Bacterial Artificial ChromosomeWhat are Vectors?A vector is a segment of DNA that serve to transport foreign genetic material into the host cell where it can replicate and exhibit genetic expression. There are various types of vectors to carry out the transformation, conjugation, and transduction-like processes. These vectors are plasmids, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Vectors are used for different purposes. They can be classified into two types' expression vectors and transcription vectors. Expression vectors are the vectors that are used to express the target gene while transcription vectors are the vectors that are used to transcribe the target gene. Shuttle vectors are those vectors that can express themselves in more than one host cell. There are several processes where vectors are used. Transformation is the insertion of vectors into bacteria and the insertion of vectors into virus is called transduction. A vector that contains larger gene sequences and can express them is called Artificial Chromosomes. Artificial chromosomes are of three types: Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs), and Human artificial chromosomes (YACs). Bacterial Artificial Chromosome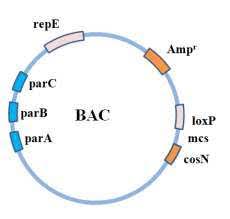
Bacterial Artificial Chromosome or BAC is circular DNA plasmids constructed with the origin of replication of E.coli. F' exists as an extra-chromosomal plasmid. BAC is developed as the first large insert cloning system to provide the construction of DNA libraries to analyze genomic data. Bacterial artificial chromosomes were developed to study the genetics and functionality of viruses like the Herpes virus. Since BAC technology has been promoted in every sector of genetics such as in fingerprinting, human genome sequencing, development of vaccines, and transgenic techniques. Bacterial Artificial Chromosome is a DNA construct based on fertility plasmid (F plasmid) that is used for transformation and cloning in bacteria, primarily E.coli. F plasmids contain partition genes that ensure the even distribution of plasmids after cell division. The BAC typically inserts a size of about 150-350 kbp. PAC is another cloning vector that has been produced from the genetic material P1 bacteriophage. BAC is usually utilized to sequence the genome of different organisms for example Human genome project. A small segment of DNA of an organism is applied as an insert in BAC and then sequenced. Then the sequenced DNA gets arranged on silicon leading to the complete genomic sequence of the organism. BACs are replaced with the use of whole-genome shotgun sequencing and now with Next Generation sequencing. This evolution saved the time and laborious work of sequencing. Bacterial Artificial chromosomeBAC contains basic components in their constructs.
How to make BAC libraries?For the making of the BAC library, first, you have to isolate cells that contain the DNA you want to store. Then mix these cells with hot agarose solution. Then pour the liquid mixture into a mold to produce a set of a small box, each box with thousands of isolated cells. Then these cells were treated with specific enzymes to disintegrate their cell walls and release DNA into the agarose gel Then the add restriction enzyme cuts the DNA into small fragments of 200,000 base pairs in length. Then DNA is inserted into a comb containing holes in a slab of agarose gel. Then these fragments of DNA are separated based on their size by the electrophoresis process. On one slab of agarose gel, a solution of DNA ladder or markers is inserted. Markers are DNA fragments f known size that is used as a reference to identify the size of the inserted DNA fragment. Then, the DNA fragments are cut out and extracted out of the gel. These extracted DNA fragments are then inserted into Bacterial artificial chromosome vectors using a ligase enzyme that joins the two segments of DNA together. Now, we can call them BAC clones. These BAC clones are then inserted into the host cell usually E.coli bacterium. The bacteria are then distributed on nutrient-rich plates that allow only the bacteria carrying BAC clones to grow on the medium. These bacteria grow rapidly leading to an increase in a large number of bacterial cells each bacterium containing a copy of the BAC clone. After the growth of Bacteria containing BAC clones, they are picked into plates of 96 or 384 so that each tube has at least one BAC clone constituting bacteria. The bacteria can also be copied again or stored by freezing so that the researcher can use the DNA later for sequencing. Finally, BAC library has been created. Contribution of BACs to models of diseasesBacterial Artificial chromosomes are now being used for greater significance like modeling genetic diseases. BACs have proven to be useful in the studies as they are complex genes with many regulatory sequences located upstream of the encoding sequence, and various promoter genes are also present that will lead to an expression of the gene. BAC is also incorporated with Mice to study neurological diseases like Alzheimer's disease or in some cases aneuploidy disorders with down-syndrome disease.
Applications
Advantages of BAC Vectors
Limitation of BAC vectors
Next TopicBacterial Skin Infection
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










