Viral DiseasesIntroductionViral diseases are diseases that are caused by viruses. One of the most prevalent illnesses that affect people is viral infections. Viruses are responsible for many common infectious ailments, including the flu, the common cold, and warts. They also spread serious diseases such as COVID-19, Ebola, influenza, and the HIV/AIDS virus. Although there may be millions of distinct viral types, just 5,000 have been recognized by scientists thus far. A virus in the body can infect a person and lead to a viral disease. Virtually any type of body tissue, including the brain and skin, can become infected by one of the many different viruses that exist. What is Virus?A virus is a tiny living organism, in other words, a Virus is a microscopic parasitic structure with nucleic acid inside and a protein coat surrounding it. There are many types of viruses. Some viruses only affect animals, while others only affect people. Few viruses can infect both humans and animals. They usually damage and then kill the cell. However, some viruses can live for a long time inside cells without harming them. 
Types of Viral DiseaseViruses cause various diseases in humans and animals. Here are a few types of viral diseases: 1. Neurologic Viral DiseasesYou must have seen those who often complain of trembling, stretching, or pain in the legs while sleeping. In the absence of correct information, people often take calcium without the advice of a doctor considering it to be arthritis or osteoporosis. In the absence of accurate information, consumers frequently begin using calcium without first seeing a doctor, mistaking it for osteoporosis or arthritis. But because it is a neurological condition, doctors cannot eliminate the discomfort. 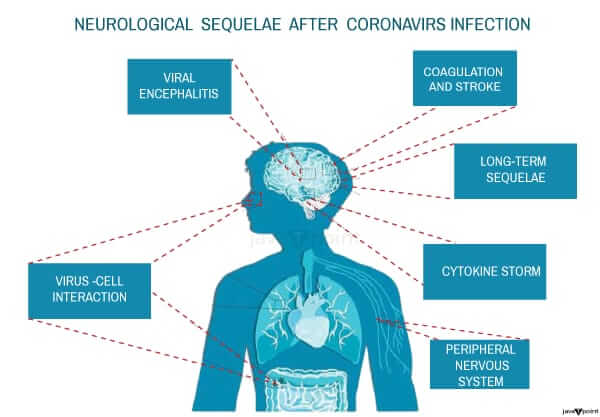
Reason In normal conditions, electrical waves flow through neurotransmitters from the brain to keep the muscles and joints of the legs active. Naturally, this flow stops automatically in the position of sitting or lying down, but when the electrical waves are continuously flowing through the brain, the vibration in the legs continues even when lying down or sitting. Dopamine, a hormone released from the brain, controls the flow of these waves, and due to its deficiency, these waves flow continuously in the same way, as if the tap is not closed properly, drops of water keep dripping from it. Apart from this, diabetes and kidney, patients can also have such problems. Some women experience these issues even throughout pregnancy, and they naturally resolve themselves following delivery. They experience these issues as a result of the body's hormonal abnormalities. These symptoms are also frequently present in people with high blood pressure. In some cases, hereditary factors are also to blame for this issue. The primary causes of this are deficiencies in the vitamins B-12 and iron. Symptoms Even though anyone can have this issue, its symptoms typically don't start to manifest until after the age of forty. Like arthritis, it also causes pain in the legs, but with restless leg (RLS) syndrome, pain is accompanied by tremors, tingling, and restlessness. This also disrupts sleep. The person feels as if something is crawling inside his legs and moving them gives him some relief. That's why such patients are unconsciously moving their legs. The pain gets worse on sleeping or sitting, but there is some relief on getting up and walking. While in the case of arthritis, after waking up in the morning, there is severe pain in the feet of the person and it gets relief after lying down at night. 2. Respiratory Viral DiseasesThe combination of tissues and organs known as the respiratory system is what enables us to breathe by allowing us to inhale oxygen-rich air and exhale carbon dioxide. Our respiratory system is particularly susceptible to several viruses that can lead to the flu, the common cold, and other ailments. Dr. Ziad R. Mattar, a pulmonologist and specialist in critical care medicine at Orlando Health in Orlando, Florida, claims that viruses are the tiniest microorganisms that can damage human cells and result in sickness or illness. 
In all age categories worldwide, acute respiratory disorders are the most common disease. A small number of cases can proceed to pneumonia and bronchiolitis, lower respiratory tract infections that are typically contained to the upper airways, and self-limiting. Particularly in underdeveloped nations, the risks to children and the elderly are greater. Viruses of the Respiratory System There are around 200 viruses that can affect the human Respiratory System with illness. Our respiratory system is very sensitive to several viruses that can lead to the flu, the common cold, and other ailments. A virus particularly affecting the upper, lower, or both respiratory tracts is referred to as a respiratory viral infection. Respiratory droplets, which are minute drops primarily consisting of water and formed when someone coughs, sneezes, or talks, are often how we contract a respiratory virus infection through the mouth or nose. In general, it is believed that the viruses in these droplets are contagious if you are within 6 feet of the person who makes them. You can become ill from contacting surfaces that have viruses in droplets living on them for several hours. Nearly all viruses that affect the respiratory system are similar in structure and are spread by respiratory droplets. In addition, they are all seasonal, appearing only at specific seasons of the year and spreading illness. Viruses can have varying effects on the respiratory system depending on where they start. For instance, a virus that affects the lungs and airways may make breathing more difficult and result in wheezing. You could feel congested if you have a virus in your nose or nasal cavities. Other regions of the body may occasionally be impacted by these illnesses. Some Examples of Respiratory viruses are:
Corona Virus Coronavirus, which first appeared last year at a seafood and poultry market in China's Wuhan region, has now spread around the world. After spreading to 70 nations, this virus has claimed the lives of over 3,000 individuals and infected over 10,000 more. Coronavirus is a zoonotic illness, which means it is spread by animals. This virus may infect both people and animals. This virus is now known as "SARS-CoV-2," and the sickness it causes is known as "Corona Disease 2019," shortened as "COVID-19". These symptoms are mainly harmless and are usually disregarded. Despite being sick, some people may not exhibit any symptoms. These infections can arise even when there are no evident signs. Your viral load (the number of viruses in your body) may be comparable to that of a person experiencing severe symptoms. This implies you are at the same risk of infection as a serious COVID-19 patient, and 80 percent of individuals recover without any additional therapy. If you just returned from a trip to a COVID-19 containment zone, you and anybody who comes into touch with you or your family may be infected. This virus enters the body when a person with this disease touches their eyes, nose, or mouth, or comes into contact with a location or object where they cough or sneeze. Inhaling these droplets might also expose them to the infection. A space of one meter (3 feet) should be kept between you and the persons infected by this sickness. 3. Viral Skin InfectionsViral skin problems, which are more varied than adult skin conditions, are more common in children. When compared to historical statistics, the widespread practice of early immunization in pediatrics has significantly reduced the frequency of viral illnesses that are now active. However, they continue to have a significant negative impact on numerous youngsters worldwide each year. 
Definition of Skin Infection Your skin is the greatest organ in your body. It protects and covers your body among its many other functions. It helps keep infections at bay. However, the microorganisms can occasionally cause skin disease. It frequently occurs when the bacteria enter your body through a skin wound, crack, or cut. Where skin scrapes on the skin, particularly in moist areas, other skin infections may develop. Additionally, infections can occur if a part of your body has inadequate blood flow or if your immune system is compromised as a result of another illness or medical procedure. The most prevalent viral skin condition is herpes simplex. The symptoms vary depending on the ailment. Some symptoms of various skin conditions include rashes, swelling, redness, pain, pus, and itching. Treatment of Skin Diseases The type of infection and how serious it is have an impact on the treatment plan. Some infections will go away on their own. If you do need medical attention, your skin may need to be treated by using a cream or lotion. The use of medications and a pus-draining operation are further potential treatments. 4. Hepatitis Viral DiseasesThe liver plays a very crucial role in the body. It also carries out some other crucial tasks including protein synthesis and toxin clearance in addition to digesting. 
This disease is caused mostly by four viruses - A, B, C, and E - and is usually avoidable. Hepatitis A and E are the least dangerous and typically short-lived of the four viruses (recovering on their own in most cases). Hepatitis B and C are the virus's most deadly types that cause chronic sickness. Infection with the hepatitis B or C virus can cause severe liver damage, ranging from cirrhosis (complete scarring) to failure of the liver and, in uncommon instances, liver cancer. In the last stages, the only therapeutic option is a liver transplant, which is expensive and has a success rate of 85 to 95%. Most people are unaware that they have hepatitis B or C; they are generally discovered years later after serious liver damage has occurred and consequences of liver failure have arisen. It is sometimes discovered during a standard medical examination. Hepatitis C, fortunately, is now treatable with modern medications (within 3 to 6 months) if identified early. Although hepatitis B virus infection is not curable, it can be efficiently treated with medications such that most people stay healthy for the rest of their lives. Hepatitis B vaccination is now available to all babies and at-risk adults to protect them from the disease. According to the WHO 2017 estimate, 40 million individuals in India have Hepatitis B, while roughly 12 million have Hepatitis C. However, because symptoms show at a late stage of the disease, more than 90% of persons with hepatitis B and C are unaware they are afflicted. Without presenting any symptoms, the virus can induce silent liver damage for years. Many of these people may develop significant, life-threatening liver disease if the infection is not identified, monitored, and treated. Given the high illness burden and high mortality rate, if left untreated, the World Health Organization established World Hepatitis Day on July 28 each year and actively advocates to eradicate viral hepatitis by 2030. Last year, the Indian government joined the effort by launching a nationwide viral hepatitis control program. Both lethal illnesses (hepatitis B and C) are transmitted by contaminated blood transfer from an infected person, needle and injection sharing among drug users, unprotected ear piercing and tattooing, unprotected intercourse from mother to child, and sharing shaving razors, nail cutters, and other personal items. It's crucial to remember how dangerous hepatitis may be. More people are infected and killed by this disease than by HIV, malaria, and tuberculosis combined. More than 80% of liver cancer cases are caused by viral hepatitis. Some Deadly Viral Diseases1) AIDSAIDS means acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is the last stage of HIV infection. HIV is the acronym for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV assaults and weakens the immune system's cells. These are CD4 cells, which are a kind of white blood cell. If the virus is not controlled with treatment, the HIV bacterium can infect CD4 cells, transforming them into factories that produce millions of virus copies. It eventually manifests as AIDS. There are several forms of HIV. These are divided into two categories:
HIV targets the immune system's CD4 cells, causing the body to develop AIDS. When the body loses an excessive number of CD4 cells, it becomes more susceptible to serious and potentially deadly infections. When someone dies with AIDS, it is frequently due to opportunistic infections and HIV's long-term consequences. AIDS is defined as a compromised immune system that is unable to fend against opportunistic infections. How can I tell whether I'm HIV-positive? Most people are unable to determine if they have been exposed to or impacted by HIV. Two to four weeks after HIV infection, moderate HIV symptoms may occur. Among these indicators are:
Some people dismiss these symptoms because they appear to be minor, or they believe they have a cold or flu. Even when these "flu-like" symptoms have subsided, an HIV-infected individual can live for years with no symptoms. Transmission Process? HIV is mostly transmitted through contact with the following bodily fluids: Other male sexual substances (sexual secretions) besides sperm vaginal secretions. When persons who have HIV take their HIV medicine as directed and reduce their virus load, their risks of spreading HIV to other people through bodily fluids decrease. This is referred to as HIV prevention. If an HIV-positive individual uses HIV medication and keeps an extremely low virus load (too low to be detected by routine testing), their sperm or vaginal secretions will not transfer HIV to their sexual partners. The most common ways HIV is spread is through unprotected sex (without using a condom, another barrier, or treatment as prevention), sharing needles used to inject drugs or pregnant mother-to-child. (During pregnancy or from breastfeeding). HIV is not transmitted by the following bodily fluids:
In simple terms, you do not obtain HIV by touching or embracing an HIV-positive person, kissing them, or using their bathroom. Preventions
2) Dengue FeverThe dengue virus (DENV) causes dengue, which is transmitted to humans through mosquito bites. The unpleasant and incapacitating dengue fever is spread by mosquitoes, and people who contract the virus a second time. Dengue fever symptoms include high fever, rash, headache, muscle, and joint discomfort. Some severe cases lead to bleeding and shock, which can be catastrophic. Causes Dengue fever is not transmitted by contact with an infected person; rather, it is spread by mosquito bites. These viruses share a connection with the viruses that cause yellow fever and West Nile illness. After recovering from dengue fever, you have lifetime immunity to the virus that initially infected you, but not to the other three dengue fever virus strains. Symptoms Here are some symptoms of Dengue Fever:
Next TopicTumor Suppressor Gene
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









