Bacterial Disease in Humans - TuberculosisDo you realise that germs outnumber human cells in the body? One of the oldest living forms found on Earth is bacteria, which are crucial to maintaining the planet's environment. 
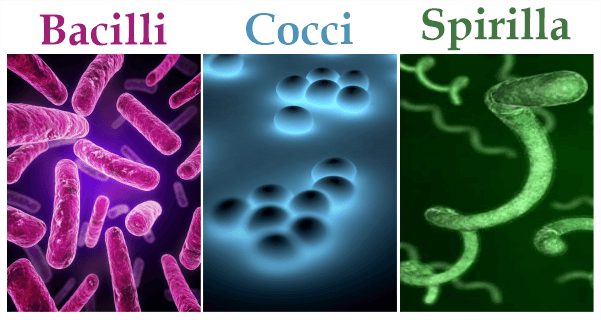
They are essential for metabolic activities, including vitamin absorption, food digestion, and even defence against dangerous microorganisms. Even in the harshest environments, particular small single-celled creatures are capable of surviving. While most bacteria are beneficial and safe, certain pathogen-classified bacteria are dangerous to humans and can infect and cause illnesses. Pathogens are the name given to these harmful organisms. Diseases brought on by bacteria are called bacterial infections. The human body contains a variety of microbes. Many are "healthy bacteria" since they don't lead to diseases. The term "harmful bacteria" refers to bacteria that make people sick. Numerous helpful bacteria for humans are found in large numbers in the gut. Less than 100 types of bacteria cause disease in humans. Diseases caused by bacteria can be transmitted from one person to another. Bacterial illnesses are contagious illnesses that can be spread by water, air, food, insects, vectors, bodily fluids, etc. Despite all the advances in medical science, bacterial illness in humans continues to be one of the leading causes of mortality. In the past, bacterial illnesses were feared infections; however, medicines are now available to treat these diseases. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that vaccinations avert between two and three million deaths annually. Food poisoning, pneumonia, and meningitis are all frequent ailments from bacterial infections. Antibiotics successfully treat and prevent bacterial illness, but over time some bacterial strains develop resistance to them. Causes of Bacterial DiseasesThe bacteria cause bacterial infections by entering the human body through various routes. Bacterial illnesses can spread to other people. Bacteria can spread by direct touch, as well as through food, drink, air, etc. Among these sources are:
Bacteria can harm the host cell directly or trigger an inflammatory immune response that does the same. People with weakened immune systems are more vulnerable to bacterial infections. Bacteria use the following mechanisms to inflict harm:
Symptoms of Bacterial DiseasesSeveral interrelated factors, including the patient's age, the kind of infection, the sensitivity of the afflicted area, and medical history, influence the symptoms of bacterial illness. See your doctor for a correct diagnosis and treatment plan if you suffer any of the symptoms listed below because bacterial illnesses have distinct symptoms similar to viral or influenza infections. 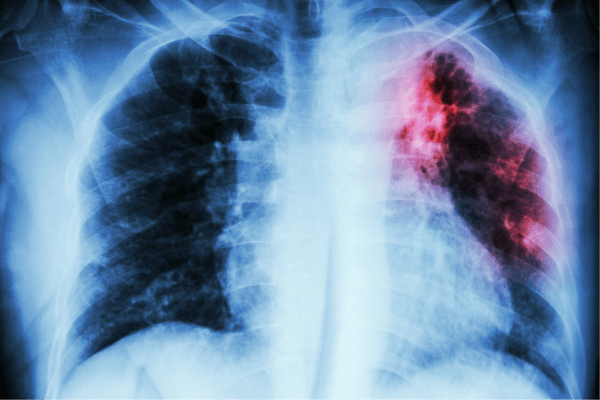
Typical Signs of Bacterial Illnesses are as follows:
Treatment of Human Bacterial DiseasesAntibiotics can be used to treat bacterial illnesses. While bacteriostatic medications stop germs from growing, bacteriocidal drugs destroy bacteria. Additionally, certain bacterial infections are treated using bacteriophages. Phage treatment is the name for it. Although antibiotics are available to treat different bacterial infections in humans, the leading cause for concern is continually changing bacteria and the development of antibiotic resistance. The overuse of antibiotics in intensive agricultural practices and the treatment of bacterial infections in people has been significant factor in the rise of bacterial antibiotic resistance. TuberculosisA bacterial illness known as tuberculosis is also referred to as TB. If not treated, it could be deadly. Though TB often affects the lungs, it can also harm other organs, including the brain. About TuberculosisTuberculosis is an infection caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria typically infect the lungs of human beings. Still, it has recently been shown to infect other parts of the body like the spinal cord, kidneys, or brain, thus causing tuberculosis infection in organs other than the lungs. Tuberculosis is a deadly infection because it is very contagious. It is spread from an infected person to an uninfected person merely by the closure. The disease spreads quickly if an uninfected person comes close to the infected person. 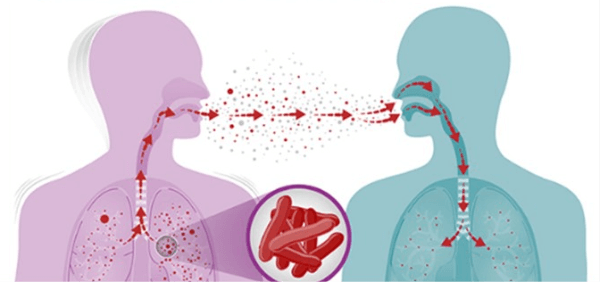
The word "tuberculosis" originated from the Latin word "nodules." This is because when bacteria infect the organs of the human body, it starts producing nodules of the infection. Tuberculosis, in layman's language, is called TB. It is only sometimes valid that if someone comes in contact with an infected person, they will catch the infection. The spread of infection mainly depends on the strength of the immune system. If a person has a weak immune system, then the probability of their catching an infection is higher than one with a strong immune system. There are many cases where a person does catch bacteria in the body but shows no symptoms. This type of infection is called latent TB or dormant TB. Although a person will appear perfectly fine from the outside, bacteria remain in the system and becomes active when there are favourable conditions for them to multiply. But once the bacteria start multiplying, the infection becomes active, and it is called active TB. The infected person starts showing symptoms at this point, and treatment is necessary. These Are The Three Phases Of TB
How Widespread is Tuberculosis?Around 10 million individuals worldwide contracted TB, and 1.5 million people passed away from it in 2020. TB was previously the top cause of mortality in the U.S., but when medicines became available in the 1940s and 1950s, the incidence of the disease dropped sharply. 
According to statistics, 7,860 TB cases were registered in the United States in 2021. The incidence rate across the country is 2.4 cases per 100,000 persons. Do Distinct Strains of TB Exist?Different people infected with tuberculosis show different signs and symptoms. This is because different types of tuberculosis-infected are present, which show different infection symptoms in the body. The most common is a lung infection. But apart from infecting the lungs, the bacteria can also infect other parts of the body, called extrapulmonary tuberculosis infection or simple tuberculosis outside the lungs. Different types of bacterial infection in the human body are as follows:
How does TB Start?Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacteria that causes TB. The airborne bacteria often affect the lungs but can also affect other body regions. They are transferred via airborne contact. Despite being contagious, TB is difficult to spread. To catch it, you often need to be around an infected person for a long period. 
How is the Disease Transmitted?A person infected with tuberculosis can transfer the bacteria into the system of other human beings through sneezing, coughing, exhaling too closely, talking, singing, laughing and eating together. The bacteria are dispersed into the air, which comes in contact with the body of an uninfected or healthy human and infects them. Contagious lung infections only affect those who have them actively. The majority of individuals who inhale TB germs are able to combat it and prevent it from spreading. These people have a latent infection while the bacteria become dormant. Up to 13 million Americans may have latent TB. Even if the bacteria are dormant, they are still present in the body and can later become active. Some individuals can live a life with a latent TB infection that never becomes active and progresses to TB illness. Latent tuberculosis in the body can take an active form if the body's immune system gets weak and cannot fight the bacteria causing tuberculosis. At this point, the latent TB infection manifests itself as TB. To prevent this from happening, several researchers are developing remedies. What Symptoms and Indicators are Associated with Tuberculosis?Inactive TB patients don't show any symptoms. They could, however, test positive for a skin response or blood test. People who have a positive infection of tuberculosis suffer from various symptoms. Some of them are:
What Types of Tests are Used to Identify Tuberculosis?A tiny quantity of a material known as pure protein derivative (PPD) will be injected under the skin of your forearm by a medical professional for the TST. You must return to the doctor or other healthcare professional after two to three days so they may examine the injection site. 
A medical professional will take blood and submit the sample to the lab for the IGRA. Additional examinations to identify whether an infection is present or whether your lungs are affected include:
You Might Wish to Have a TB Test if
Or at least six to nine months, you must take your prescriptions. Uninfected people susceptible to the infection of tuberculosis are:
How is the Disease Treated?These medications are used to treat TB infection and disease:
If you don't take the total dose of the medication your doctor recommends, not all of the germs will be eliminated. You will be required to take these drugs for the duration specified by your doctor, which may be up to nine months. Some TB strains have developed drug resistance. It's really essential, and your doctor may probably treat your TB with more than one medication. It's crucial to follow your prescription strictly. Treatment Side Effects/ComplicationsThe medications used to treat TB can have adverse effects on some persons, which may include:
How Soon Will I Feel Better After Beginning Therapy for Active TB?Before you begin to feel more energised and experience fewer days with symptoms, it will likely take weeks. The duration of your therapy will be longer than that. Prescriptions must be continued for additional six to nine months for effective treatment. 
How Can We Stop or Prevent the Spread of the Disease?Tuberculosis is not easily transmitted from one person to another. To be able to catch the infection from the infected person, one should have been in very close proximity for a considerable amount of time. Specific instructions are provided to prevent the spread of infection if anyone from the family is infected. Some of them are:
Vaccine Against TuberculosisA TB vaccination known as Bacillus Calmette-Guerin is utilised in several nations (but not the United States) (BCG). Children in countries with high TB prevalence are typically given the vaccination to protect against meningitis and military tuberculosis, a deadly form of TB. The vaccination could reduce the precision of TB skin testing. How likely is it that someone with TB will recover? Provided you have TB and are receiving treatment. Your prognosis will be favourable if you follow instructions and take your meds as prescribed for the recommended time. 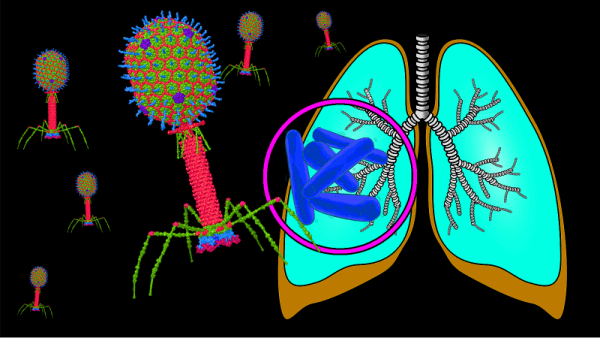
When Should I Visit my Physician?You should consult your healthcare physician immediately if you believe you may have been exposed to TB. They can assist you in deciding whether to be tested. If you've started experiencing any illness-related symptoms that may indicate you're infectious, that choice is more crucial. Keep in mind that while TB is treatable, it can also be lethal if left untreated. ConclusionThe illness known as tuberculosis is airborne. Despite being treatable, it continues to be a significant cause of mortality globally. If you suspect you may have been exposed to TB or are experiencing TB symptoms, be careful to call your healthcare professional. If you are receiving TB treatment, adhere to the directions carefully. If you have any questions, ask your healthcare practitioner.
Next TopicStomach Ache or Abdominal Pain
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









