Bacterial DiseasesWhat are Germs?Microscopic organisms, which are also called germs, are omnipresent. Germs are referred to as microbes in scientific language. That is, germs are present everywhere in our environment. There is no place on earth where they are not present. They are found everywhere, i.e., on Land, air, sea, ocean, thermal springs, etc. 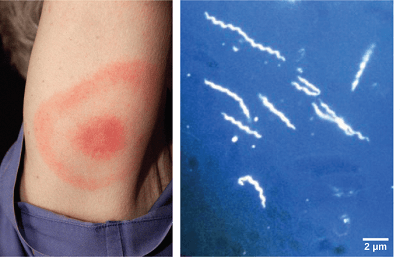
Your immune system defends you against infectious pathogens. Most germs are harmless. But all of them are not harmless, and they can be our biggest foe. Microbes get stronger because they are continuously evolving themselves against the immune system. Understanding how bacteria function might help you avoid illness. Agents of the DiseasesInfectious agents exist in a variety of sizes and forms. These include:
BacteriaBacteria are single-celled creatures that can only be seen under a microscope. It is impossible to see them through naked eyes. They are so tiny that even if thousands of bacteria pile up against each other, forming a group, they won't make it to the size of a pencil tip. The term bacterial is not always associated with diseases and infections. There are so many bacteria present in our environment that help us in our day-to-day lives. Lactobacillus acidophilus, for example, is a harmless bacterium that lives in your intestines and aids with digestion, the destruction of some disease-causing organisms, and the provision of nutrients. 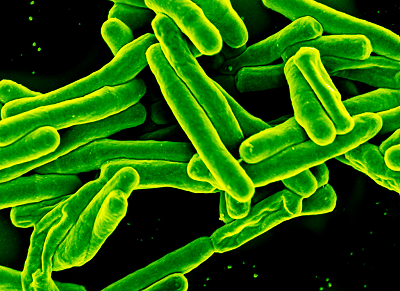
Toxins are strong compounds produced by many disease-causing bacteria that harm cells and make you sick. Other bacteria can infiltrate and destroy tissues directly. Some of the common bacterial diseases are:
VirusesViruses are cellular microbes. Viruses are far smaller than cells. In reality, viruses are just genetic material-containing capsules. Viruses infect cells in your body to multiply, stealing the machinery that allows cells to function. During this procedure, host cells are frequently killed. Viruses are responsible for several deadly diseases like:
But the worst part about viral diseases is that they are unaffected by antibiotics developed for bacteria. FungiFungi come in many different forms, and many of them are edible. Molds that generate the blue or green veins in certain cheeses are fungus, as are mushrooms. Yeast is another form of fungus and is also required in making bread. Another form of fungus can make you sick. Candida is an example of Ascomycota (fungus) that can cause infection. Candida can cause thrush, a mouth and throat infection in new-borns and individuals on medications, or weakened immune systems. Fungi can also cause skin problems like athlete's foot and ringworm. ProtozoansProtozoans are single-celled creatures seeking and gathering other microorganisms for food, much like microscopic animals. Many protozoans dwell in your intestine and are completely safe. Others produce illnesses like:
Protozoans frequently spend a portion of their lives outside of people or other hosts, i.e., food, soil, water, or insects. Some protozoans enter your body through the food or water you consume. HelminthsHelminths are considered one of the most powerful disease-causing organisms. They are very deadly parasites. They are present in the form of worms. Their mode of attack is by laying eggs inside the body. Once they have entered the body, they will produce eggs and start inhabiting body parts like the intestine, liver, skin, lungs, heart, etc. After inhabiting, they will start feeding on the body's nutrition. Some of the most common Helminths are tapeworm and roundworm. What Exactly Are Bacterial Diseases?All the diseases which are due to bacteria are called bacterial diseases. Although bacteria are very small and can only be seen under a microscope, their influence is highly dangerous. This is because of their prevalence. They are always present everywhere. Thousands of bacteria are present on the skin. Our body is continuously fighting against these bacteria. Although most bacteria are not very harmful, but there are still many deadly bacteria that can cause several infections and allergies. On the other hand, bacteria are also essential for certain processes and thus help us in our lives. These bacteria are known as "good bacteria" or "healthy bacteria". 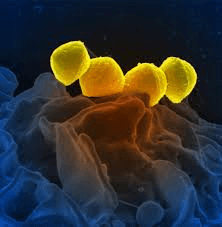
Pathogenic bacteria are harmful bacteria that cause bacterial infections and sickness. Bacterial illnesses develop when dangerous bacteria enter the body and reproduce, drive out beneficial bacteria, or thrive in normally sterile tissues. Toxins produced by harmful bacteria can cause harm to the body. Bacterial illnesses are infectious and can cause various serious or fatal consequences, including blood poisoning (bacteremia), renal failure, and toxic shock syndrome. What Are the Signs of Bacterial Diseases?The signs and symptoms vary based on the type of bacteria and what infections it causes. They also vary from person to person based on the immune system, age, living conditions, health history, etc. There is also a possibility that different bacterial infections may cause the same symptoms. A fever is the hallmark sign of a bacterial illness, albeit not everyone who has a bacterial infection has a fever. 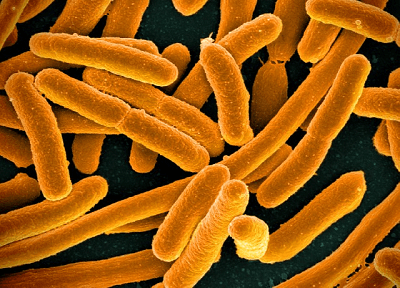
Some of the most common symptoms associated with bacterial infections include;
Children and babies show symptoms that are different from adults. These include ;
Apart from the general symptoms resulting from bacterial infections, there are specific symptoms also. These are called serious symptoms and suggest a potentially fatal condition. Many bacterial infections are deadly and can cause the death of an individual. If serious symptoms are visible, one should consult the physician as soon as possible and get emergency medical attention. Some of the serious symptoms include:
What Causes Bacterial Diseases?Bacterial diseases are brought on by pathogenic microorganisms (pathogenic bacteria). As already discussed, our body has many bacteria which are not harmful. Some of them are helpful, and they're required for optimum health. There is a specific reason for any bacterial infection or bacteria to occur. Infections or diseases mainly arise when any sterile part of the body like the bladder, bowels, vagina, or mouth gets inhabited by harmful bacteria. The other condition is when the harmless bacteria excessively increase in number such that they become harmful. 
Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the body in a variety of ways.
When the body first encounters bacteria, the body's immune system comes into play. They recognize the foreign material in the body and fight against it to remove its presence and stop its multiplication. But this can only happen if the body's immune system is strong enough to tackle it or if the bacteria infection has not spread much into the system. Even if the body is strong and a person is healthy enough, bacteria can still proliferate and reproduce. As the bad bacteria multiply, they can push out good bacteria and germs and create toxins that destroy the body's cells. Other Factors Responsible for Bacterial DiseasesBacterial diseases can affect anybody of any age or demographic. Bacterial illnesses do not affect everyone who has risk factors. However, a variety of variables enhance the likelihood of having bacterial diseases. Various factors responsible for bacterial diseases and infection are:
How To Avoid Bacterial Diseases?To avoid infections, lower your chances of contracting bacterial infections.
How Are Bacterial Diseases Treated?Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial diseases. Antibiotics function by either killing or preventing hazardous germs from growing and spreading. Different antibiotics are effective against different types of bacteria. Depending on the nature and severity of the bacterial condition and other circumstances, antibiotics may be administered orally, intravenously, or intramuscularly. Common examples of antibiotics are -
Apart from eating a healthy diet and proper medication, other treatment methods also include getting proper health care. Sometimes in serious conditions, intensive care is necessary. Even in the lack of symptoms, those who have had intimate contact with someone who has a dangerous bacterial disease, such as bacterial meningitis, may need to be treated and monitored for the disease. Sometimes an antibiotic that used to be effective in treating a bacterial condition no longer seems beneficial. This is known as antibiotic resistance. It complicates the treatment of bacterial diseases and can lead to significant consequences such as sepsis, coma, and death. What Are the Potential Consequences of Bacterial Diseases?Bacterial illnesses can cause significant, even life-threatening, consequences in certain people. As a result, if you have signs of a bacterial infection, you should see your doctor as soon as possible. After determining the underlying illness, following your doctor's treatment plan might help reduce any potential problems. Some of the impacts of bacterial diseases on the body are:
Next TopicInfections Caused by Bacteria
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










