetic factors or disorders such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome, neurofibromatosis, nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, Turcot syndrome, and von Hippel-Lindau disease may cause approximately 5% of brain tumours. Scientists have also discovered "clusters" of brain tumours in some families that have no connection to these established genetic disorders. Many Studies are being conducted and many other are conducting to determine the root cause of these clusters.
- Exposure to infections, viruses, and allergens. Infection with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) increases the risk of developing lymphoma of the central nervous system (CNS). EBV is also known as the mononucleosis virus, or simply "mono." In another study, substantial amounts of a common virus known as cytomegalovirus (CMV) were discovered in brain tumour tissue. The significance of this discovery is being investigated. Several additional viruses have been identified in animal studies to cause brain tumours. More research is needed to determine whether infection, other viruses, or allergies raise the chance of a brain tumour in humans. It is worth noting that people with a history of allergies or skin disorders have a lower risk of developing glioma.
- Electromagnetic fields. Most studies on the effects of electromagnetic fields, such as power lines or cell phone use, show no link to an increased risk of getting a brain tumour in adults. The World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends restricting mobile phone use and encourages adults and children to use a hands-free headset due to conflicting findings regarding risk in youngsters.
- Race and White people in the United States are more likely than Black people to get gliomas, although they are less likely to develop meningioma. Furthermore, Northern Europeans are more than twice as likely as Japanese people to develop a brain tumour.
- Ionizing radiation.Previous ionising radiation treatment to the brain or skull, including x-rays, has been linked to an increased chance of developing a brain tumour.
- Head injury and seizures. Serious head trauma has long been studied in respect to its link to brain tumours. Some studies have found a relationship between head trauma and meningioma but not between head trauma and glioma. Seizures have also been related to brain tumours; however, because seizures can be caused by a brain tumour, it is unclear if seizures increase the risk of brain tumours, seizures occur because of the tumour, or anti-seizure medicine increases the risk.
- N-nitroso compounds- According to certain dietary and vitamin supplementation study, dietary N-nitroso compounds may increase the occurrence of both paediatric and adult brain tumours. Dietary N-nitroso compounds are formed in the body from nitrites or nitrates found in some cured meats, cigarette smoke, and cosmetics. However, further research is required before a conclusive correlation can be established.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









