Function of Pons in BrainThe pons is a portion of the brainstem, which connects the brain to the spinal cord. It oversees unconscious processes and functions like sleeping, waking up, and breathing. It also has multiple junction places for nerves that govern muscles and carry information from the brain and face's sensors. What is the Pons?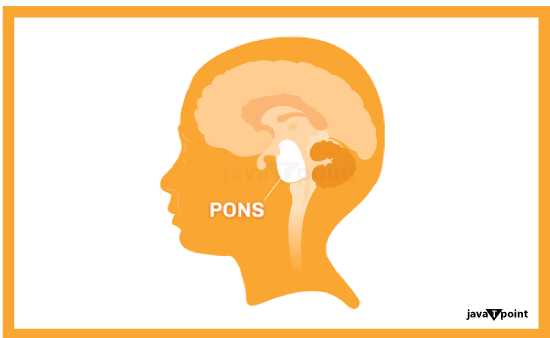
The pons is the brainstem's second-lowest region, right above the medulla oblongata. It connects the brain above it with the oblongata medulla and spinal cord below it. The pons is an important junction location for several of the cranial nerves, which are nerves that link directly to the brain. Those nerve connections are critical, since they aid in several of the senses, as well as the ability to move various portions of the face and mouth. What is the Function of the Pons?The pons is a portion of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord. As a result, the pons is an important part of the neurological system, providing a pathway for impulses to and from the brain. Several neurotransmitters in the pons help with brain function, especially sleep. The pons can handle a variety of crucial tasks on its own:
Cranial Nerve ConnectionsFurthermore, the pons has numerous crucial junctions for 4 of the 12 cranial nerves, which connect directly to the brain. The cranial nerves (which are numbered using Roman numerals) that attach to the pons are:
How does it Help with Other Organs?By conveying sensory input and directly managing some of the body's unconscious activities, the pons assists other organs. These include the person's sleep-wake cycle and breathing patterns. The pons also manages the capacity to sense pain, and that sensation of pain can help people react to limit or prevent injuries. AnatomyWhere is the pons located?The pons is one of the lowest structures in the brain and is found towards the base of the skull. It's located right above the medulla oblongata, which links to the spinal cord via the opening at the base of the skull. What does it look like?The pons is off-white or beige in colour. It resembles the upper stem of a cauliflower branch. How big is it?Pons' dimensions are: Height: 1.06 inches tall (27 millimetres [mm]). Width: 1.49 inches (38 mm). Depth: 0.98 inches (25 mm). What is it made of?The pons, like the rest of the brain and nervous system, is made up of many types of nervous system cells and structures. The nuclei (plural for "nucleus") are nerves or clusters of brain cells that perform the same function or connect to the same locations. The nuclei are made up of the following cell types:
NeuronsNeurons are the cells in the brain that send and relay impulses utilising both electrical and chemical signals. Each neuron is made up of the following components:
Neuron connections are extremely complicated, with a single neuron's dendrites connecting to thousands of other synapses. Some neurons are longer or shorter in length depending on where they are in the body and what they do. Glial cellsGlial (pronounced glee-uhl) cells provide a variety of functions, including assisting in the development and maintenance of neurons during childhood and directing how neurons function throughout life. They also defend the nervous system from infections, regulate the nervous system's chemical equilibrium, and form the myelin covering on the axons of neurons. Glial cells outnumber neurons in the brain by a factor of ten. What are the Common Conditions and Disorders that affect the Pons?Many of the disorders that affect the brain can also have an impact on the pons. Some conditions have a direct impact on the pons. Here are some examples (in alphabetical order):
Common Signs or Symptoms of Pons Conditions?The indications and symptoms of pons disorders vary greatly depending on the affected area. Damage to different parts of the pons will have varied effects on the rest of the body. Some of the most prevalent symptoms are as follows:
Common Tests to Check the Health of the Body Organ?When healthcare experts are identifying issues relating to the pons, the following tests may be performed:
PET (positron emission tomography) scan How to Prevent Problems with the Pons?Some pons problems are preventable, but others occur unexpectedly. In many circumstances, people can lower the likelihood of developing specific ailments or difficulties. The most effective preventive measures are as follows:
Doctor's NoteThe pons is a small but vital component of the brain. Though it is a portion of the brain that is often overlooked, it is nevertheless an important aspect of how people conduct their life and get information about the world around people. It aids in the control of the body's respiration, balance, hearing, and other bodily functions. As a result, safeguarding the condition of the brain from injuries and preventable disorders is an important element of how people live their life.
Next Topic#
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









